Sierra Wireless WMP100 Quadband GSM Module User Manual Wireless Microprocessor WMP100 OASS1 0
Sierra Wireless, Inc. Quadband GSM Module Wireless Microprocessor WMP100 OASS1 0
Contents
- 1. User Manual
- 2. User Guide
User Manual

Wireless Microprocesso
r
® WMP100/
Open AT® Software Suite v1.0
Product Technical Specification and
Customer Design Guidelines
Reference:
W
M_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
Revision: 002
Date: March 19, 2007
WMP100/Open AT® Software
Suite v1.0
Product Technical Specification &
Customer Design Guidelines
Reference:
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
Revision:
002
Date:
March 19, 2007
Powered by the Wavecom Open AT® Software Suite
confidential © Page : 1 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 2 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Document Information
Level Date History of the evolution
001 19/10/2006 Creation (Preliminary version)
002 19/03/2007 Updates

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 3 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Overview
This document defines and specifies the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite
v1.0 available in a GSM/GPRS Class 10 quad-band version.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 4 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Table of Contents
Document Information......................................................................... 2
Overview ............................................................................................. 3
Table of Contents................................................................................ 4
Table of Figures................................................................................. 10
Cautions ............................................................................................ 12
Trademarks ....................................................................................... 12
Copyright .......................................................................................... 12
1 References................................................................................ 13
1.1 Reference documents ............................................................................13
1.1.1 WAVECOM reference documentation ............................................13
1.1.2 General reference documentation ..................................................13
1.2 List of abbreviations ..............................................................................14
2 General description................................................................... 17
2.1 General information...............................................................................17
2.1.1 Overall dimensions ........................................................................17
2.1.2 Environment and mechanics..........................................................17
2.1.3 GSM/GPRS Features ......................................................................17
2.1.4 Interfaces.......................................................................................18
2.1.5 Operating system ..........................................................................18
2.2 Functional description ...........................................................................19
2.2.1 RF functionalities ...........................................................................20
2.2.2 Baseband functionalities................................................................20
2.3 Software description .............................................................................20
3 Interfaces ................................................................................. 21
3.1 General Interfaces .................................................................................21
3.2 Power supply ........................................................................................22
3.2.1 Power supply description ..............................................................22
3.2.2 Power supply constraints on VBATT-RF ........................................22
3.2.3 Power supply constraints on VBATT-BB........................................23
3.2.4 Electrical characteristics ................................................................23
3.2.5 Pin description...............................................................................23

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 5 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.2.6 Application ....................................................................................24
3.3 Power consumption ..............................................................................25
3.3.1.1 Power consumption without Open AT® processing .................26
3.3.1.2 Power consumption with a Dhrystone Open AT® application...27
3.3.1.3 Consumption waveform samples.............................................28
3.3.1.3.1 Connected mode current waveform .......................................28
3.3.1.3.2 Slow Idle mode current waveform .........................................29
3.3.1.3.3 Fast Idle mode current waveform ..........................................30
3.3.1.3.4 Transfer mode Class 10 current waveform ............................31
3.4 Electrical information for digital I/O........................................................32
3.5 SPI Bus .................................................................................................34
3.5.1 Features ........................................................................................34
3.5.1.1 Characteristics .........................................................................34
3.5.1.2 SPI configuration .....................................................................34
3.5.1.3 SPI waveforms ........................................................................35
3.5.2 Pin description...............................................................................36
3.5.3 Application ....................................................................................36
3.5.3.1 4-wire interface .......................................................................36
3.5.3.2 3-wire interface .......................................................................37
3.6 I2C bus..................................................................................................38
3.6.1 Features ........................................................................................38
3.6.1.1 Characteristics .........................................................................38
3.6.1.2 I²C waveforms .........................................................................38
3.6.2 Pin description...............................................................................39
3.6.3 Application ....................................................................................39
3.7 Keyboard interface.................................................................................40
3.7.1 Features ........................................................................................40
3.7.2 Pin description...............................................................................41
3.7.3 Application ....................................................................................42
3.8 Main serial link (UART1)........................................................................42
3.8.1 Features ........................................................................................42
3.8.2 Pin description...............................................................................43
3.8.3 First download ..............................................................................45
3.8.4 Application ....................................................................................46
3.9 Auxiliary serial link (UART2) ..................................................................50
3.9.1 Features ........................................................................................50
3.9.2 Pin description...............................................................................51
3.9.3 Application ....................................................................................51
3.10 SIM Interface.........................................................................................52
3.10.1 Features ........................................................................................52
3.10.2 Pin description...............................................................................54
3.10.3 Application ....................................................................................54
3.11 General Purpose Input/Output ...............................................................56
3.11.1 Features ........................................................................................56
3.11.2 Pin description...............................................................................56
3.12 Analog to Digital Converter....................................................................58
3.12.1 Features ........................................................................................58
3.12.2 Pin description...............................................................................58
3.12.3 Application ....................................................................................59
3.13 Digital to Analog Converter....................................................................60

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 6 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.13.1 Features ........................................................................................60
3.13.2 Pin description...............................................................................60
3.14 Analogue audio interface.......................................................................61
3.14.1 Microphone Features.....................................................................61
3.14.1.1 Electrical characteristics...........................................................61
3.14.1.1.1 MIC1 Microphone Inputs ...................................................61
3.14.1.1.2 MIC2 Microphone Inputs ...................................................62
3.14.2 Speaker Features ...........................................................................64
3.14.2.1 Speakers Outputs Power .........................................................64
3.14.2.1.1 SPK1 Speaker Outputs.......................................................64
3.14.2.1.2 SPK2 Speaker Outputs......................................................66
3.14.3 Pin description...............................................................................67
3.14.4 Application ....................................................................................67
3.14.4.1 Microphone .............................................................................67
3.14.4.1.1 MIC2 Differential connection example................................67
3.14.4.1.2 MIC2 single-ended connection example ............................69
3.14.4.1.3 MIC1 Differential connection example................................70
3.14.4.1.4 MIC1 Single-ended connection example ............................72
3.14.4.2 Speaker ...................................................................................73
3.14.4.2.1 SPK2 Differential connection..............................................73
3.14.4.2.2 SPKx Single-ended connection ..........................................74
3.14.5 Design recommendation................................................................74
3.14.5.1 General ....................................................................................74
3.14.5.2 Recommended microphone characteristics..............................74
3.14.5.3 Recommended speaker characteristics ....................................75
3.14.5.4 Recommended filtering components........................................75
3.14.5.5 Audio track and PCB layout recommendation ..........................77
3.15 PWM / Buzzer Output ...........................................................................78
3.15.1 Features ........................................................................................78
3.15.2 Pin description...............................................................................78
3.15.3 Application ....................................................................................79
3.16 Battery charging interface .....................................................................80
3.16.1 Feature ..........................................................................................80
3.16.1.1 Pre-Charging ...........................................................................81
3.16.1.2 Temperature monitoring ..........................................................81
3.16.2 Pin description...............................................................................82
3.16.3 Application ....................................................................................82
3.17 ON / ~OFF signal...................................................................................84
3.17.1 Features ........................................................................................84
3.17.2 Pin description...............................................................................84
3.17.3 Application ....................................................................................84
3.17.3.1 Power ON................................................................................85
3.17.3.2 Power OFF...............................................................................87
3.18 BOOT signal ..........................................................................................88
3.18.1 Features ........................................................................................88
3.18.2 Pin description...............................................................................88
3.18.3 Application ....................................................................................88
3.19 Reset signals .........................................................................................89
3.19.1 Features ........................................................................................89
3.19.2 Pin description...............................................................................92
3.19.3 Application ....................................................................................93
3.20 External Interrupt ..................................................................................94

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 7 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.20.1 Features ........................................................................................94
3.20.2 Pin description...............................................................................94
3.20.3 Application ....................................................................................95
3.21 VCC_2V8 and VCC_1V8 output ..............................................................96
3.21.1 Features ........................................................................................96
3.21.2 Pin description...............................................................................96
3.21.3 Application ....................................................................................96
3.22 Real Time Clock.....................................................................................97
3.22.1 Features ........................................................................................97
3.22.2 Pin description...............................................................................97
3.22.3 Application ....................................................................................98
3.22.4 Design recommendation................................................................98
3.23 BAT-RTC (Backup Battery) ....................................................................99
3.23.1 Features ........................................................................................99
3.23.2 Pin description.............................................................................100
3.23.3 Application ..................................................................................100
3.23.3.1 Super Capacitor .....................................................................100
3.23.3.2 Non Rechargeable battery......................................................101
3.23.3.3 Rechargeable battery cell.......................................................101
3.24 FLASH-LED signal ...............................................................................102
3.24.1 Features ......................................................................................102
3.24.2 Pin description.............................................................................103
3.24.3 Application ..................................................................................104
3.25 Digital audio interface (PCM) ...............................................................104
3.25.1 Features ......................................................................................104
3.25.2 Pin description.............................................................................107
3.25.3 Application TBD...........................................................................107
3.26 USB 2.0 interface ................................................................................107
3.26.1 Features ......................................................................................107
3.26.2 Pin description.............................................................................108
3.26.3 Application ..................................................................................109
3.27 Memory interface ................................................................................110
3.27.1 Features ......................................................................................111
3.27.1.1 Generic Description................................................................111
3.27.1.2 Case of ST 32/8 (M36W0R5030T0ZAQF) ..............................112
3.27.1.3 Access bus Waveform ...........................................................113
3.27.1.4 Flash space............................................................................116
3.27.1.5 RAM space ............................................................................116
3.27.1.6 16-bit wide data bus User Space ...........................................117
3.27.2 Electrical characteristics of the signals.........................................117
3.27.3 Pin description.............................................................................117
3.27.4 Application ..................................................................................120
3.27.5 Constraints ..................................................................................121
3.28 RF interface .........................................................................................124
3.28.1 RF connection..............................................................................124
3.28.2 RF performances .........................................................................124
3.28.3 Antenna specifications ................................................................125
3.28.4 Antenna.......................................................................................125
4 Consumption measurement procedure ................................... 127

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 8 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
4.1 Hardware configuration.......................................................................127
4.1.1 Equipment ...................................................................................127
4.1.2 Wireless Microprocessor motherboard ........................................129
4.1.3 SIM cards used ...........................................................................130
4.2 Software configurations ......................................................................130
4.2.1 Wireless Microprocessor configuration ........................................130
4.2.2 Equipment configuration .............................................................131
4.3 Template .............................................................................................132
5 Technical specifications ......................................................... 133
5.1 Ball Grid Array pin out .........................................................................133
5.2 Environmental Specifications...............................................................139
5.3 MSL level ............................................................................................140
5.4 Mechanical specifications....................................................................140
5.4.1 Physical characteristics................................................................140
5.4.2 Mechanical drawings ..................................................................140
5.4.3 Mechanical constraints................................................................143
5.5 PCB specifications...............................................................................143
6 Peripheral devices references ................................................. 143
6.1 SIM Card Reader .................................................................................143
6.2 Microphone.........................................................................................143
6.3 Speaker ...............................................................................................143
6.4 Antenna Cable.....................................................................................144
6.5 GSM antenna ......................................................................................144
7 Noises and design................................................................... 145
7.1 EMC recommendations .......................................................................145
7.2 Power Supply......................................................................................145
8 Appendix................................................................................. 146
8.1 Standards and Recommendations.......................................................146
8.2 Safety recommendations (for information only) ...................................150
8.2.1 RF safety .....................................................................................150
8.2.1.1 General ..................................................................................150
8.2.1.2 Exposure to RF energy...........................................................150
8.2.1.3 Efficient terminal operation ....................................................150
8.2.1.4 Antenna care and replacement ..............................................151
8.2.2 General safety..............................................................................151
8.2.2.1 Driving...................................................................................151
8.2.2.2 Electronic devices ..................................................................151
8.2.2.3 Vehicle electronic equipment .................................................151
8.2.2.4 Medical electronic equipment ................................................151
8.2.2.5 Aircraft ..................................................................................152
8.2.2.6 Children .................................................................................152

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 9 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
8.2.2.7 Blasting areas........................................................................152
8.2.2.8 Potentially explosive atmospheres .........................................152

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 10 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Table of Figures
Figure 1 : Functional architecture ................................................................... 19
Figure 2 : Power supply during burst emission .............................................. 22
Figure 3 : Reject filter diagram........................................................................ 24
Figure 4: SPI Timing diagrams, Mode 0, Master, 4 wires ............................... 35
Figure 5: Example of 4-wire SPI bus application............................................. 36
Figure 6: Example of 3-wire SPI bus application............................................. 37
Figure 7: I²C Timing diagrams, Master ........................................................... 38
Figure 8: First example of I²C bus application................................................. 39
Figure 9: Second example of I²C bus application ............................................ 40
Figure 10: Example of keyboard implementation ............................................ 42
Figure 11: Example of UART1 connection for download with another device on
the link...................................................................................................... 45
Figure 12: Example of RS-232 level shifter implementation for UART1........... 46
Figure 13: Example of V24/CMOS serial link implementation for UART1 ........ 48
Figure 14: Example of full modem V24/CMOS serial link implementation for
UART1 ...................................................................................................... 49
Figure 15: Example of RS-232 level shifter implementation for UART2........... 51
Figure 16: Example of SIM Socket implementation......................................... 54
Figure 17: Example of MIC2 input differential connection with LC filter.......... 67
Figure 18: Example of MIC2 input differential connection without LC filter..... 68
Figure 19: Example of MIC2 input single-ended connection with LC filter ...... 69
Figure 20: Example of MIC2 input single-ended connection without LC filter . 69
Figure 21: Example of MIC1 input differential connection with LC filter.......... 70
Figure 22: Example of MIC1 input differential connection without LC filter..... 71
Figure 23: Example of MIC1 input single-ended connection with LC filter ...... 72
Figure 24: Example of MIC1 input single-ended connection without LC filter . 72
Figure 25: Example of Speaker differential connection.................................... 73
Figure 26: Example of Speaker single-ended connection ................................ 74
Figure 27: Microphone ................................................................................... 75
Figure 28: Audio track design......................................................................... 77
Figure 29: Example of buzzer implementation ................................................ 79
Figure 30: Example of LED driven by the BUZZ-OUT output........................... 79
Figure 31: Charging block diagram................................................................. 80
Figure 32: Charging schematic for Li-Ion ........................................................ 82

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 11 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Figure 33: Example of ON/~OFF pin connection ............................................. 84
Figure 34 : Power-ON sequence (no PIN code activated) ................................ 85
Figure 35 : Power-OFF sequence ................................................................... 87
Figure 36: Example of BOOT pin implementation ........................................... 88
Figure 37 : Reset functional block................................................................... 89
Figure 38 : Reset waveform events ................................................................ 90
Figure 39 : Reset sequence waveform............................................................ 91
Figure 40 : BOOT sequence waveform .......................................................... 92
Figure 41: Example of ~RESET pin connection with push button configuration
................................................................................................................. 93
Figure 42: Example of ~RESET pin connection with transistor configuration.. 93
Figure 43: Example of INTx driving example with open collector.................... 95
Figure 44: Example of INTx driving example with open collector.................... 95
Figure 45 : PCB lay out for the crystal MS2V-T1S .......................................... 98
Figure 46 : Real Time Clock power supply...................................................... 99
Figure 47: RTC supplied by a gold capacitor................................................. 100
Figure 48: RTC supplied by a non rechargeable battery................................ 101
Figure 49: RTC supplied by a rechargeable battery cell ................................ 101
Figure 50 : FLASH-LED state during RESET and Initialization time ............... 103
Figure 51: Example of GSM activity status implementation.......................... 104
Figure 52 : PCM Frame waveform................................................................ 106
Figure 53 : PCM Sampling waveform........................................................... 106
Figure 54: Example of USB implementation.................................................. 109
Figure 55: Memory bus ................................................................................ 110
Figure 56: Read synchronous timing ............................................................ 113
Figure 57: Write synchronous timing ........................................................... 114
Figure 58: Read / Write Asynchronous timing .............................................. 115
Figure 59: Memory connection schematic .................................................... 120
Figure 60: Memory PCB ............................................................................... 123
Figure 61: Antenna and ground balls placement .......................................... 126
Figure 62: RF 50 ohms embedded line ......................................................... 126
Figure 63: Antenna connection point keep away area .................................. 126
Figure 64: RF connector and ESD protection example .................................. 127
Figure 65: Typical hardware configuration ................................................... 128
Figure 66 : Environmental classes ................................................................ 139
Figure 67 : Mechanical drawing ................................................................... 141
Figure 68 : Mechanical drawing ................................................................... 142

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Cautions
This platform contains a modular transmitter. This device is used for wireless
applications. Note that all electronics parts and elements are ESD sensitive.
Information provided herein by WAVECOM is accurate and reliable. However
no responsibility is assumed for its use and any of such WAVECOM
information is herein provided “as is” without any warranty of any kind,
whether express or implied.
General information about WAVECOM and its range of products is available at
the following internet address: http://www.wavecom.com
Trademarks
®, WAVECOM®, WISMO®, Open AT®, Wireless Microprocessor®, Wireless
CPU®, and certain other trademarks and logos appearing on this document, are
filed or registered trademarks of Wavecom S.A. in France or in other countries.
All other company and/or product names mentioned may be filed or registered
trademarks of their respective owners.
Copyright
This manual is copyrighted by WAVECOM with all rights reserved. No part of
this manual may be reproduced in any form without the prior written
permission of WAVECOM. No patent liability is assumed with respect to the
use of their respective owners.
confidential © Page : 12 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 13 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
1 References
1.1 Reference documents
For more details, several documents are referenced in this specification. The
WAVECOM documents references herein are provided in the WAVECOM
documentation package; the general reference documents which are not
WAVECOM owned are not provided in the documentation package.
1.1.1 WAVECOM reference documentation
[1] Wireless Microprocessor® WMP100 Technical Specification
Reference: WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_004
[2] WMP100 Development Kit User Guide
Reference: WM_DEV_WUP_UGD_001
[3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5
Reference: WM_DEV_OAT_UGD_035
1.1.2 General reference documentation
[4] “I²C Bus Specification”, Version 2.0, Philips Semiconductor 1998
[5] ISO 7816-3 Standard

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 14 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
1.2 List of abbreviations
Abbreviation
Definition
AC Alternative Current
ADC Analog to Digital Converter
A/D Analog to Digital conversion
AF Audio-Frequency
AT ATtention (prefix for modem commands)
AUX AUXiliary
CAN Controller Area Network
CB Cell Broadcast
CEP Circular Error Probable
CLK CLocK
CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
CS Coding Scheme
CTS Clear To Send
DAC Digital to Analogue Converter
dB Decibel
DC Direct Current
DCD Data Carrier Detect
DCE Data Communication Equipment
DCS Digital Cellular System
DR Dynamic Range
DSR Data Set Ready
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
DTR Data Terminal Ready
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
E-GSM Extended GSM
EMC ElectroMagnetic Compatibility
EMI ElectroMagnetic Interference
EMS Enhanced Message Service
EN ENable
ESD ElectroStatic Discharges
FIFO First In First Out
FR Full Rate
FTA Full Type Approval

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 15 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Abbreviation
Definition
GND GrouND
GPI General Purpose Input
GPC General Purpose Connector
GPIO General Purpose Input Output
GPO General Purpose Output
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GPS Global Positioning System
GSM Global System for Mobile communications
HR Half Rate
I/O Input / Output
LED Light Emitting Diode
LNA Low Noise Amplifier
MAX MAXimum
MIC MICrophone
MIN MINimum
MMS Multimedia Message Service
MO Mobile Originated
MT Mobile Terminated
na Not Applicable
NF Noise Factor
NMEA National Marine Electronics Association
NOM NOMinal
NTC Négative Temperature Coefficient
PA Power Amplifier
Pa Pascal (for speaker sound pressure measurements)
PBCCH Packet Broadcast Control CHannel
PC Personal Computer
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PDA Personal Digital Assistant
PFM Power Frequency Modulation
PSM Phase Shift Modulation
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
RAM Random Access Memory
RF Radio Frequency
RFI Radio Frequency Interference

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 16 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Abbreviation
Definition
RHCP Right Hand Circular Polarization
RI Ring Indicator
RST ReSeT
RTC Real Time Clock
RTCM Radio Technical Commission for Maritime services
RTS Request To Send
RX Receive
SCL Serial CLock
SDA Serial DAta
SIM Subscriber Identification Module
SMS Short Message Service
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
SPL Sound Pressure Level
SPK SPeaKer
SRAM Static RAM
TBC To Be Confirmed
TDMA Time Division Multiple Access
TP Test Point
TVS Transient Voltage Suppressor
TX Transmit
TYP TYPical
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter
USB Universal Serial Bus
USSD Unstructured Supplementary Services Data
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 17 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
2 General description
2.1 General information
The WMP100 Wireless Microprocessor® is a self-contained E-GSM/GPRS
900/1800 and 850/1900 quad-band processor, including the characteristics
listed in the subsection below.
2.1.1 Overall dimensions
• Length: 25 mm
• Width: 25 mm
• Thickness: 3.65 mm
• Weight: 4.25 g
• Package: WMBGA576 / ball Ø 0,6 mm @ pitch 1mm
2.1.2 Environment and mechanics
• Green policy: Restriction of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and
Electronic Equipment (RoHS) compliant
• Complete shielding
The WMP100 is compliant with RoHS Directive 2002/95/EC which sets limits
for the use of certain restricted hazardous substances. This directive states
that “from 1st July 2006, new electrical and electronic equipment put on the
market does not contain lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium,
polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) or polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE)”.
2.1.3 GSM/GPRS Features
• 2 Watts EGSM 900/GSM 850 radio section running under 3.6 Volts
• 1 Watt GSM1800/1900 radio section running under 3.6 Volts
• Hardware GPRS class 10 capable

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 18 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
2.1.4 Interfaces
• Digital section running under 2.8 Volts and 1.8Volts.
• 3V/1V8 SIM interface
• 1.8V Parallel interface for devices (memories, LCD…)
• Power supply
• Watchdog
• Serial links (UART)
• Analogue audio
• ADC / DAC
• PCM digital audio
• Keyboard
• USB 2.0 slave
• Serial buses (I2C,SPI)
• PWM
• GPIOs
2.1.5 Operating system
• Real Time Clock with calendar
• Echo Cancellation + noise reduction (quadri codec)
• Full GSM or GSM/GPRS Operating System stack

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 19 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
2.2 Functional description
The global architecture of WMP100 is described below:
32768
kHz
WMP100
ARM 946
32bit
core
DSP
core
Radio
GSM / GPRS
Digital Interfaces
Analog Interfaces
Extended Memory Bridge
SPI
1,2
I²C
GPIOs
ITs
USB 2.0
UART
1,2
KEYPAD
PCM
DAC
ADCs
AUDIO
CH1 & CH2
SIM
Control &
Power
AHB bus
ControlDataAddress
reset
RTC
power
supplys
Charging PWM
Figure 1 : Functional architecture
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
2.2.1 RF functionalities
The Radio Frequency (RF) range complies with the Phase II EGSM 900/DCS
1800 and GSM 850/PCS 1900 recommendation. The frequencies are listed in
the table below.
Transmit band (Tx) Receive band (Rx)
GSM 850 824 to 849 MHz 869 to 894 MHz
E-GSM 900 880 to 915 MHz 925 to 960 MHz
DCS 1800 1710 to 1785 MHz 1805 to 1880 MHz
PCS 1900 1850 to 1910 MHz 1930 to 1990 MHz
The RF part is based on a specific quad band chip including:
• a Digital low-IF receiver
• a Quad-band LNAs (Low Noise Amplifier)
• an Offset PLL (Phase Locked Loop) transmitter
• a Frequency synthesizer
• a Digitally controlled crystal oscillator (DCXO)
• a Tx/Rx FEM (Front-End Wireless Microprocessor®) for quad-band
GSM/GPRS
2.2.2 Baseband functionalities
The Baseband is composed of an ARM9, a DSP and an analog element (with
audio signals, I/Q signals, ADC, DAC).
The core power supply is to 1.8 volts. The analog power supply is to 2.8v
2.3 Software description
The Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 is the software package that supports
WMP100. It consists of:
• An Open AT® Firmware v6.5 which drives the WMP100 thanks to an AT
command interface over a serial port or USB.
• An Open AT® Operating System (OS) v5.0 which runs various types of
applications (telemetry, multimedia, automotive…)
• An Open AT® Integrated Development Environment (IDE) which builds
and debugs applications over the Open AT® Operating System
• Several Open AT® plug-ins which are software provided by Wavecom
that are able to run over the Open AT® Operating System
confidential © Page : 20 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 21 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3 Interfaces
3.1 General Interfaces
The WMP100 is provided with a “Development Kit Wireless Microprocessor®”
containing an access to the all interfaces.
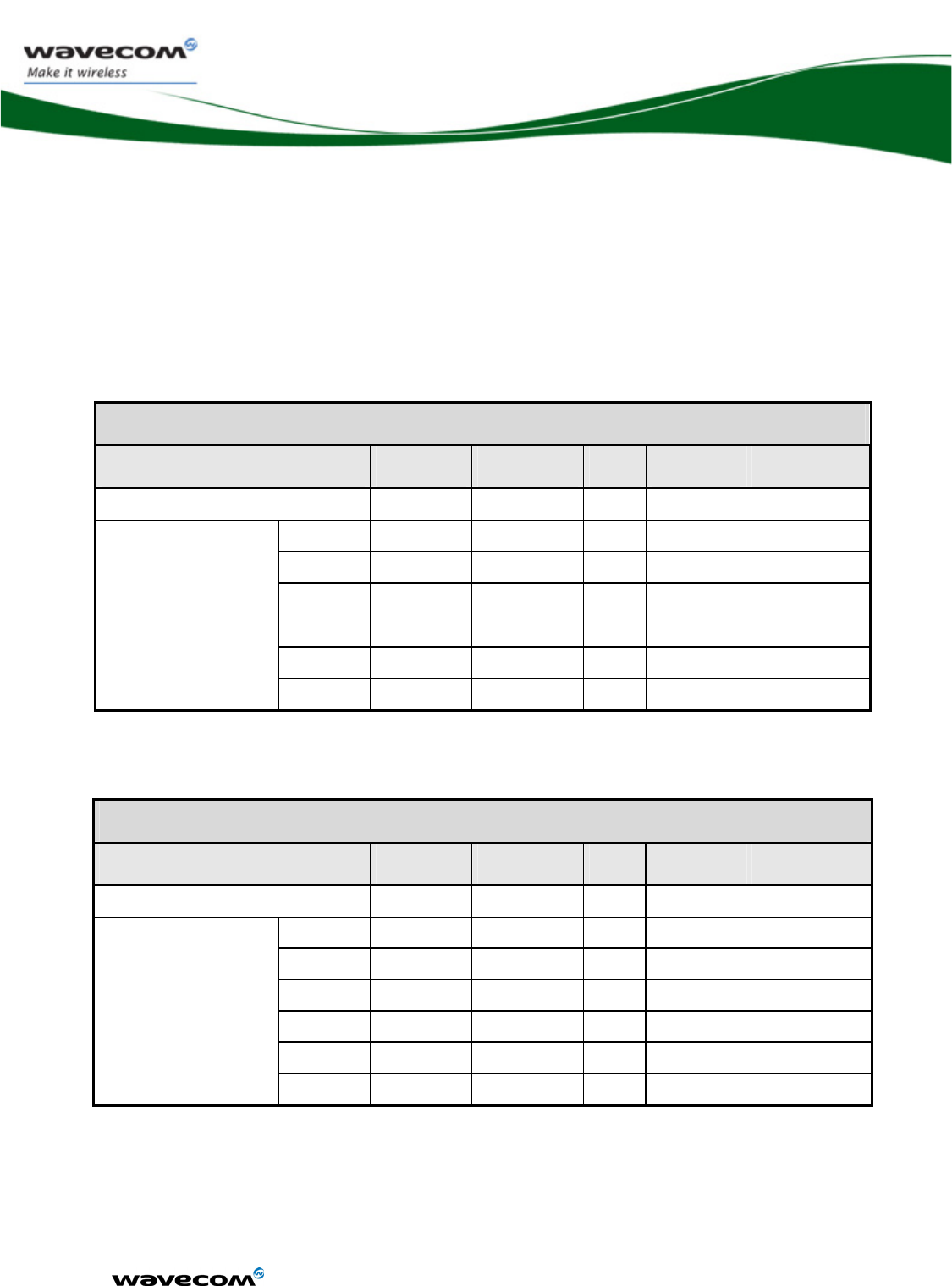
The available interfaces are described in the table below.
chapter Name Driven by
Open AT®
Firmware
v6.5
Not
driven by
Open AT®
Firmware
v6.5
Driven by
Open AT®
OS v5.0
Not
driven by
Open AT®
OS v5.0
18.5.1 SPI Bus X X
18.5.2 I2C Bus X X
11 Keyboard Interface X X
12.2 Main Serial Link X X
13.2 Auxiliary Serial Link X X
14 SIM Interface X X
3 General Purpose IO X X
18.3 Analog to Digital
Converter
X X
18.4 Digital to Analog
Converter
X X
16 Analog audio Interface
X X
9 PWM / Buzzer Output X X
18.3.1 Battery charging
interface
X X
18.7 External Interruption X X
18.1 VCC_2V8 and
VCC_1V8
X X
17 Real Time Clock X X
18.2 BAT-RTC (Backup
Battery)
X X
8 FLASH-LED signal X X
18.6 Digital Audio Interface
(PCM)
X X
15 USB 2.0 Interface X X
4 Memory interface
(on parallel interface)
X X

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 22 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.2 Power supply
3.2.1 Power supply description
The power supply is one of the key elements in the design of a GSM terminal.
The WMP100 is powered by a single power supply VBATT. This power supply
feeds two inputs to the supply, VBATT-BB and VBATT-RF.
VBATT-RF powers all the radio components of the WMP100. It has to be
carefully designed because most of the current is transmitted through this
input. The VBATT-RF current is bursted due to the GSM / GPRS transmission
protocol.
VBATT-BB supplies the digital part of the WMP100. VBATT-BB is directly
connected to the internal power management unit of the WMP100. This unit
controls the VBATT-BB voltage and provides the power supplies like VCC_1V8
and VCC_2V8.
Note: The VBATT-BB input generates noise, so the VBATT must be filtered by a
band reject filter.
3.2.2 Power supply constraints on VBATT-RF
Due to the bursted emission in GSM / GPRS, the power supply must be able to
deliver high current peaks in a short time. During the peaks the ripple (Uripp) on
the supply voltage must not exceed a certain limit (see Table 1 Power supply
voltage for details).
• In communication mode, a GSM/GPRS class 2 terminal emits 577μs
radio bursts every 4.615ms. (See Figure 2 below.)
Uripp
VBATT-RFT
Uripp
T = 4,615 ms
t = 577 μs
Figure 2 : Power supply during burst emission
• In communication mode, a GPRS class 10 terminal emits 1154μs radio
bursts every 4.615ms.
VBATT-RF:
• supplies the RF components with 3.6 V directly. It is essential to keep a
minimum voltage ripple at this connection in order to avoid any phase
error.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
The RF Power Amplifier current (1.5 A peak in GSM /GPRS mode) flows
with a ratio of:
o 1/8 of the time (around 577μs every 4.615ms for GSM /GPRS cl. 2)
and
o 2/8 of the time (around 1154μs every 4.615ms for GSM /GPRS cl.
10).
The rising time is around 10μs.
3.2.3 Power supply constraints on VBATT-BB
The VBATT-BB input is used as well to supply the WMP100 core as well to
monitor the level voltage of VBATT.
VBATT-BB is internally connected to several regulators and to a switching
regulator which provides the VCC_1V8 voltage internally. Because the
switching regulator generates perturbation on the VBATT signal, it is
mandatory to add an external reject filter between VBATT and VBATT-BB.
3.2.4 Electrical characteristics
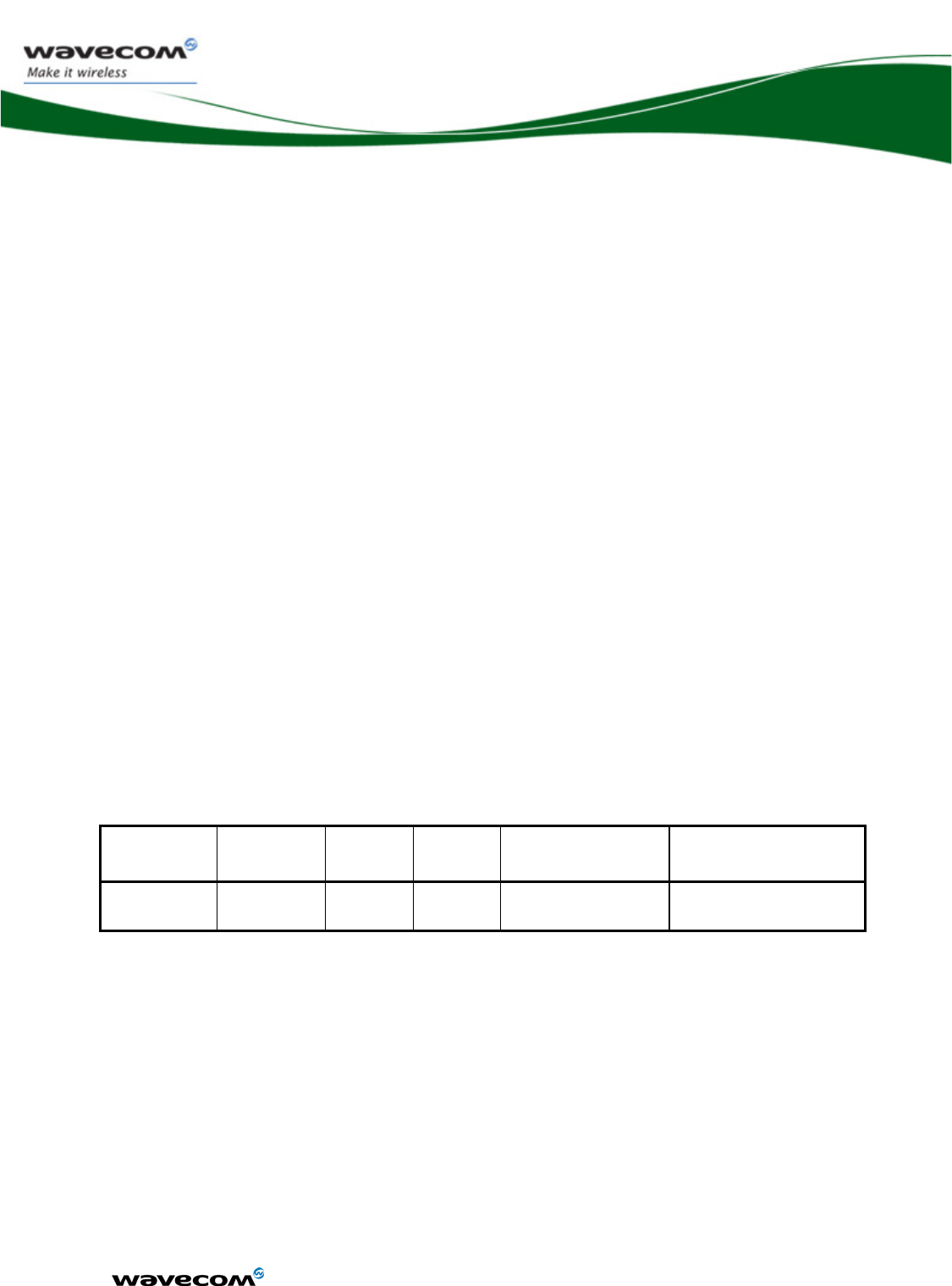
Input power Supply Voltage
VMIN VNOM VMAX IMAX Ripple max (Uripp)
VBATT-BB 3.2 3.6 4.8 0.3 A (TBC) (TBD)
VBATT-RF1,2 3.2 3.6 4.8 1.5 A (TBC) 10mV(TBC)
Table 1 Power supply voltage
(1): This value has to be guaranteed during the burst (with 1.5A Peak in GSM
or GPRS mode)
(2): Maximum operating Voltage Stationary Wave Ratio (VSWR) 2:1
When powering the WMP100 with a battery, the total impedance
(battery+protections+PCB) should be <150 mOhms.
3.2.5 Pin description
confidential © Page : 23 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 24 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Pin number
VBATT-BB AC1,AC2,AD1,AD2
VBATT-RF A12,A13,A14,B12,B13,B14
3.2.6 Application
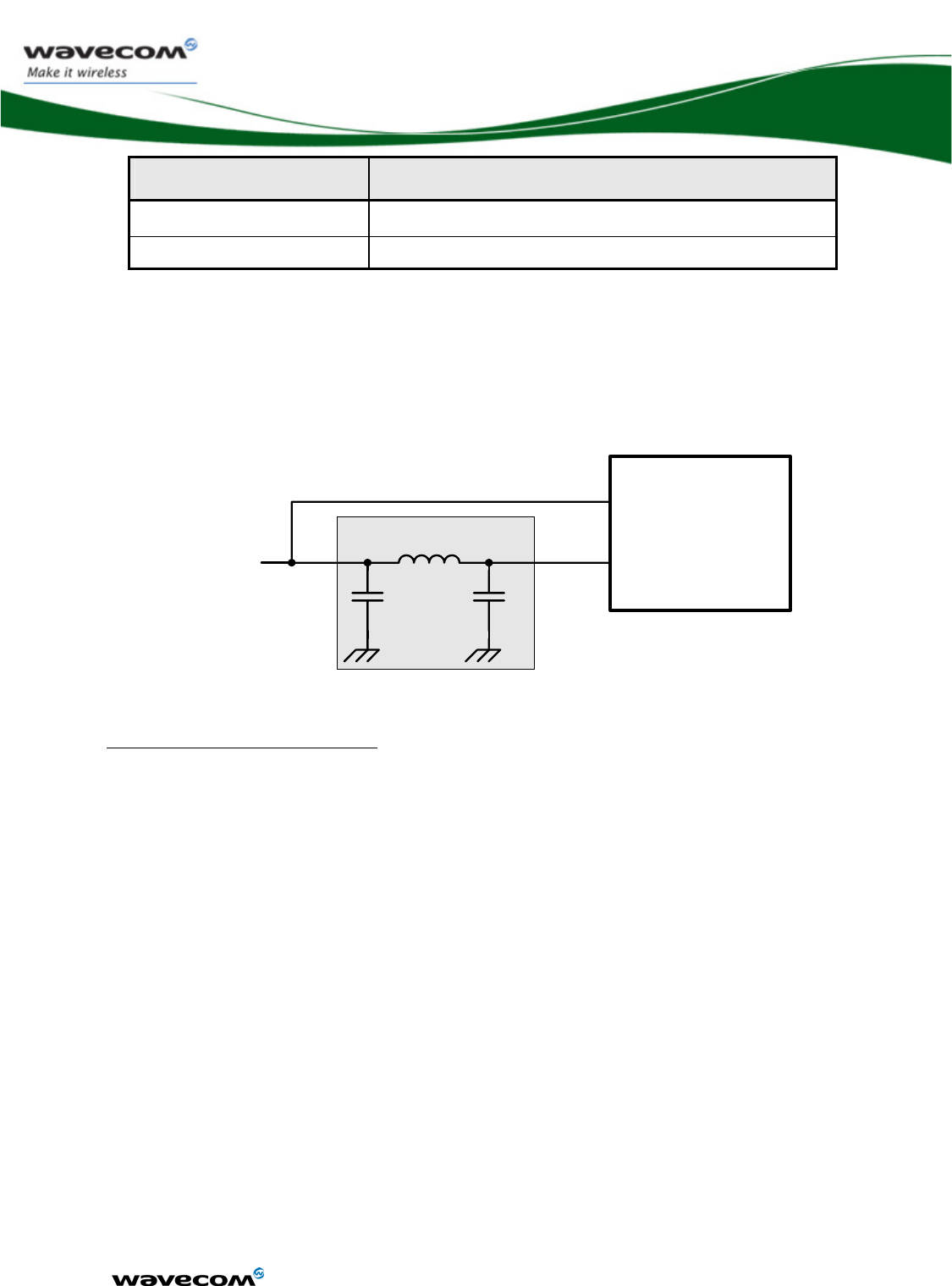
The reject filter must be connected between VBATT and VBATT-BB.
Filter WMP100
VBATT VBATT-BB
L1
C1 C2
VBATT-RF
Figure 3 : Reject filter diagram
Recommended components:
C1, C2: 10μF +/-20%
o GRM21BR60J106KE19L from MURATA
o CM21X5R106M06AT from KYOCERA
o JMK212BJ106MG-T from TAYO YUDEN
o C2012X5R0J106MT from TDK
L1: 220nH +/-5%
o 0805CS-221XJLC from COILCRAFT
o 0805G221J E from STETCO

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.3 Power consumption
Power consumption depends on the configuration used. It is for this reason
that the following consumption values are given for each mode, RF band and
type of software used (with or without an Open AT® application).
Note: All of the following information is given assuming a 50 Ω RF output.
The following consumption values were obtained by performing measurements
on WMP100 samples at a temperature of 25° C.
Three VBATT values are used to measure the consumption, VBATTMIN (3.2V),
VBATTMAX (4.8V) and VBATTTYP (3.6V).
The average current is given for the three VBATT values and the peak current
given is the maximum current peak measured with the three VBATT voltages.
For a more detailed description of the operating modes, (refer to the document
[3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5).
For more information about the consumption measurement procedure, refer to
§ 4.
All following consumption measurement values have to be confirmed.
confidential © Page : 25 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 26 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
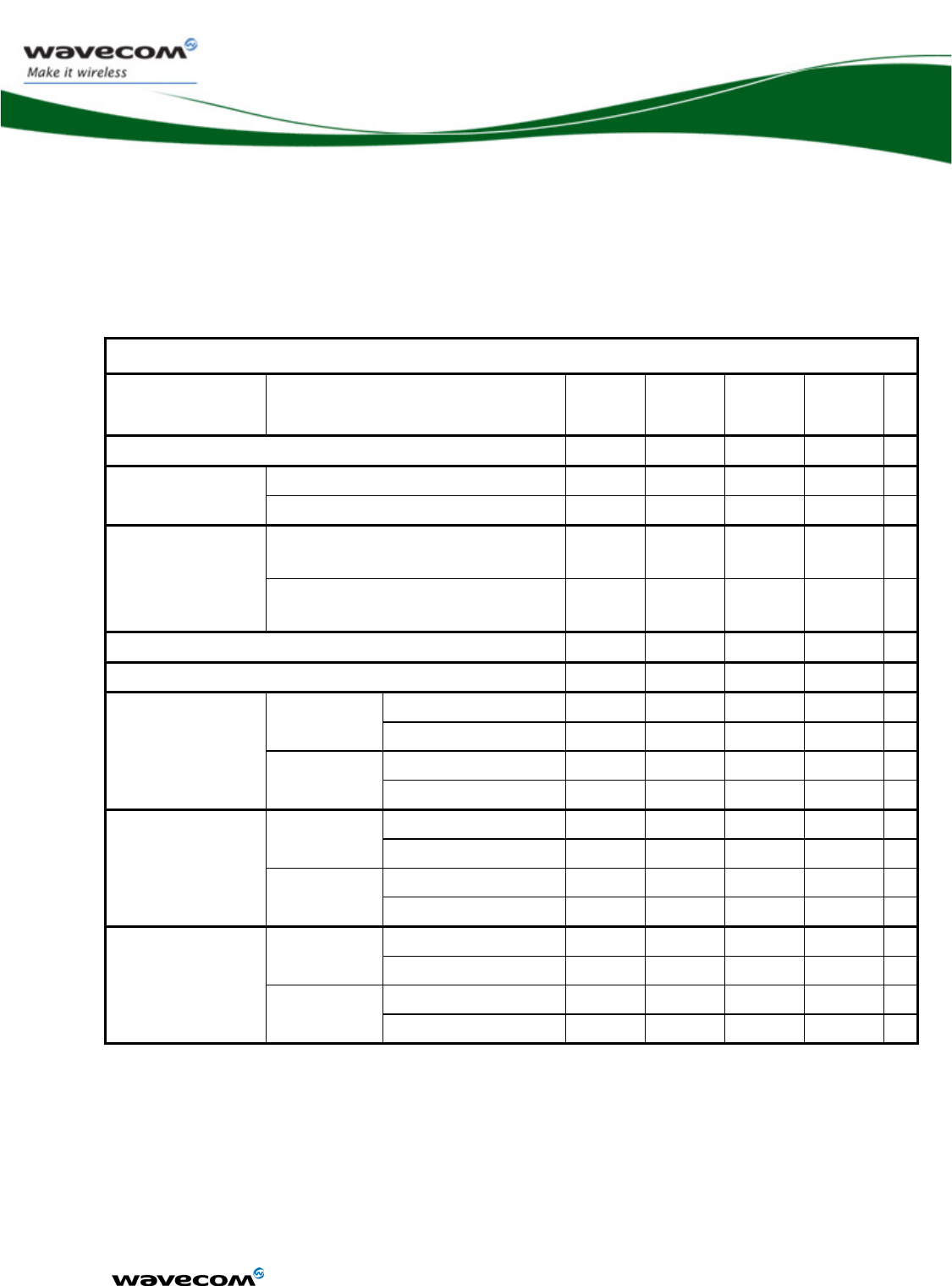
3.3.1.1 Power consumption without Open AT® processing
The following measurement results are relevant when:
¾ There is no Open AT® application
¾ The Open AT® application is disabled
¾ No processing is required by the Open AT® application
Power consumption without Open AT® processing
Operating mode Parameters
IMIN
average
VBATT=4,8V
INOM
average
VBATT=3,6V
IMAX
average
VBATT=3,2V
IMAX
peak unit
Alarm Mode 21 16 15 µA
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s) 15 17 18 160
RX mA
Fast Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s) 17 18 19 160
RX mA
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s) 1.5
(1.5 to 1.75)
1.6
(1.6 to 1.9)
1.7
(1.7 to 2.05) 160 RX mA
Slow Idle Mode 1
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s) 4
(4 to 4.3)
4.4
(4.4 to 4.75)
4.6
(4.6 to 4.95) 160 RX mA
Fast Standby Mode 30 36 39 mA
Slow Standby Mode 1.4 1.4 1.5 mA
PCL5 (TX power 33dBm) 210 218 222 1450
TX mA
850/900 MHz
PCL19 (TX power 5dBm) 81 89 92 270
TX mA
PCL0 (TX power 30dBm) 145 153 157 850
TX mA
Connected Mode
1800/1900 MHz
PCL15 (TX power 0dBm) 77 85 88 250
TX mA
gam. 3(TX power 33dBm) 201 209 213 1450
TX mA
850/900 MHz
gam.17(TX power 5dBm) 78 85 88 270
TX mA
gam.3(TX power 30dBm) 138 146 149 850
TX mA
Transfer Mode
class 8 (4Rx/1Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
gam.18(TX power 0dBm) 74 81 84 250
TX mA
gam.3 (TX power 33dBm) 364 372 378 1450
TX mA
850/900 MHz
gam.17 (TX power 5dBm) 112 120 123 270
TX mA
gam.3 (TX power 30dBm) 237 245 248 850
TX mA
Transfer Mode
class 10 (3Rx/2Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
gam.18 (TX power 0dBm) 104 111 115 250
TX mA
TX means that the current peak is the RF transmission burst (Tx burst)
RX means that the current peak is the RF reception burst (Rx burst)
1Slow Idle Mode consumption depends on the SIM card used. Some SIM cards
respond faster than others, in which case the longer the response time is, the
higher the consumption is. These measurements were performed with a large
number of 3V SIM cards, the results in brackets are the minimum and
maximum currents measured from among all the SIMs used.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 27 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.3.1.2 Power consumption with a Dhrystone Open AT® application
The Open AT® application used is the Dhrystone application. The following
consumption results are measured during the run of the Dhrystone application.
Power consumption with Dhrystone Open AT® application
Operating mode Parameters
IMIN
average
VBATT=4,8V
INOM
average
VBATT=3,6V
IMAX
average
VBATT=3,2V
IMAX
peak unit
Alarm Mode N/A N/A N/A µA
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s) 31 38 41 160
RX mA
Fast Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s) 32 39 42 160
RX mA
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s) N/A N/A N/A 160
RX mA
Slow Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s) N/A N/A N/A 160
RX mA
Fast Standby Mode 31 38 41 mA
Slow Standby Mode N/A N/A N/A mA
PCL5 (TX power 33dBm) 211 219 223 1450
TX mA
850/900 MHz
PCL19 (TX power 5dBm) 82 90 93 270
TX mA
PCL0 (TX power 30dBm) 146 154 159 850
TX mA
Connected Mode
1800/1900 MHz
PCL15 (TX power 0dBm) 78 85 89 250
TX mA
gam. 3(TX power 33dBm) 202 210 214 1450
TX mA
850/900 MHz
gam.17(TX power 5dBm) 78 86 89 270
TX mA
gam.3(TX power 30dBm) 140 148 151 850
TX mA
Transfer Mode
class 8 (4Rx/1Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
gam.18(TX power 0dBm) 75 82 85 250
TX mA
gam.3 (TX power 33dBm) 365 373 379 1450
TX mA
850/900 MHz
gam.17 (TX power 5dBm) 113 121 125 270
TX mA
gam.3 (TX power 30dBm) 239 247 250 850
TX mA
Transfer Mode
class 10 (3Rx/2Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
gam.18 (TX power 0dBm) 105 113 117 250
TX mA
TX means that the current peak is the RF transmission burst (Tx burst)
RX means that the current peak is the RF reception burst (Rx burst)
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 28 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
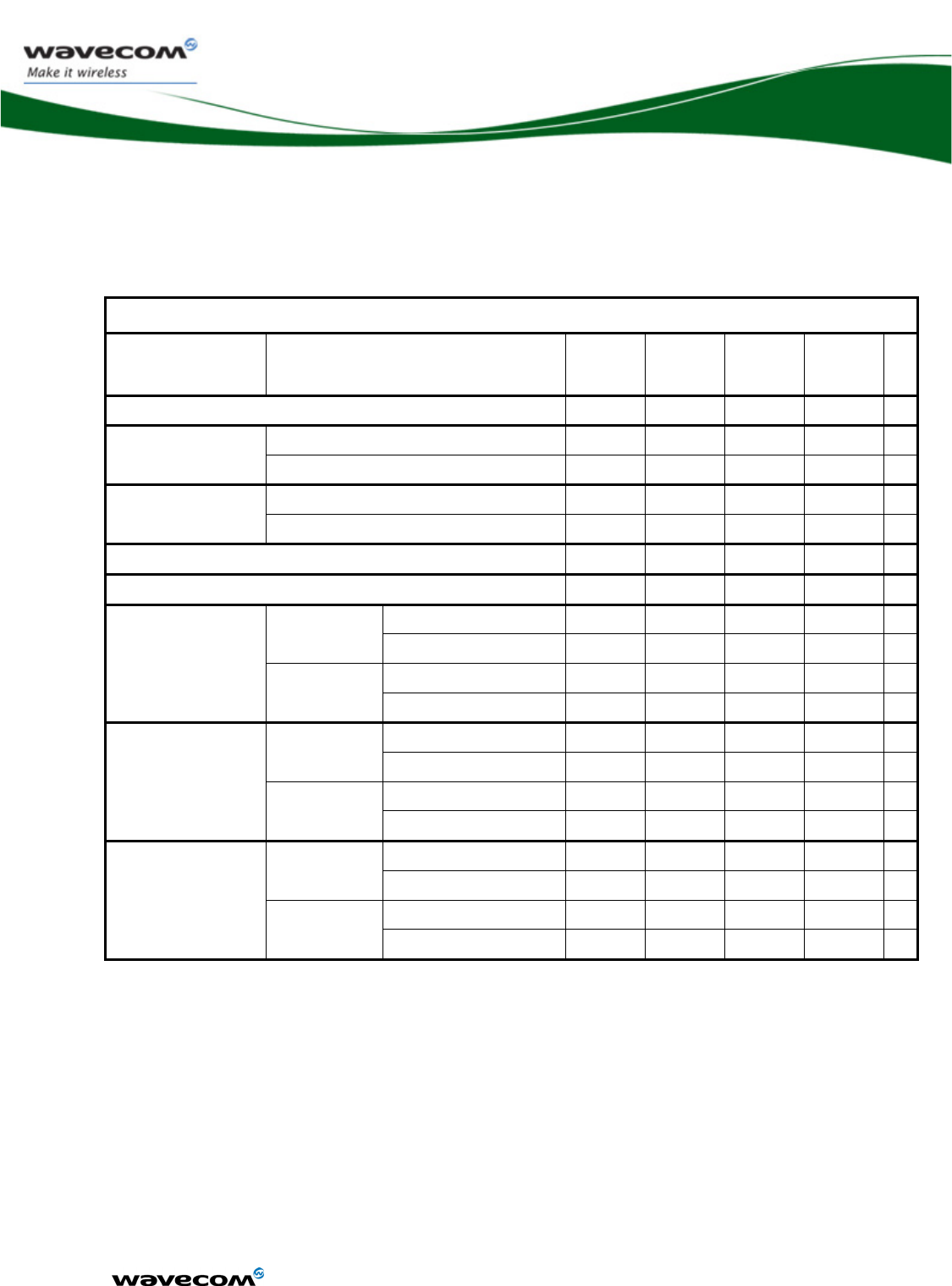
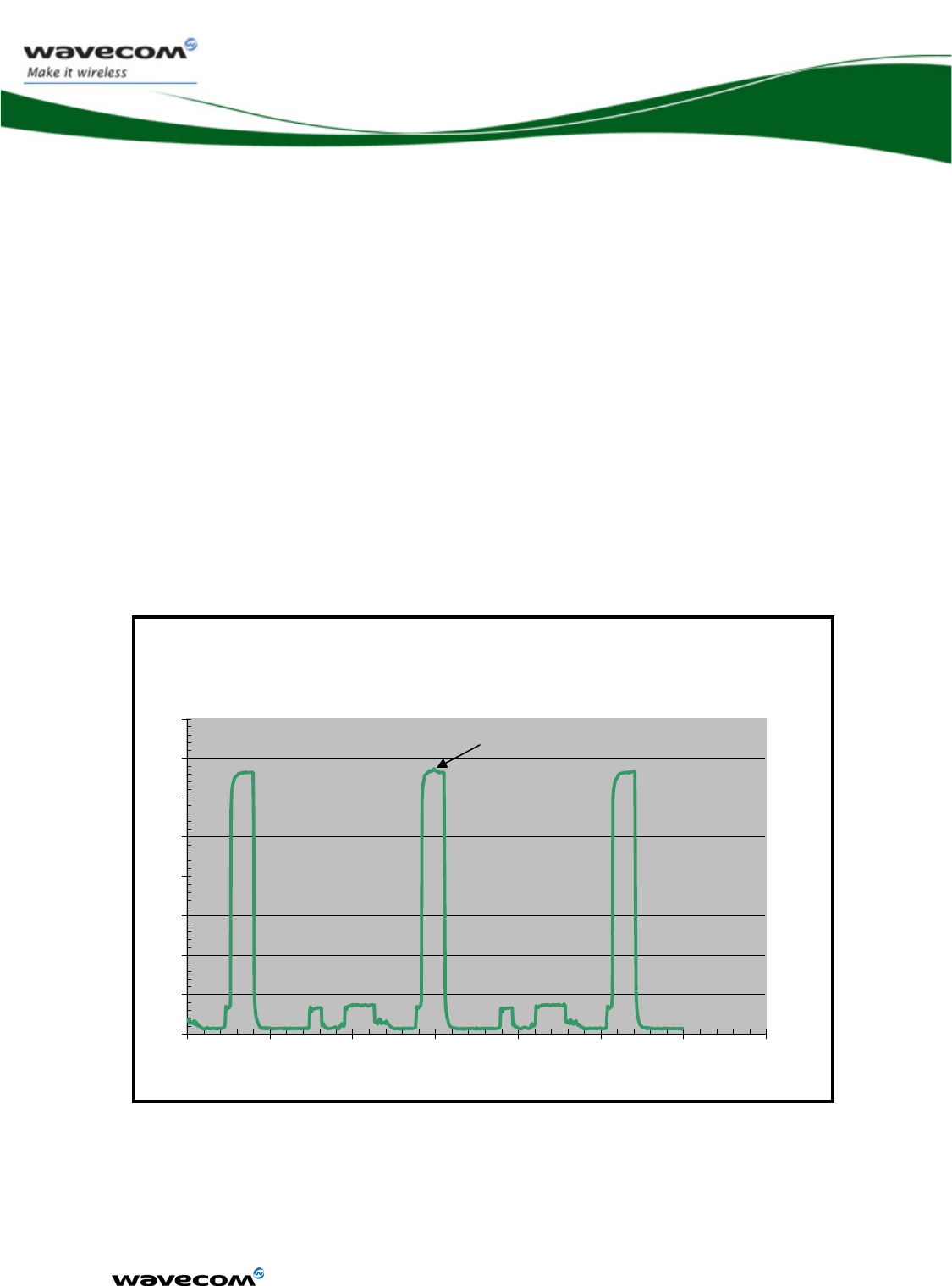
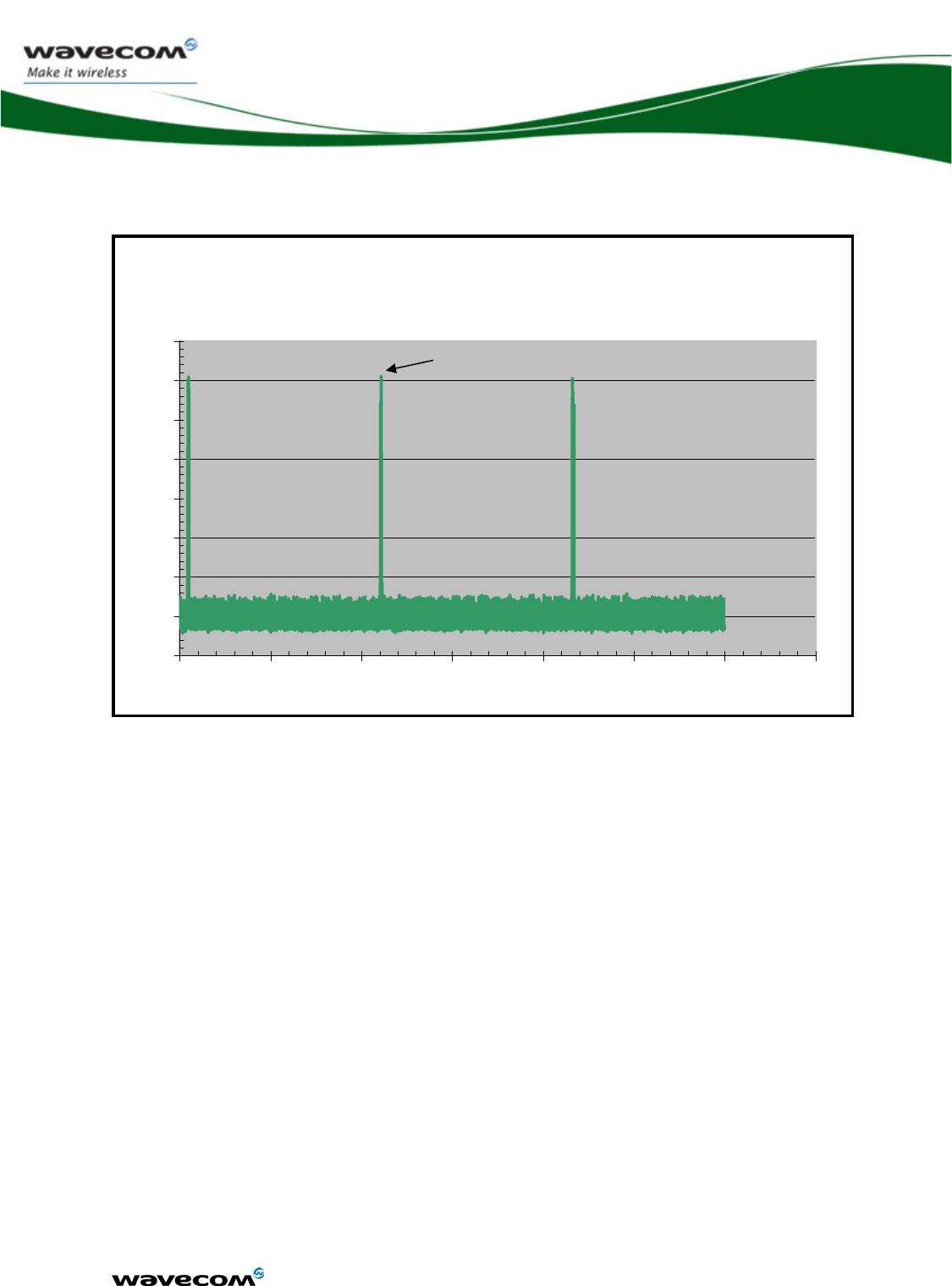
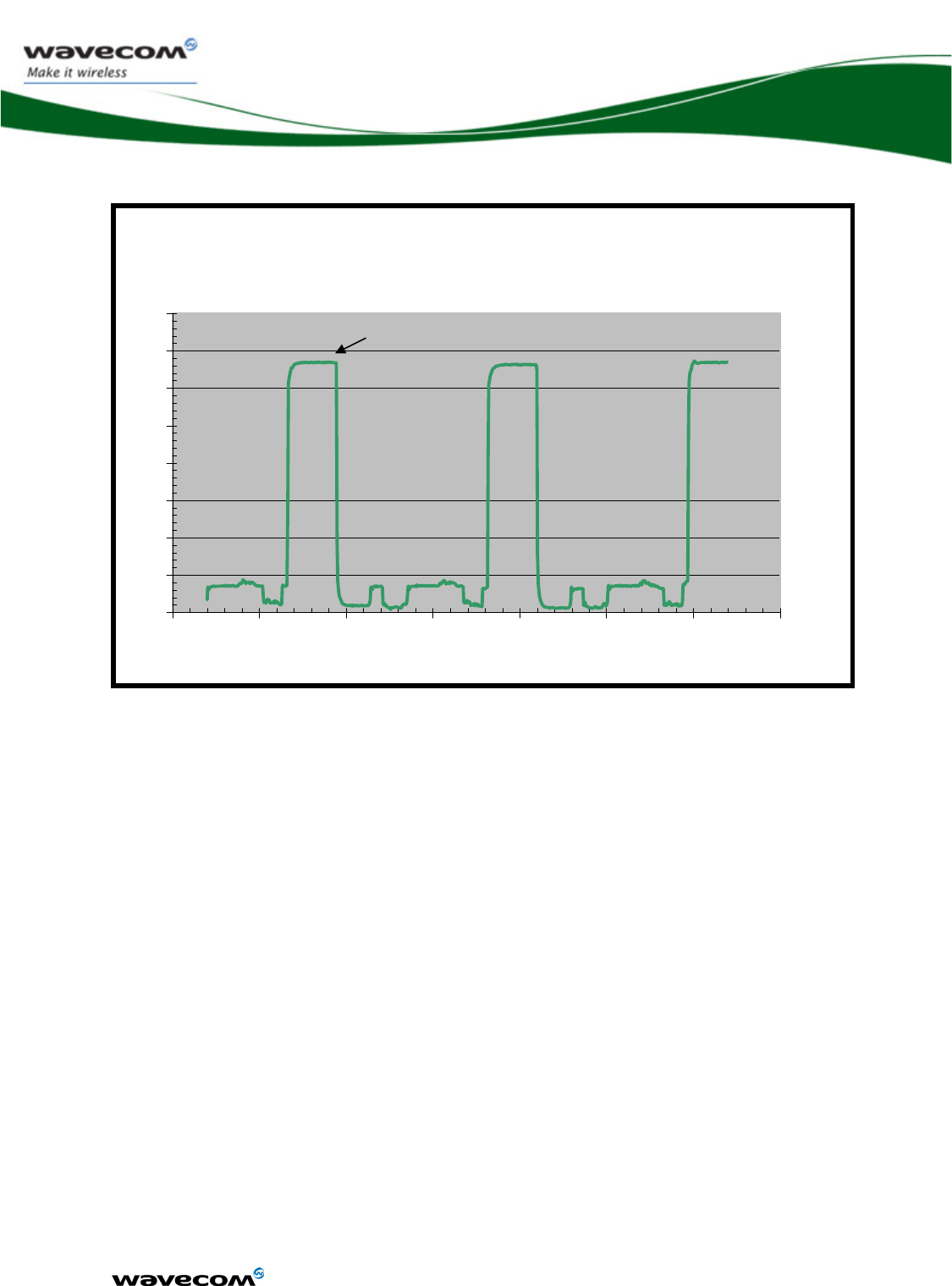
3.3.1.3 Consumption waveform samples
The consumption waveforms presented below are for an EGSM900 network
configuration without the Open AT® Software Suite running on the WMP100.
The typical VBATT voltage is 3.6V.
Four significant operating mode consumption waveforms are described:
¾ Connected Mode (PCL5: Tx power 33dBm)
¾ Slow Idle mode (Paging 9)
¾ Fast idle mode (Paging 9)
¾ Transfer mode (GPRS class 10, gam.3: Tx power 33dBm )
The following waveform shows only the form of the current.
3.3.1.3.1 Connected mode current waveform
Connected mode 33dBm
Current(A) / Time (s)
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
0
0.002
0.004
0.006
0.008
0.01
0.012
0.014
TX PEAK

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.3.1.3.2 Slow Idle mode current waveform
Slow Idle mode Paging ~2s
Current(A) / Time (s)
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
0.12
0.14
0.16
-0.02
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
RX PEAK
confidential © Page : 29 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.3.1.3.3 Fast Idle mode current waveform
Fast Idle mode Paging ~2s
Current(A) / Time (s)
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
0.12
0.14
0.16
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
RX PEAK
confidential © Page : 30 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.3.1.3.4 Transfer mode Class 10 current waveform
Transfer mode Class 10 33dBm
Current(A) / Time (s)
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
0
0.002
0.004
0.006
0.008
0.01
0.012
0.014
TX PEAK
confidential © Page : 31 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.4 Electrical information for digital I/O
There are three types of digital I/O on the WMP100: 2.8Volt CMOS, 1.8Volt
CMOS and Open drain.
The I/O concerned are all interfaces like GPIOs, SPIs, Keypad, etc.
The three types are described below.
Electrical characteristics of digital I/O
2.8 Volts type (2V8 )
Parameter I/O type Minim. Typ Maxim. Condition
Internal 2.8V power supply VCC_2V8
2.74V 2.8V
2.86V
VIL CMOS -0.5V* 0.84V
VIH CMOS 1.96V 3.2V*
VOL CMOS 0.4V IOL = - 4 mA
VOH CMOS 2.4V IOH = 4 mA
IOH 4mA
Input / Output pin
IOL - 4mA
*Absolute maximum ratings
1.8 Volts type (1V8)
Parameter I/O type Minim. Typ Maxim. Condition
Internal 1V8 power supply VCC_1V8
1.76V 1.8V
1.94V
VIL CMOS -0.5V* 0.54V
VIH CMOS 1.33V 2.2V*
VOL CMOS 0.4V IOL = - 4 mA
VOH CMOS 1.4V IOH = 4 mA
IOH 4mA
Input / Output pin
IOL - 4mA
*Absolute maximum ratings
confidential © Page : 32 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 33 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Open drain outputs type
Signal name Parameter I/O type Minimum Typ Maximum Condition
VOL Open Drain
0.4V
FLASH-LED
IOL Open Drain
8mA
VOL Open Drain
0.4V BUZZ-OUT
IOL Open Drain
100mA
VTOL Open Drain
3.3V Tolerated
voltage
VIH Open Drain
2V
VIL Open Drain
0.8V
VOL Open Drain
0.4V
SDA /
GPIO27
and
SCL /
GPIO26
IOL Open Drain
3mA
The reset states of each I/O are given in their corresponding interface’s chapter
descriptions. The states definitions are defined below:
Reset state definition
Parameter Definition
0 Set to GND
1 Set to supply 1V8 or 2V8 depending of I/O type
Pull down Internal pull down with ~60K resistor.
Pull up Internal pull up with ~60K resistor to supply 1V8 or 2V8
depending of I/O type.
Z High impedance
Undefined Be careful, undefined mustn’t be used in your application if
a special state at reset is needed. Those pins can be a
toggling signal during reset.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 34 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.5 SPI Bus
The WMP100 provides two SPI bus (i.e. for LCD, memories…).
3.5.1 Features
• a CLK signal
• an I/O signal
• an I signal
• a CS signal complying with standard SPI bus.
3.5.1.1 Characteristics
• Master mode operation
• The Hardware CS is usable only for word handling mode. In normal
mode the CS can be any GPIO.
• The SPI speed is from 102 Kbit/s up to 13 Mbit/s in master mode
operation
• 3 or 4-wire interface
• SPI-mode configuration: 0 to 3 (for more details, refer to document [3]
AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5).
• 1 to 16 bits data length
3.5.1.2 SPI configuration
Operation Maximum
Speed
SPI-
Mode
Duplex
3-wire type 4-wire type
Master 13 Mb/s 0,1,2,3
Half SPIx-CLK; SPIx-
IO; ~SPIx-CS
SPIx-CLK; SPIx-IO;
SPIx-I; ~SPIx-CS
For the 4-wire configuration, SPIx-I/O is used as output only, SPIx-I is used as input only.
For the 3-wire configuration, SPIx-I/O is used as input and output.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 35 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
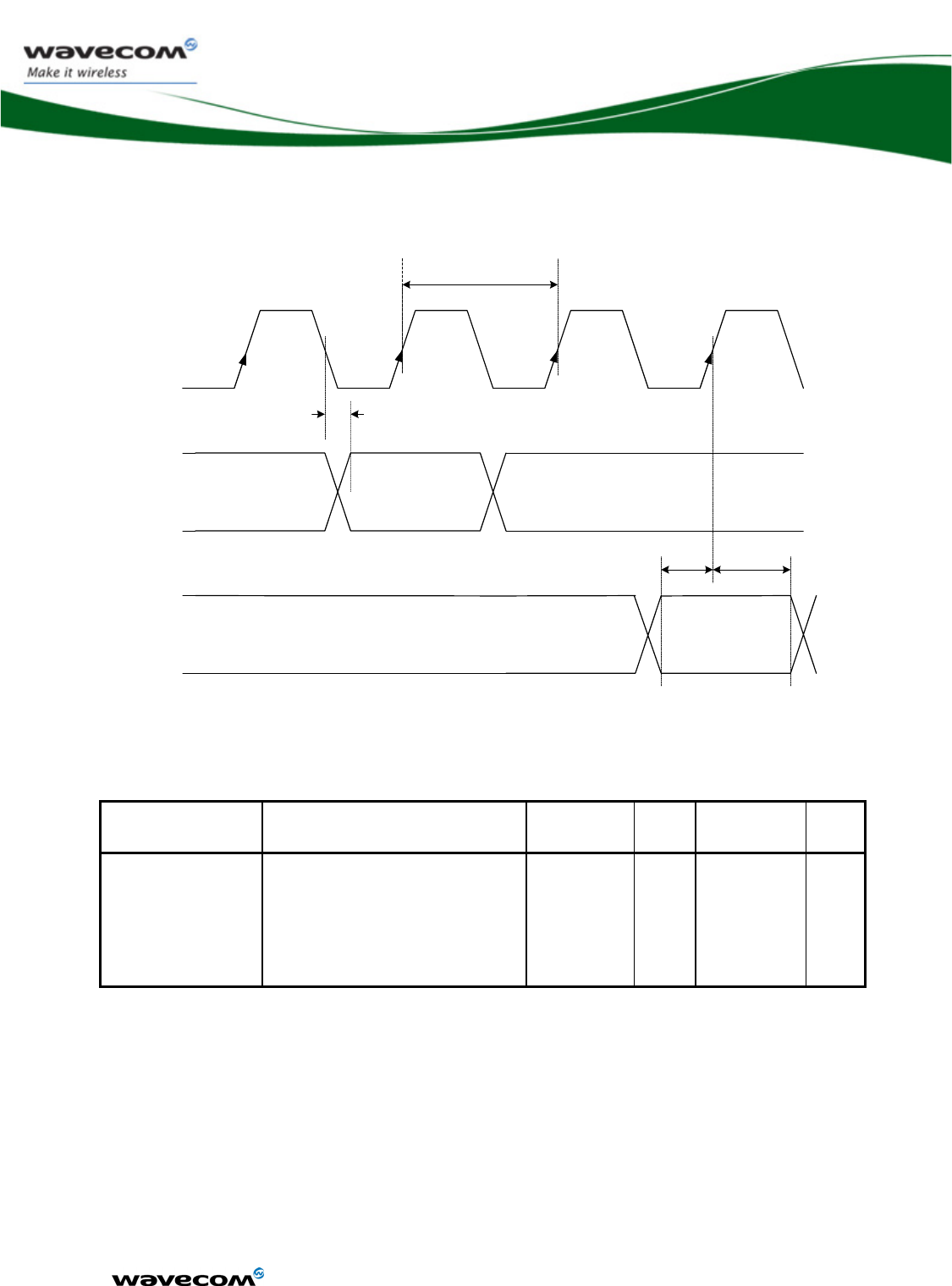
3.5.1.3 SPI waveforms
Waveform for SPI transfer with 4-wire configuration in master mode 0 (chip
select is not represented).
Data-OUTdelay
CLK-cycle
Data-IN-hold
Data-IN-setup
SPIx-IO
Data valid
Data valid
SPIx-CLK
SPIx-I
Figure 4: SPI Timing diagrams, Mode 0, Master, 4 wires
AC characteristics
Signal Description Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
CLK-cycle SPI clock frequency 0.1015 13 MHz
Data-OUT delay Data out ready delay time 10 ns
Data-IN-setup Data in setup time 2 ns
Data-OUT-hold Data out hold time 2 ns
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
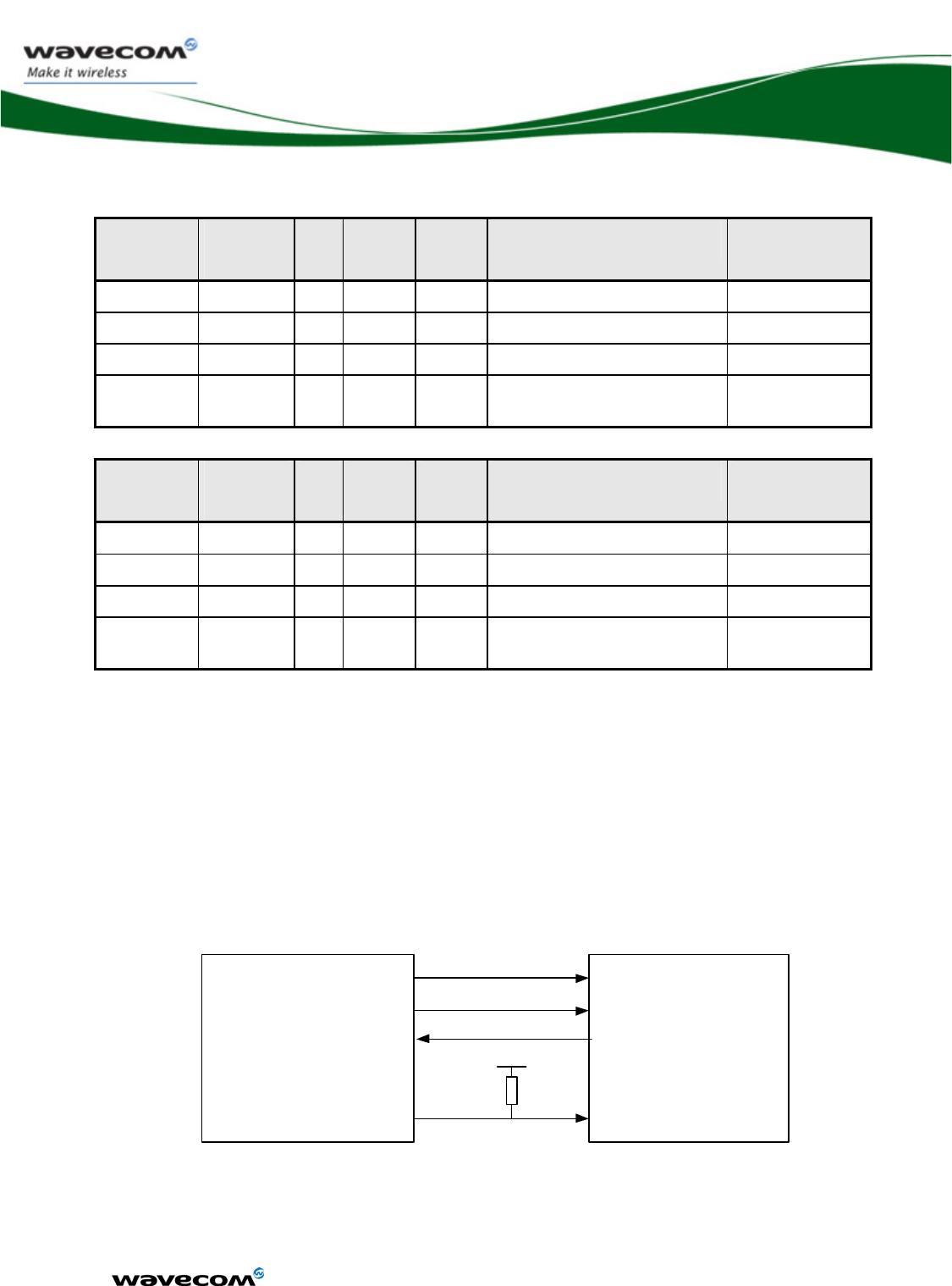
3.5.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O
type
Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
SPI1-CLK U15 O 2V8 Z SPI Serial Clock GPIO28
SPI1-IO V12 I/O 2V8 Z SPI Serial input/output GPIO29
SPI1-I R13 I 2V8 Z SPI Serial input GPIO30
~SPI1-CS M14 O 2V8 Z SPI Enable GPIO31 /
INT5
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O
type
Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
SPI2-CLK
R15 O 2V8 Z SPI Serial Clock GPIO32
SPI2-IO M13 I/O 2V8 Z SPI Serial input/output GPIO33
SP2-I U16 I 2V8 Z SPI Serial input GPIO34
~SPI2-CS T18 O 2V8 Z SPI Enable GPIO35 /
INT4
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8 voltage
characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.5.3 Application
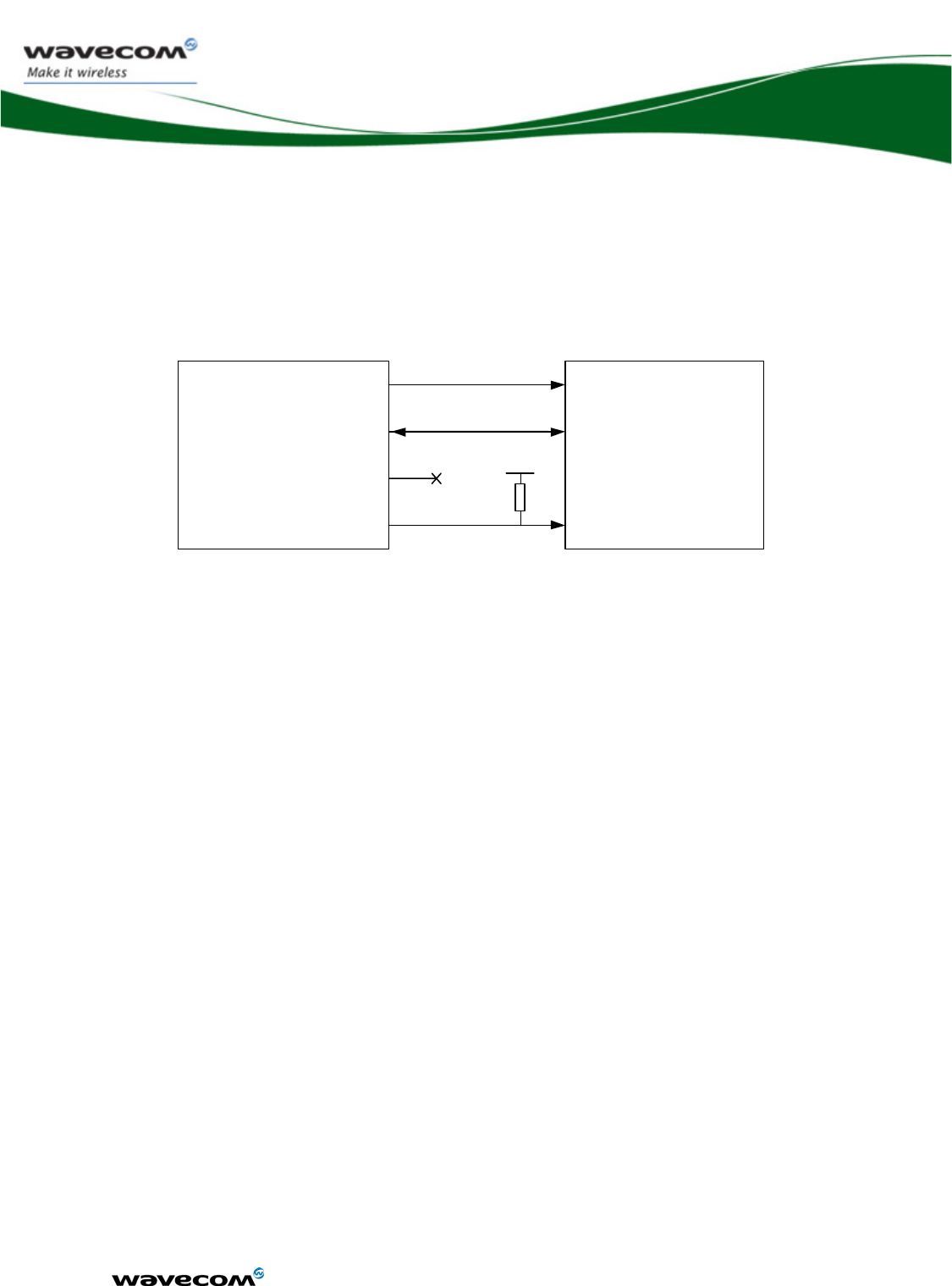
3.5.3.1 4-wire interface
The particularity of the 4-wire serial interface (SPI bus) is that the input and the
output data lines are dissociated. The SPIx-IO signal is used only for data
output and the SPIx-I signal is used only for data input.
SPIx-I
SPIx-IO
SPIx-CLK
~SPIx-CS
Customer
application
WMP100 VCC_2V8
R1
Figure 5: Example of 4-wire SPI bus application
One pull up resistor R is needed to set the SPIx-CS level during the reset state.
confidential © Page : 36 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Except for R, no external component is needed if the electrical specification of
the customer application complies with the WMP100 SPIx interface electrical
specification.
3.5.3.2 3-wire interface
When used in 3-wire interface (SPI bus), only the line SPIx-IO is used for
output and input data.
SPIx-I
SPIx-IO
SPIx-CLK
~SPIx-CS
Customer
application
WMP100 VCC_2V8
R1
Figure 6: Example of 3-wire SPI bus application
The SPIx-I line is not used in 3-wire configuration. This line can be left opened
or used as GPIO for a different application functionality.
One pull up resistor R is needed to set the SPIx-CS level during the reset state.
Except for R, no external component is needed if the electrical specification of
the customer application complies with the WMP100 SPIx interface electrical
specification.
The SPIx interface voltage range is 2.8V. It can be powered by the VCC_2V8
(ball R1) of the WMP100 or by another power supply.
R value depends on the peripheral plugged on the SPIx interface.
confidential © Page : 37 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.6 I2C bus
3.6.1 Features
The I2C interface includes a clock signal (SCL) and a data signal (SDA)
complying with a 100Kbit/s-standard interface (standard mode: s-mode).
3.6.1.1 Characteristics
The I²C bus is always master.
The maximum speed transfer range is 400Kbit/s (Fast mode: f-mode).
For more information on the bus, see document [4] “I²C Bus Specification”,
Version 2.0, Philips Semiconductor 1998.
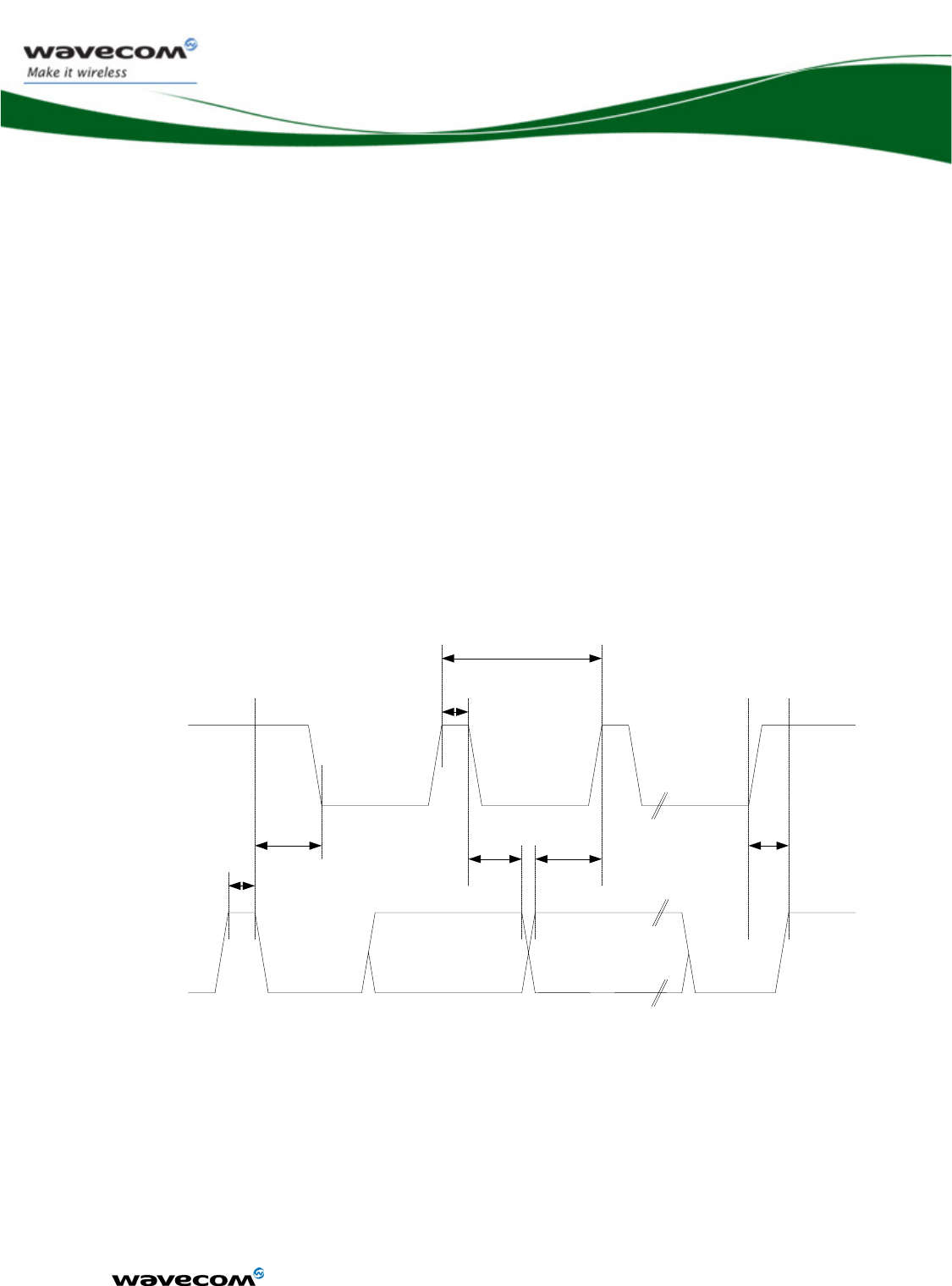
3.6.1.2 I²C waveforms
I²C bus waveform in master mode configuration:
confidential © Page : 38 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Data valid
SCL-freq
T-free
T-start
T-high
T-data-
setup
T-data-
hold
T-stop
SCL
SDA
Data valid
Figure 7: I²C Timing diagrams, Master
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
AC characteristics
Signal Description Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
SCL-freq I²C clock frequency 100 400 KHz
T-start Hold time START condition 0.6 μs
T-stop Setup time STOP condition 0.6 μs
T-free Bus free time, STOP to START
1.3 μs
T-high High period for clock 0.6 μs
T-data-hold Data hold time 0 0.9 μs
T-data-setup Data setup time 100 ns
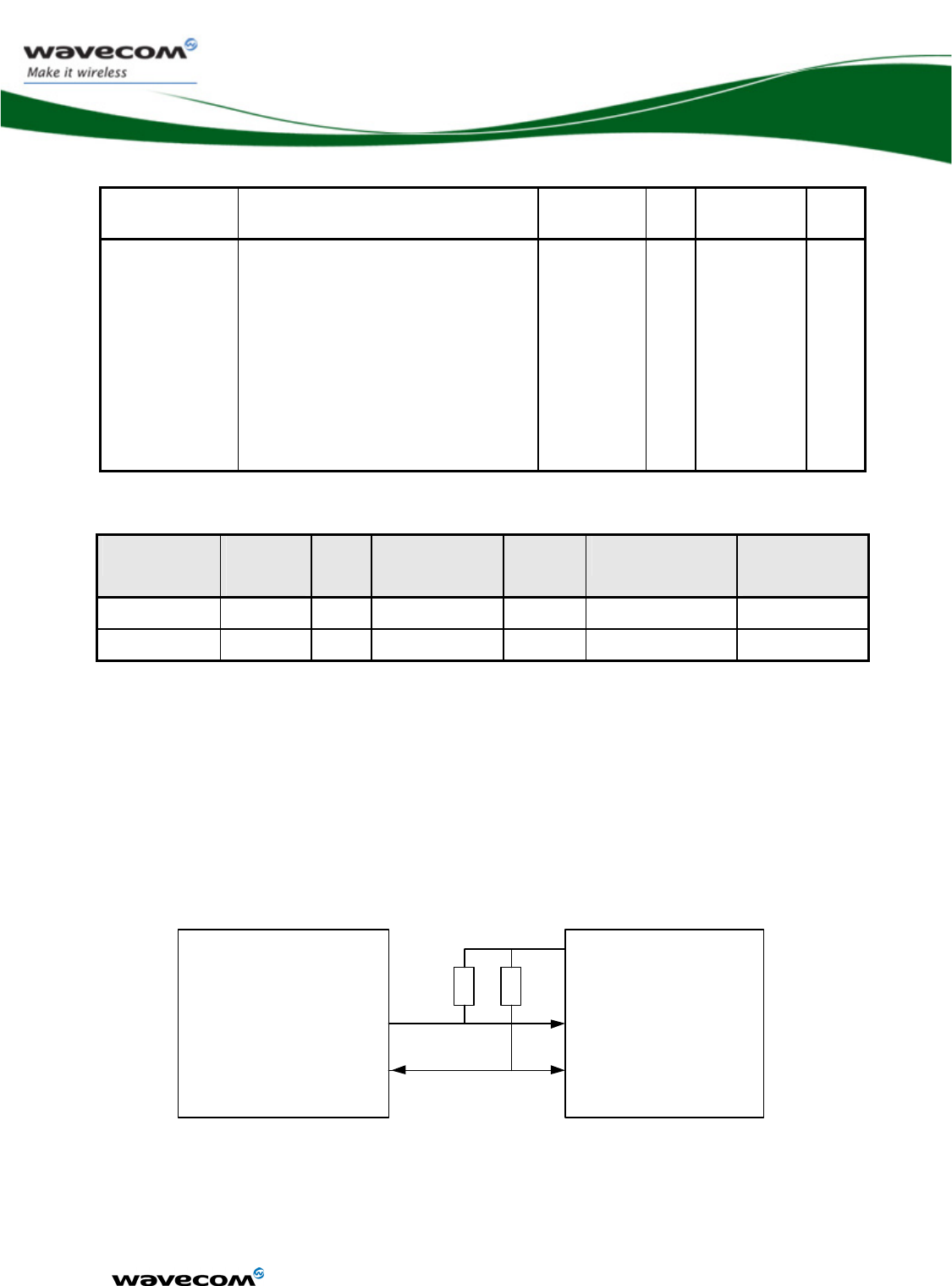
3.6.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
SCL AA15 O Open drain Z Serial Clock GPIO26
SDA AA16 I/O Open drain Z Serial Data GPIO27
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8 voltage
characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.6.3 Application
The two lines need to be pull up to the VI²C voltage. The VI²C voltage is
dependent on the customer application component connected on the I²C bus.
Nevertheless, the VI²C must complying with the WMP100 electrical
specification (3.3V Max).
The VCC_2V8 (ball R1) of the WMP100 can be used to connect the pull up
resistors, if the I²C bus voltage is 2.8 V.
confidential © Page : 39 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Customer
application
WMP100
SDA
SCL
VI²C
1K 1K
Figure 8: First example of I²C bus application

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
The I²C bus is complying with the Standard mode (baud rate 100Kbit/s) and
the Fast mode (baud rate 400Kbit/s). The pull up resistor value choice depends
on the mode used. For the Fast mode, it is recommended to use 1K ohm
resistor to ensure the compliance with the I²C specification. For the Standard
mode, higher values of resistors can be used to save power consumption.
confidential © Page : 40 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Customer
application
WMP100
SDA
SCL
1K 1K
VCC_2V8
R1
Figure 9: Second example of I²C bus application
3.7 Keyboard interface
3.7.1 Features
This interface provides 10 connections:
5 rows (ROW0 to ROW4),
5 columns (COL0 to COL4).
The scanning is a digital one, and the debouncing is done in the WMP100. No
discrete components like resistors or capacitors are needed.
The keyboard scanner is equipped with:
• internal pull-down resistors for the rows
• pull-up resistors for the columns.
Current only flows from the column pins to the row pins. This allows a
transistor to be used in place of the switch for power-on functions.
No discrete components like R, C (Resistor, Capacitor) are needed.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
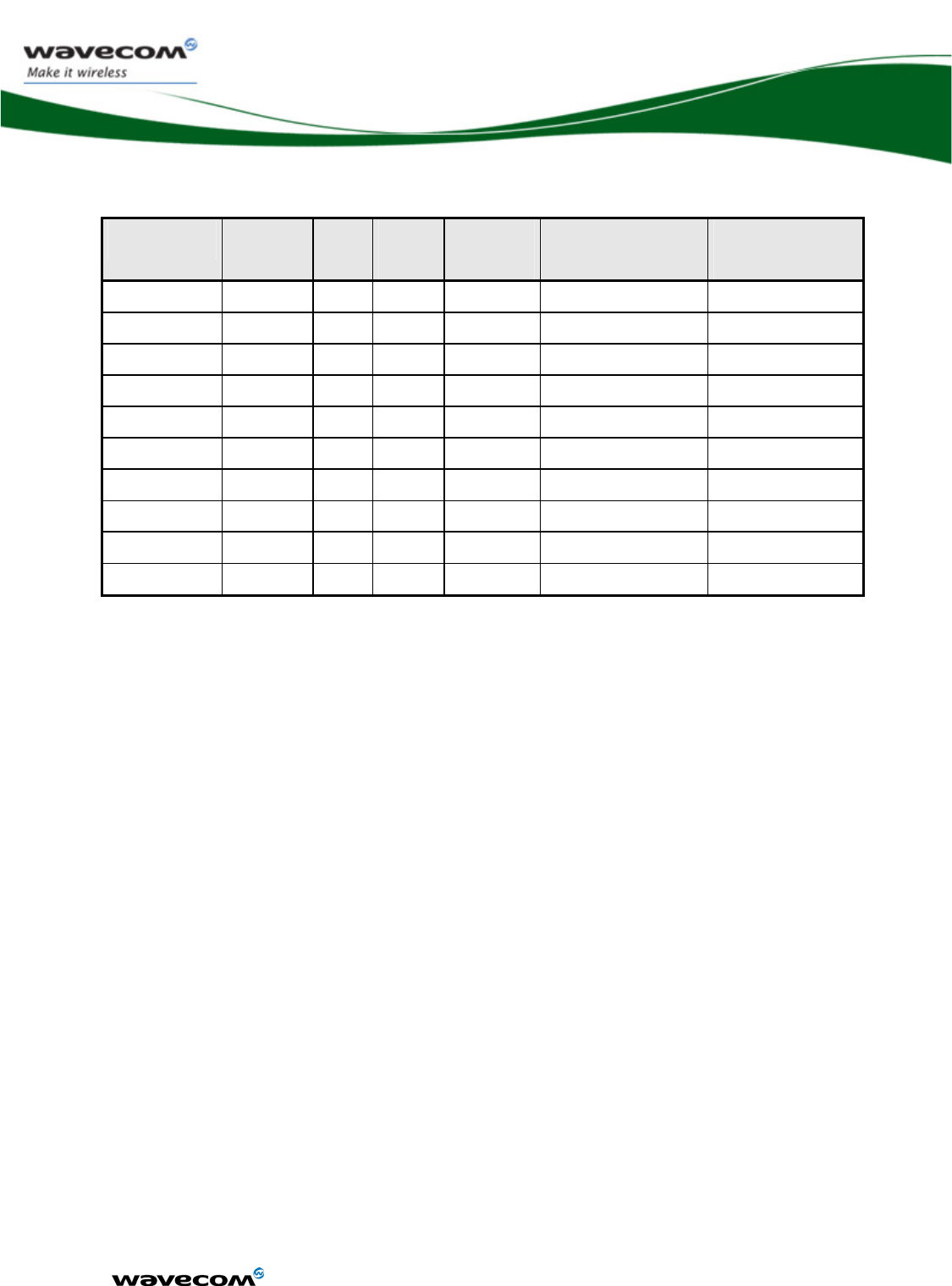
3.7.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O
type
Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
ROW0 AC23 I/O 1V8 0 Row scan GPIO9
ROW1 AD22 I/O 1V8 0 Row scan GPIO10
ROW2 AD21 I/O 1V8 0 Row scan GPIO11
ROW3 AC22 I/O 1V8 0 Row scan GPIO12
ROW4 AD23 I/O 1V8 0 Row scan GPIO13
COL0 AD19 I/O 1V8 Pull up Column scan GPIO4
COL1 AD20 I/O 1V8 Pull up Column scan GPIO5
COL2 AC20 I/O 1V8 Pull up Column scan GPIO6
COL3 AC19 I/O 1V8 Pull up Column scan GPIO7
COL4 AC21 I/O 1V8 Pull up Column scan GPIO8
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8 voltage
characteristics and for Reset state definition.
confidential © Page : 41 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 42 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.7.3 Application
Keypad matrix application allows for up to 25 keys.
Col 1
Col 2
Col 3
Col 4
Col 0
Row 0
Row 1
Row 2
Row 3
Row 4
Figure 10: Example of keyboard implementation
3.8 Main serial link (UART1)
A flexible 8-wire serial interface is available complying with V24 protocol
signaling but not with V28 (electrical interface) due to a 2.8 Volts interface.
3.8.1 Features
The maximum baud rate of the UART1 is 460 Kbit/s.
The signals are the follows:
• TX data (CT103/TX)
• RX data (CT104/RX)
• Request To Send (~CT105/RTS)
• Clear To Send (~CT106/CTS)
• Data Terminal Ready (~CT108-2/DTR)
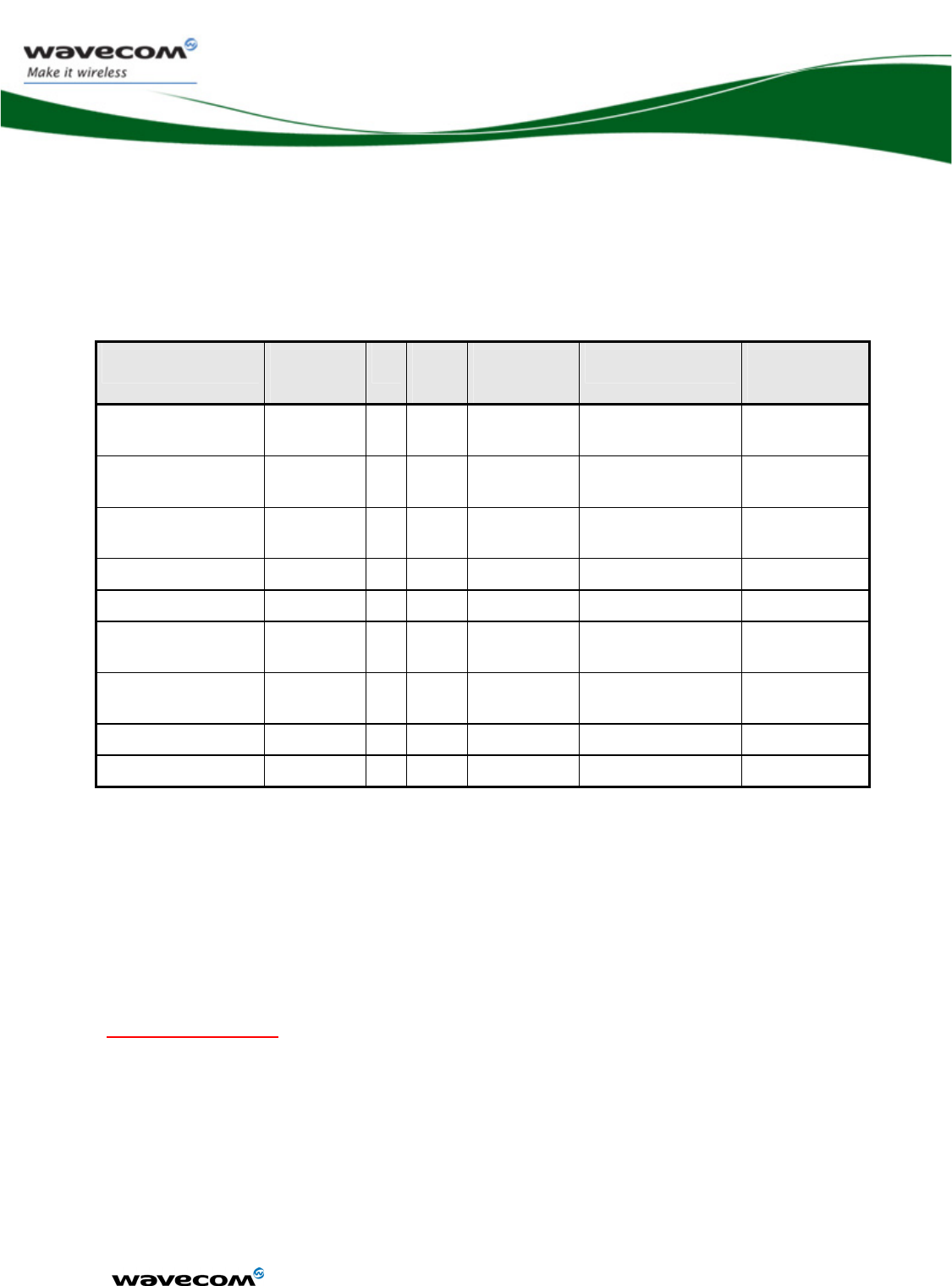
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
• Data Set Ready (~CT107/DSR)
• Data Carrier Detect (~CT109/DCD)
• Ring Indicator (~CT125/RI).
3.8.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O
I/O
type
Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
CT103/TXD1* R17 I 2V8 Z Transmit serial
data
GPIO36
CT104/RXD1* T13 O 2V8 1 Receive serial
data
GPIO37
~CT105/RTS1* Y18 I 2V8 Z Request To
Send
GPIO38
~CT106/CTS1* N15 O 2V8 Z Clear To Send GPIO39
~CT107/DSR1* T12 O 2V8 Z Data Set Ready GPIO40
~CT108-
2/DTR1*
M16 I 2V8 Z Data Terminal
Ready
GPIO41
~CT109/DCD1 * AB16 O 2V8 Undefined
Data Carrier
Detect
GPIO43
~CT125/RI1 * AA18 O 2V8 Undefined
Ring Indicator GPIO42
CT102/GND* AA19 GND
Ground
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8 voltage
characteristics and for Reset state definition.
*According to PC view
The rising time and falling time of the reception signals (mainly CT103) have to
be less than 300 ns.
Recommendation:
The WMP100 is designed to operate using all the serial interface signals. In
particular, it is mandatory to use RTS and CTS for hardware flow control in
order to avoid data corruption during transmission.
confidential © Page : 43 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
For the use case with 5-wire serial interface
• Signal: CT103/TXD1*, CT104/RXD1*, ~CT105/RTS1*, ~CT106/CTS1*
• The signal ~CT108-2/DTR1* must be managed following the V24
protocol signalling if we want to use the slow idle mode
• The other signals and their multiplexed are not available
• Please refer to the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open
AT® Firmware v6.5 for more information.
For the use case with 4-wire serial interface
• CT103/TXD1*, CT104/RXD1*, ~CT105/RTS1*, ~CT106/CTS1*
• The signal ~CT108-2/DTR1* must be configured at the low level
• The other signals and their multiplexed are not available
• Please refer to the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open
AT® Firmware v6.5 for more information.
For the use case with 2-wire serial interface
• This case is possible for connected external chip but not recommended
(and forbidden for AT command or modem use)
• The external chip must be a flow control
• CT103/TXD1*, CT104/RXD1*
• The signal ~CT108-2/DTR1* must be configured at the low level
• The signals ~CT105/RTS1*, ~CT106/CTS1* are not used, please
configure the AT command (AT+IFC=0,0 see document [3] AT
Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5).
• The signal ~CT105/RTS1* must be configured at the low level
• The other signals and their multiplexed are not available
• Please refer to the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open
AT® Firmware v6.5 for more information.
confidential © Page : 44 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 45 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.8.3 First download
The first download of the Flash (when Flash is blank) of the WMP100 must be
done through the UART1 serial interface. That’s mandatory that the UART1 is
available for the first download, so it’s necessary to be careful about the
connectivity of the UART1 with others devices used in the application.
If no device is connected and there are no conflicts, the computer can be
directly connected on the WMP100 through a RS232 level shifter.
When a device is used on UART1, allowing for the ability to unselect the device
during the download is recommended (via the enable signal).
Figure 11: Example of UART1 connection for download with another device
on the link
The Download connector is directly connected on the four UART1 signals,
which may create conflicts with the Device lines. For this reason an enable
must be available on the device to set the device output signals at High
impedance.
NOTE:
• In this configuration (4-wire), the signal ~CT108-2/DTR1 (ball M16)
must be configured at the low level.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
At the same time, to run the first download, the BOOT signal of the WMP100
must be driven. The switch S2 must be closed. After the download started S2
can be open. See the BOOT signal chapter (§ 3.18) for more information.
If the WMP100 is power ON (VBATT present), S1 must be closed for enable
the WMP100.
Start the specific PC software tool provided by WAVECOM.
S3 must be closed* (a pulse to 0L during at least 200μs) for start the
download. See RESET signals chapter (§3.19) for more information.
* S3 can be not use if the condition on S1 and S2 are respected before than the
power supply is applied.(There is in this case an automatic internal reset).
If a computer is used for the first download, a RS232 level shifter must be used
(See the application with the ADM3307EACP in this chapter).
Note: XMODEM download can be launched through UART1 and UART2, but
first download has to be launched with a specific PC software tool provided by
WAVECOM only through UART1.
3.8.4 Application
The level shifter must be a 2.8V with V28 electrical signal compliant.
Figure 12: Example of RS-232 level shifter implementation for UART1
U1 chip also protects the WMP100 against ESD at 15KV. (Air Discharge)
confidential © Page : 46 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Recommended components:
R1, R2 : 15Kohm
C1, C2, C3, C4, C5 : 1uF
C6 : 100nF
C7 : 6.8uF TANTAL 10V CP32136 AVX
U1 : ADM3307EACP ANALOG DEVICES
J1 : SUB-D9 female
R1 and R2 are necessary only during Reset state to forced ~CT1125-RI1 and
~CT109-DCD1 signal to high level.
The ADM3307EACP chip is able to speed up to 921Kb/s*. If others level
shifters are used, ensured that their speed are compliant with the UART1
speed useful.
*: For this baud rate the power supply must be provided by an external
regulator at 3.0 V.
The ADM3307EACP can be powered by the VCC_2V8 (ball R1) of the WMP100
or by an external regulator at 2.8 V (the baud rate will be limited up to
720kbps).
If the UART1 interface is connected directly to a host processor, it is not
necessary to used level shifters. The interface can be connected as shown
below:
confidential © Page : 47 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 48 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
V24/CMOS possible design:
Customer application
( DTE )
WMP100
( DCE )
~RESET
ON / ~OFF
CT103-TXD1 / GPIO36
CT104-RXD1 / GPIO37
~CT105-RTS1 / GPIO38
~CT106-CTS1 / GOPI39
U5
M16
Y18
T13
V6
R17
GND
Rx
RTS
CTS
GND
Tx
N15
Figure 13: Example of V24/CMOS serial link implementation for UART1
The design shown in the above figure is a basic design.
However, a more flexible design to access this serial link with all modem
signals is shown below
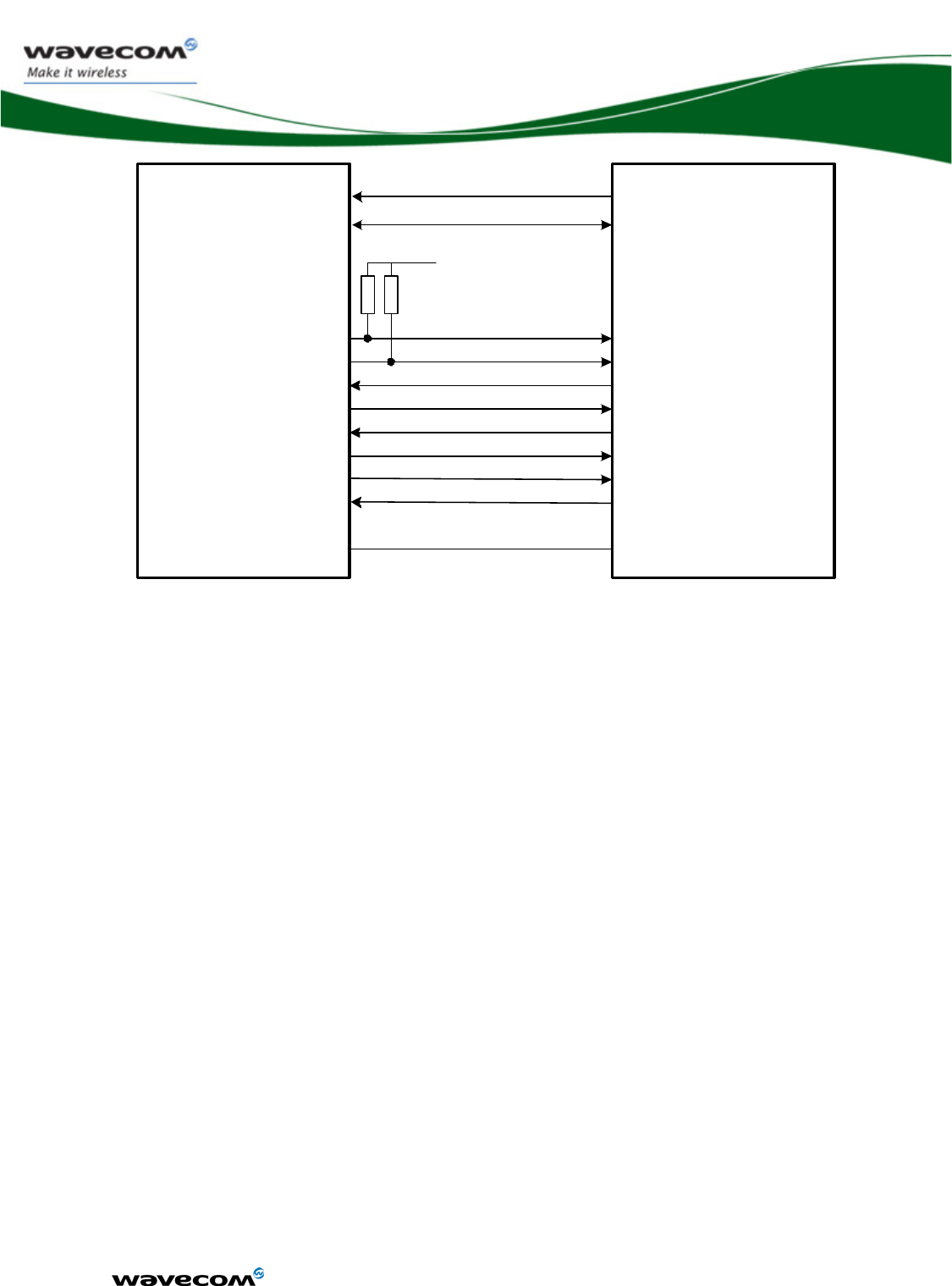
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Customer
application
( DTE )
WMP100
( DCE )
GND
~RESET
~CT107-DSR1 / GPIO40
~CT109-DCD1 / GPIO43
~CT108-2-DTR1 / GPIO41
~CT125-RI1 / GPIO42
AB16
M16
AA18
V6
T12
GND
DCD
DTR
RI
GND
DSR
ON / ~OFF
U5
CT103-TXD1 / GPIO36
CT104-RXD1 / GPIO37
~CT105-RTS1 / GPIO38
~CT106-CTS1 / GOPI39
N15
Y18
T13
R17
Rx
RTS
CTS
Tx
2x 15K
2.8Volt
Figure 14: Example of full modem V24/CMOS serial link implementation for
UART1
It is recommended to add a 15K-ohm pull-up resistor on ~CT125-RI1 and
~CT109-DCD1 to set high level during reset state.
The UART1 interface is 2.8 Volt type, but is 3 Volt tolerant.
The WMP100 UART1 is designed to operate using all the serial interface
signals. In particular, it is mandatory to use RTS and CTS for hardware flow
control in order to avoid data corruption during transmission.
Warning: If you want to activate Power Down mode (Wavecom 32K mode) in
your Open AT® application, you need to wire the DTR ball to a GPIO. Please
refer to the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware
v6.5 (see the “Appendixes”) for more information on Wavecom 32K mode
activation using the Open AT® Software Suite.
confidential © Page : 49 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.9 Auxiliary serial link (UART2)
An auxiliary serial interface (UART2) is available on WMP100. This interface
may be used to connect a Bluetooth or a GPS chip controlled by an Open AT®
Plug-in.
3.9.1 Features
Maximum baud rate of the UART2 is 460 Kbit/s.
The signals are the follows:
• TX data (CT103/TX)
• RX data (CT104/RX)
• Request To Send (~CT105/RTS)
• Clear To Send (~CT106/CTS)
The WMP100 is designed to operate using all the serial interface signals. In
particular, it is mandatory to use RTS and CTS for hardware flow control in
order to avoid data corruption during transmission.
For the use case with 2-wire serial interface
• This case is possible for connected external chip but not recommended
(and forbidden for AT command or modem use)
• The external chip must be a flow control
• CT103/TXD2*, CT104/RXD2*
• The signals ~CT105/RTS2*, ~CT106/CTS2* are not used, please
configure the AT command (AT+IFC=0,0. Please refer to the document
[3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5.
• The signal ~CT105/RTS2* must be configured at the low level
• The other signal and their multiplexed are not available
• Please refer to the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open
AT® Firmware v6.5 (see the “Appendixes”).
confidential © Page : 50 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 51 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.9.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
CT103 /
TXD2*
T16 I 1V8 Z Transmit serial data
GPIO14 /
INT6
CT104 /
RXD2*
U17 O 1V8 Z Receive serial data GPIO15
~CT106 /
CTS2*
W17 O 1V8 Z Clear To Send GPIO16
~CT105 /
RTS2*
V13 I 1V8 Z Request To Send GPIO17 /
INT7
CT102/GND* V15 GND Ground
* According to PC view
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8 voltage
characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.9.3 Application
The voltage level shifter must be a 1.8V with V28 electrical signal compliant.
Figure 15: Example of RS-232 level shifter implementation for UART2

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Recommended components:
Capacitors
C1 : 220nF
C2, C3, C4 : 1μF
Inductor
L1 : 10μH
RS-232 Transceiver
U1 : LINEAR TECHNOLOGY LTC®2804IGN
J1 : SUB-D9 female
The LTC2804 can be powered by the VCC_1V8 (ball AD5) of the WMP100 or
by an external regulator at 1.8 V.
The UART2 interface can be connected directly to others components if the
voltage interface is 1.8 V.
3.10 SIM Interface
The Subscriber Identification Module can be directly connected to the
WMP100 through this dedicated interface.
3.10.1 Features
The SIM interface controls 1.8V and 3V SIM card.
It is recommended to add Transient Voltage Suppressor diodes (TVS) on the
signal connected to the SIM socket in order to prevent any Electrostatics
Discharge.
TVS diodes with low capacitance (less than 10 pF) have to be connected on
SIM-CLK and SIM-IO signals to avoid any disturbance of the rising and falling
edge.
These types of diodes are mandatory for the Full Type Approval. They shall be
placed as close as possible to the SIM socket.
The following references can be used: DALC208SC6 from ST Microelectronics.
5 signals exist:
• SIM-VCC: SIM power supply.
• ~SIM-RST: reset.
• SIM-CLK: clock.
• SIM-IO: I/O port.
• SIMPRES: SIM card detect.
The SIM interface controls a 3V / 1V8 SIM. This interface is fully compliant
with GSM 11.11 recommendations concerning SIM functions.
confidential © Page : 52 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
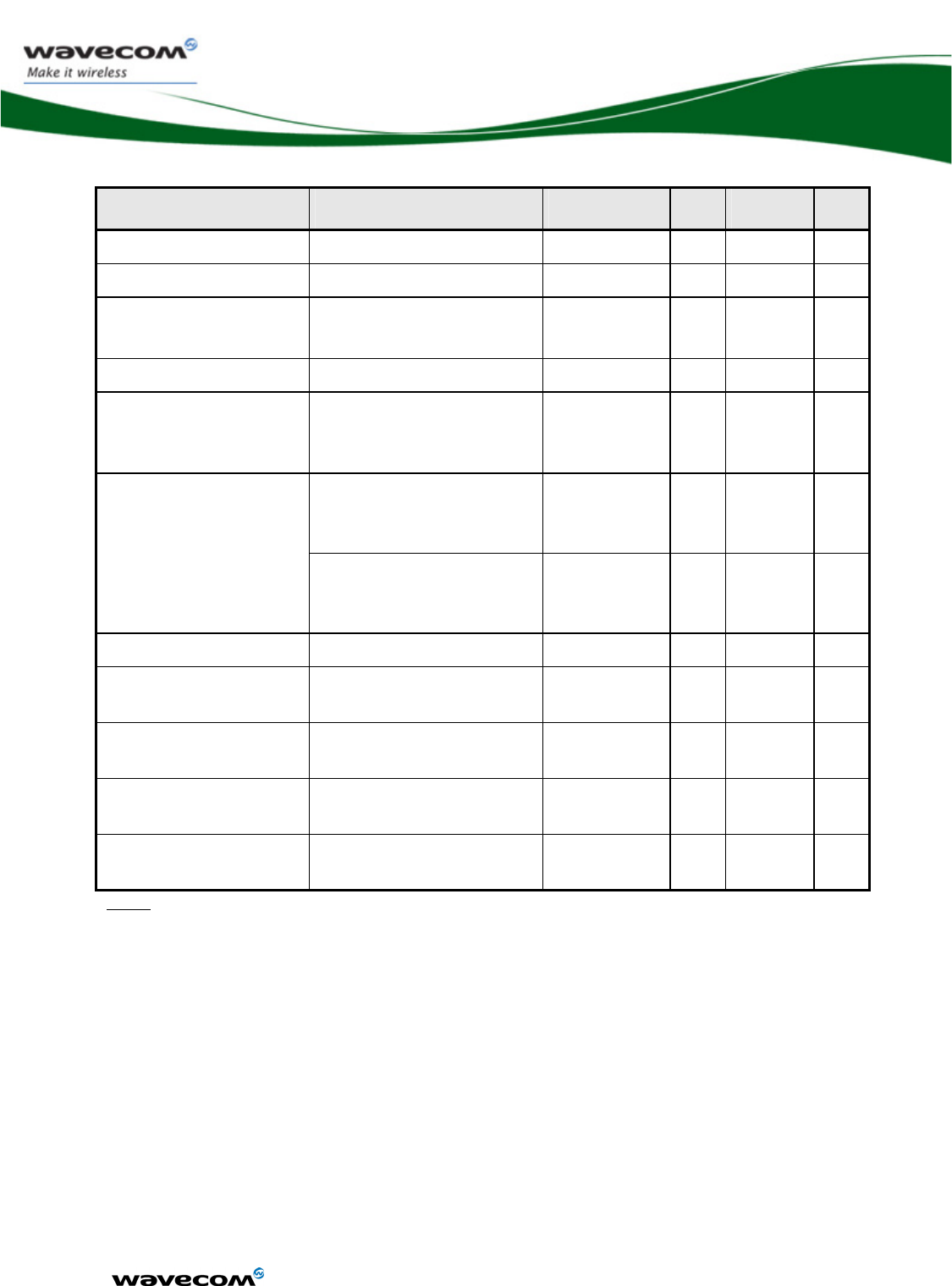
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 53 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Electrical Characteristics of SIM interface
Parameter Conditions Minim. Typ Maxim.
Unit
SIM-IO VIH IIH = ± 20μA 0.7xSIMVCC
V
SIM-IO VIL I
IL = 1mA 0.4 V
~SIM-RST, SIM-CLK
VOH
Source current = 20μA 0.9xSIMVCC
V
SIM-IO VOH Source current = 20μA 0.8xSIMVCC
~SIM-RST, SIM-IO,
SIM-CLK
VOL
Sink current =
-200μA
0.4 V
SIMVCC = 2.9V
IVCC= 1mA
2.84 2.9 2.96
V SIM-VCC Output
Voltage
SIMVCC = 1.8V
IVCC= 1mA
1.74 1.8 1.86
V
SIM-VCC current VBATT = 3.6V 10
mA
SIM-CLK Rise/Fall
Time
Loaded with 30pF 20 ns
~SIM-RST, Rise/Fall
Time
Loaded with 30pF 20 ns
SIM-IO Rise/Fall
Time
Loaded with 30pF
0.7 1 μs
SIM-CLK Frequency Loaded with 30pF 3.25 MH
z
Note:
When SIMPRES is used, a low to high transition means that the SIM card is
inserted and a high to low transition means that the SIM card is removed.
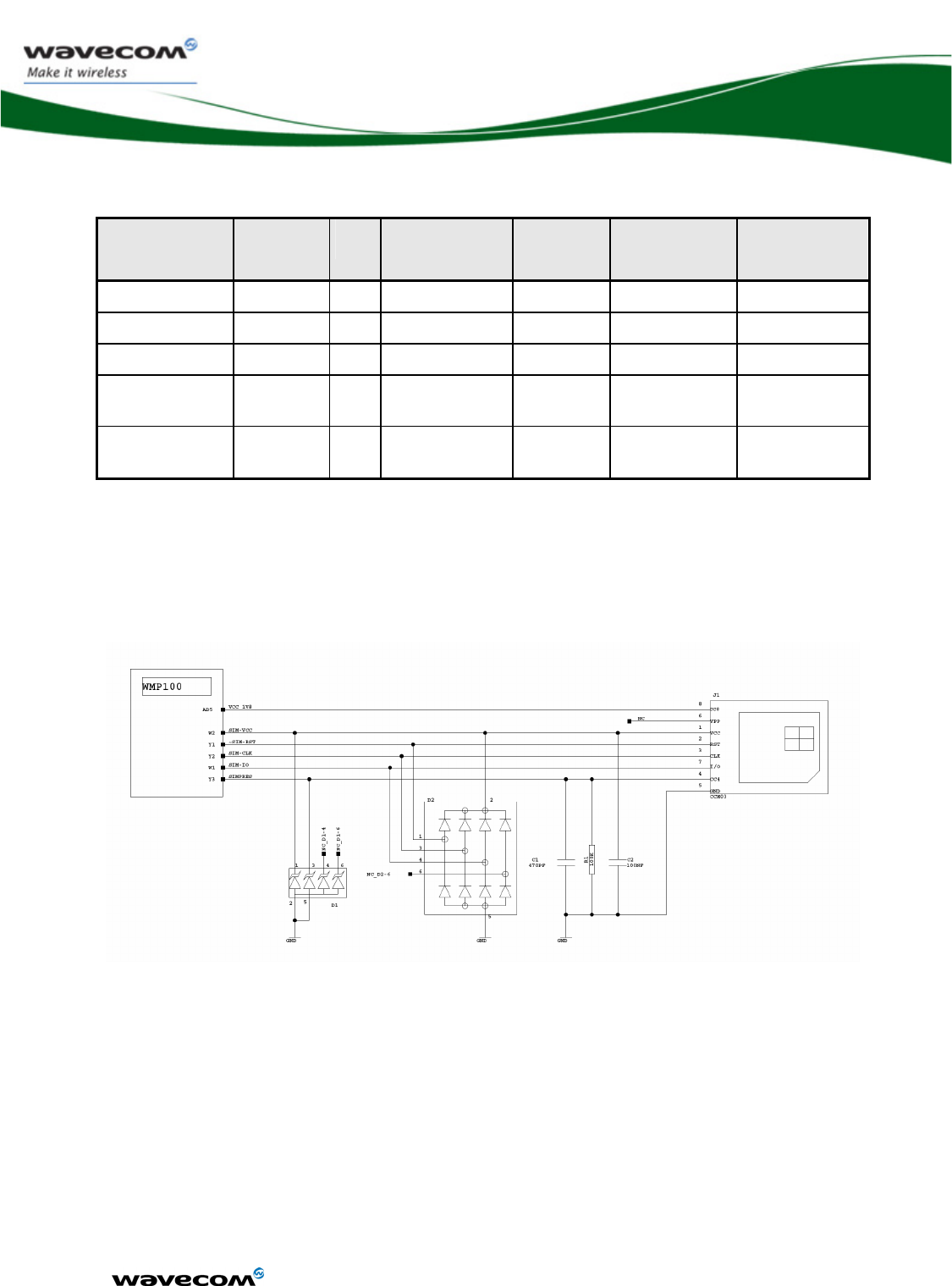
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 54 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.10.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
SIM-CLK Y2 O 2V9 / 1V8 0 SIM Clock Not mux
~SIM-RST Y1 O 2V9 / 1V8 0 SIM Reset
Not mux
SIM-IO W1 I/O 2V9 / 1V8 *Pull up SIM Data Not mux
SIM-VCC W2 O 2V9 / 1V8 SIM Power
Supply
Not mux
SIMPRES Y3 I 1V8 Z SIM Card
Detect
GPIO18 /
INT8
*SIM-IO pull up is about 10K ohm
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” on page 32 for Open drain, 2V8 and
1V8 voltage characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.10.3 Application
Figure 16: Example of SIM Socket implementation
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Recommended components:
• R1 : 100K ohm
• C1 : 470pF
• C2 : 100nF
• D1 : ESDA6V1SC6 from ST
• D2 : DALC208SC6 from SGS-THOMSON
• J1 : ITT CANNON CCM03 series (See chapter 9.2 for more information)
The capacitor (C2) placed on the SIM-VCC line must not exceed 330 nF.
SIM socket connection:
Pin description of the SIM socket
Signal Pin number Description
VCC 1 SIM-VCC
RST 2 ~SIM-RST
CLK 3 SIM-CLK
SIMPRES with 100 kΩ
pull down resistor and
470 pF capacitor
CC4 4
GND 5 GROUND
VPP 6 Not connected
I/O 7 SIM-IO
CC8 8 VCC_1V8 of WMP100 (ball AD5 )
confidential © Page : 55 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 56 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.11 General Purpose Input/Output
The Wireless Microprocessor® provides up to 49 General Purpose I/O. They are
used to control any external device such as a LCD or a Keyboard backlight...
3.11.1 Features
Reset State:
0 : Set to GND
1: Set to supply 1V8 or 2V8 depending of I/O type.
Pull down: Internal pull down with ~60K resistor.
Pull up: Internal pull up with ~60K resistor to supply 1V8 or 2V8
depending of I/O type.
Z: High impedance.
Undefined: Be careful, undefined mustn’t be used in your application if
a special state at reset is needed. Those pins can be toggling signals.
3.11.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number I/O
I/O type Reset state Multiplexed with
GPIO0 W15 I/O 1V8 0 Not mux
GPIO1 R18
I/O 1V8 Z CS2 / A25
GPIO2 U22 I/O 1V8 Z A24
GPIO3 V16 I/O 1V8 Z INT0 / A26
GPIO4 AD19 I/O 1V8 Pull up COL0
GPIO5 AD20 I/O 1V8 Pull up COL1
GPIO6 AC20 I/O 1V8 Pull up COL2
GPIO7 AC19 I/O 1V8 Pull up COL3
GPIO8 AC21 I/O 1V8 Pull up COL4
GPIO9 AC23 I/O 1V8 0 ROW0
GPIO10 AD22 I/O 1V8 0 ROW1
GPIO11 AD21 I/O 1V8 0 ROW2
GPIO12 AC22 I/O 1V8 0 ROW3
GPIO13 AD23 I/O 1V8 0 ROW4
GPIO14 T16 I/O 1V8 Z CT103-TXD2 / INT6
GPIO15 U17 I/O 1V8 Z CT104-RXD2
GPIO16 W17 I/O 1V8 Z ~CT106-CTS2
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 57 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Pin
number I/O
I/O type Reset state Multiplexed with
GPIO17 V13 I/O 1V8 Z ~CT105-RTS2 /
INT7
GPIO18 Y3 I/O 1V8 Z SIMPRES / INT8
GPIO19 AA17 I/O 2V8 Z Not mux
GPIO20 Y13 I/O 2V8 Undefined Not mux
GPIO21 AA13 I/O 2V8 Undefined Not mux
GPIO22 M15 I/O 2V8 Z Not mux
GPIO23 V17 I/O 2V8 Z Not mux
GPIO24 N16 I/O 2V8 Z Not mux
GPIO25 Y19 I/O 2V8 Z INT1
GPIO26 AA15 I/O Open
drain
Z SCL
GPIO27 AA16 I/O Open
drain
Z SDA
GPIO28 U15 I/O 2V8 Z SPI1-CLK
GPIO29 V12 I/O 2V8 Z SPI1-IO
GPIO30 R13 I/O 2V8 Z SP1-I
GPIO31 M14 I/O 2V8 Z ~SPI1-CS / INT5
GPIO32 R15 I/O 2V8 Z SPI2-CLK
GPIO33 M13 I/O 2V8 Z SPI2-IO
GPIO34 U16 I/O 2V8 Z SP2-I
GPIO35 T18 I/O 2V8 Z ~SPI2-CS / INT4
GPIO36 R17 I/O 2V8 Z CT103-TXD1
GPIO37 T13 I/O 2V8 1 CT104-RXD1
GPIO38 Y18 I/O 2V8 Z ~CT105-RTS1
GPIO39 N15 I/O 2V8 Z ~CT106-CTS1
GPIO40 T12 I/O 2V8 Z ~CT107-DSR1
GPIO41 M16 I/O 2V8 Z ~CT108-2-DTR1
GPIO42 AA18 I/O 2V8 Undefined ~CT125-RI1
GPIO43 AB16 I/O 2V8 Undefined ~CT109-DCD1
GPIO44 AB13 I/O 2V8 Undefined 32kHz buffered
output clock
GPIO45 Y17 I/O 1V8 Z INT2
GPIO46 V18 I/O 2V8 Z INT3
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 58 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Pin
number I/O
I/O type Reset state Multiplexed with
GPIO47 Y15 I/O 1V8 0 Not mux
GPIO48 Y16 I/O 1V8 0 Not mux
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8 voltage
characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.12 Analog to Digital Converter
Three Analog to Digital Converters inputs are provided by the WMP100. Those
converters are 10 bits resolution, ranging from 0 to 2V.
3.12.1 Features
BAT-TEMP / AUX-ADC2 input can be used, typically, to monitor external
temperature, useful for safety power off in case of application over heating (for
Li-Ion battery).
AUX-ADC0 and AUX-ADC1 input can be used for customer application
Electrical Characteristics of ADC
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Resolution 10 bits
Sampling rate 216 S/s
Input signal range 0 2 V
ADC Reference Accuracy TBD %
Integral Accuracy 15 mV
Differential Accuracy 2.5 mV
BAT-TEMP /
AUX-ADC2 1M
Ω
AUX-ADC0 1M
Ω
Input
impedance
AUX-ADC1 1M
Ω
3.12.2 Pin description
Signal Pin number
I/O I/O type Description
BAT-TEMP / AUX- N18 I Analog A/D converter

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 59 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
ADC2*
AUX-ADC0 N17 I Analog A/D converter
AUX-ADC1 M17 I Analog A/D converter
*This input can be used for battery charging temperature sensor,
see chapter “3.16 Battery Charging interface “.
3.12.3 Application
The BAT-TEMP / AUX-ADC2 input is used for battery monitoring during
charging of battery. All information is provided in the “Battery Charging” (see
chapter 3.16).

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 60 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.13 Digital to Analog Converter
One Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) input is provided by the Wireless
Microprocessor®.
3.13.1 Features
The converter is 8-bit resolution, guaranteed monotonic with a ranges from 0V
to 2.3V.
This output assumes a typical external load of 2kΩ and 50pF in parallel to GND.
Electrical Characteristics of the DAC
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Resolution - 8 - bits
Maximum Output voltage 2.1 2.2 2.3 V
Minimum Output voltage 0 - 40 mV
Output voltage after reset - 1.147 - V
Integral Accuracy -5 - +5 LSB
Differential Accuracy -1 - +1 LSB
Full scale settling time
(load: 50pF // 2kΩ to GND)
- 40 - μs
One LSB settling time
(load: 50pF // 2kΩ to GND
)
- 8 - μs
3.13.2 Pin description
Pin description of the DAC
Signal Pin number
I/O I/O type Description
AUX-DAC0 V14 O Analog D/A converter

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 61 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.14 Analogue audio interface
Two different microphone inputs and two different speaker outputs are
supported. The WMP100 also includes an echo cancellation feature which
allows hands free function.
In some cases, ESD protection must be added on the audio interface lines.
3.14.1 Microphone Features
The connection can be either differential or single-ended but using a differential
connection in order to reject common mode noise and TDMA noise is strongly
recommended. When using a single-ended connection, be sure to have a very
good ground plane, a very good filtering as well as shielding in order to avoid
any disturbance on the audio path.
The gain of MIC inputs is internally adjusted and can be tuned using an AT
command.
Both can be configured in differential or single ended.
The MIC2 inputs already include the biasing for an electret microphone
allowing an easy connection.
3.14.1.1 Electrical characteristics
3.14.1.1.1 MIC1 Microphone Inputs
By default, the MIC1 inputs are single-ended but it can be configured in
differential.
The MIC1 inputs do not include an internal bias . The MIC1 input needs to
have an external biasing if an electret micro is used.
AC coupling is already embedded in the Wireless Microprocessor®.
Equivalent circuits of MIC1
DC equivalent circuit AC equivalent circuit
Electrical Characteristics of MIC1
MIC1P
MIC1N
Z1
Z1
GND
MIC1P
MIC1N
DC
Blocked

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Parameters Min
Typ Max Unit
DC Characteristics N/A V
AC Characteristics
200 Hz<F<4 kHz Z1 70 120 160 KΩ
AT+VGT*=2
13.8
mVrms
AT+VGT*=1
77.5
confidential © Page : 62 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Maximum working
voltage
( MIC1P-MIC1N) AT+VGT*=0
346
Positive +7.35 V Maximum rating
voltage
(MIC1P or MIC1N) Negative -
0.9
• *The input voltage depends of the input micro gain set by AT command. Please refer to the
document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5.
3.14.1.1.2 MIC2 Microphone Inputs
By default, the MIC2 inputs are differential ones, but it can be configured in
single ended. They already include the convenient biasing for an electret
microphone. The electret microphone can be directly connected on those
inputs, thus allowing easy connection to a handset.
AC coupling is already embedded in the Wireless Microprocessor®.
Equivalent circuits of MIC2
DC equivalent circuit AC equivalent circuit
Electrical Characteristics of MIC2
MIC2P
MIC2N
Z2
Z2 GND
MIC2+
MIC2P
MIC2N
R
R
GND

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Parameters Min Typ Max Unit
MIC2+ 2 2.1 2.2 V
Output current 0.5 1.5
confidential © Page : 63 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
mA
Internal biasing
DC Characteristics
R2 1650
1900
2150 Ω
Z2 MIC2P
(MIC2N=Open)
Z2 MIC2N
(MIC2P=Open)
1.1 1.3 1.6
Z2 MIC2P
(MIC2N=GND)
Z2 MIC2N
(MIC2P=GND)
0.9 1.1 1.4
AC Characteristics
200 Hz<F<4 kHz
Impedance
between
MIC2P and
MIC2N
1.3 1.6 2
KΩ
AT+VGT*=2 13.8
AT+VGT*=1 77.5
Maximum working
voltage
( MIC2P-MIC2N) AT+VGT*=0 346
mVrms
Positive +7.35** Maximum rating
voltage
(MIC2P or MIC2N) Negative -0.9 V
• *The input voltage depends of the input micro gain set by AT command. Please refer to the
document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5
• **Because MIC2P is internally biased, it is necessary to use a coupling capacitor to
connect an audio signal provided by an active generator. Only a passive microphone can
be directly connected to the MIC2P and MIC2N inputs.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 64 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.14.2 Speaker Features
The connection is single-ended on SPK1 and is differential or single-ended on
SPK2. Using a differential connection to reject common mode noise and TDMA
noise is strongly recommended. Moreover in single-ended mode, ½ of the
power is lost. When using a single-ended connection, be sure to have a very
good ground plane, a very good filtering as well as shielding in order to avoid
any disturbance on the audio path.
Parameter Typ Unit Connection
Z (SPK1P, SPK1N) 16 or 32 Ω single-ended mode
Z (SPK2P, SPK2N) 4 Ω single-ended mode
Z (SPK2P, SPK2N) 8 Ω Differential mode
3.14.2.1 Speakers Outputs Power
The both speakers maximum power output are not similar, that is due to the
different configuration between the Speaker1 which is only single ended and
the speaker2 which can be differential, so speaker2 can provides more power.
The maximal specifications given below are available with the maximum
power output configuration values set by an AT command. The typical values
are recommanded.
3.14.2.1.1 SPK1 Speaker Outputs
With the SPK1 interface, only single ended speaker connection is allowed
Equivalent circuits of SPK1
Electrical Characteristics of SPK1
1
Ω
1
Ω
WMP100
SPK1N
SPK1P

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Parameters Min Typ Max Unit
Biasing
voltage
- 1.30 V
RL=16Ω: AT+VGR=6; single-
ended
- 1.7 - Vpp
Output
swing
voltage RL=32Ω; AT+VGR=6; single-
ended
- 1.9 2.75
Vpp
RL Load resistance 14.5 32 -
Ω
RL=16Ω - 40 85 mA
IOUT Output current;
single-ended; peak
value RL=32Ω - 22 - mA
RL=16Ω; AT+VGR*=6 - 25 mW
POUT
RL=32Ω; AT+VGR*=6 - 16 27 mW
RPD Output pull-down resistance at
power-down
28 40 52
KΩ
*The output voltage depends of the output speaker gain set by AT command. Please refer to
the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5.
confidential © Page : 65 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 66 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.14.2.1.2 SPK2 Speaker Outputs
The SPK2 interface allows differential and single ended speaker connection
Equivalent circuits of SPK2
Electrical Characteristics of SPK2
Parameters Min Typ Max Unit
Biasing
voltage
SPK2P and SPK2N 1.30 V
RL=8Ω: AT+VGR=6*; single ended
- - 2 Vpp
RL=8Ω: AT+VGR=6*; differential - - 4 Vpp
RL=32Ω: AT+VGR=6*; single
ended
- - 2.5 Vpp
Output
swing
voltage
RL=32Ω: AT+VGR=6*; differential - - 5 Vpp
RL Load resistance 6 8 -
Ω
IOUT Output current; peak value; RL=8Ω
- - 180 mA
POUT RL=8Ω; AT+VGR=6*; - - 250 mW
RPD Output pull-down resistance at
power-down
28 40 52
KΩ
VPD Output DC voltage at power-down
- - 100 mV
*The output voltage depends of the output speaker gain set by AT command. Please refer to the
document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5.
If a singled ended solution is used with the speaker2 output, only one of the
both SPK2 has to be chosen. The result is a maximal output power divided by
2.
1
Ω
1
Ω
SPK
WMP100
+
SPK2N
SPK2P

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.14.3 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Description
MIC1P AC10 I Analog Microphone 1 positive input
confidential © Page : 67 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
MIC1N AB10 I Analog Microphone 1 negative input
MIC2P AC9 I Analog Microphone 2 positive input
MIC2N AB9 I Analog Microphone 2 negative input
SPK1P AC8 O Analog Speaker 1 positive output
SPK1N AB8 O Analog Speaker 1 negative output
SPK2P AC7 O Analog Speaker 2 positive output
SPK2N AB7 O Analog Speaker 2 negative output
3.14.4 Application
3.14.4.1 Microphone
3.14.4.1.1 MIC2 Differential connection example
Figure 17: Example of MIC2 input differential connection with LC filter
*:Z2 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.2.
Note: Audio quality can be very good without L1, L2, C2, C3, C4 depending on
the design. But if there is EMI perturbation, this filter can reduce the
TDMA noise. This filter (L1, L2, C2, C3, C4) is not mandatory. If not
used, the capacitor must be removed and coil replaced by 0 Ohm
resistors as the shown in the following schematic.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Figure 18: Example of MIC2 input differential connection without LC filter
*:Z2 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.2.
The capacitor C1 is highly recommended to eliminate the TDMA noise. C1
must be close to the microphone.
Recommended components:
• C1 : 12pF to 33pF (depending of the design ,needs to be tuned)
• C2, C3, C4 : 47pF (need to be tuned depending on the design)
• L1, L2 : 100nH (need to be tuned depending on the design)
confidential © Page : 68 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.14.4.1.2 MIC2 single-ended connection example
AC9
AB9
Audio
ADC
Z2*= 1100
typ
2.1V typ
100nF
100nF
WMP100
MIC2P
MIC2N
C1MIC
L1
C2
Figure 19: Example of MIC2 input single-ended connection with LC filter
*:Z2 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.2.
Internal input impedance value becomes 1100 ohms, due to the connection of
MIC2N to ground.
The single ended design is not recommended for improve TDMA rejection
noise. Usually, it’s difficult to eliminate TDMA noise from a single ended
design.
It is recommended to add L1 and C2 footprint to add a LC filter to try to
eliminate the TDMA noise.
When not used, the filter can be removed by replacing L1 by a 0 Ohm resistor
and by disconnecting C2, as the following schematic.
Figure 20: Example of MIC2 input single-ended connection without LC filter
confidential © Page : 69 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
*:Z2 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.2.
The capacitor C1 is highly recommended to eliminate the TDMA noise. C1
must be close to the microphone.
Recommended components:
C1: 12pF to 33pF (depending of the design ,needs to be tuned )
C2: Must be tuned depending of the design.
L1: Must be tuned depending of the design.
3.14.4.1.3 MIC1 Differential connection example
VCC_2V8
confidential © Page : 70 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
C5
Audio
ADC
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
100nF
100nF
WMP100
MIC1P
MIC1N
R3
R2
R1
C2
C3
R4
C1
L1
L2
C4
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
AC10
AB10
MIC
Figure 21: Example of MIC1 input differential connection with LC filter
*:Z1 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.1.
Note : Audio quality can be very good without L1, L2, C2, C3, C4 depending on
the design. But if there is EMI perturbation, this filter can reduce the
TDMA noise. This filter (L1, L2, C2, C3, C4) is not mandatory. When not
used, the capacitor must be removed and coil replaced by 0 Ohm
resistors as shown in the following schematic.
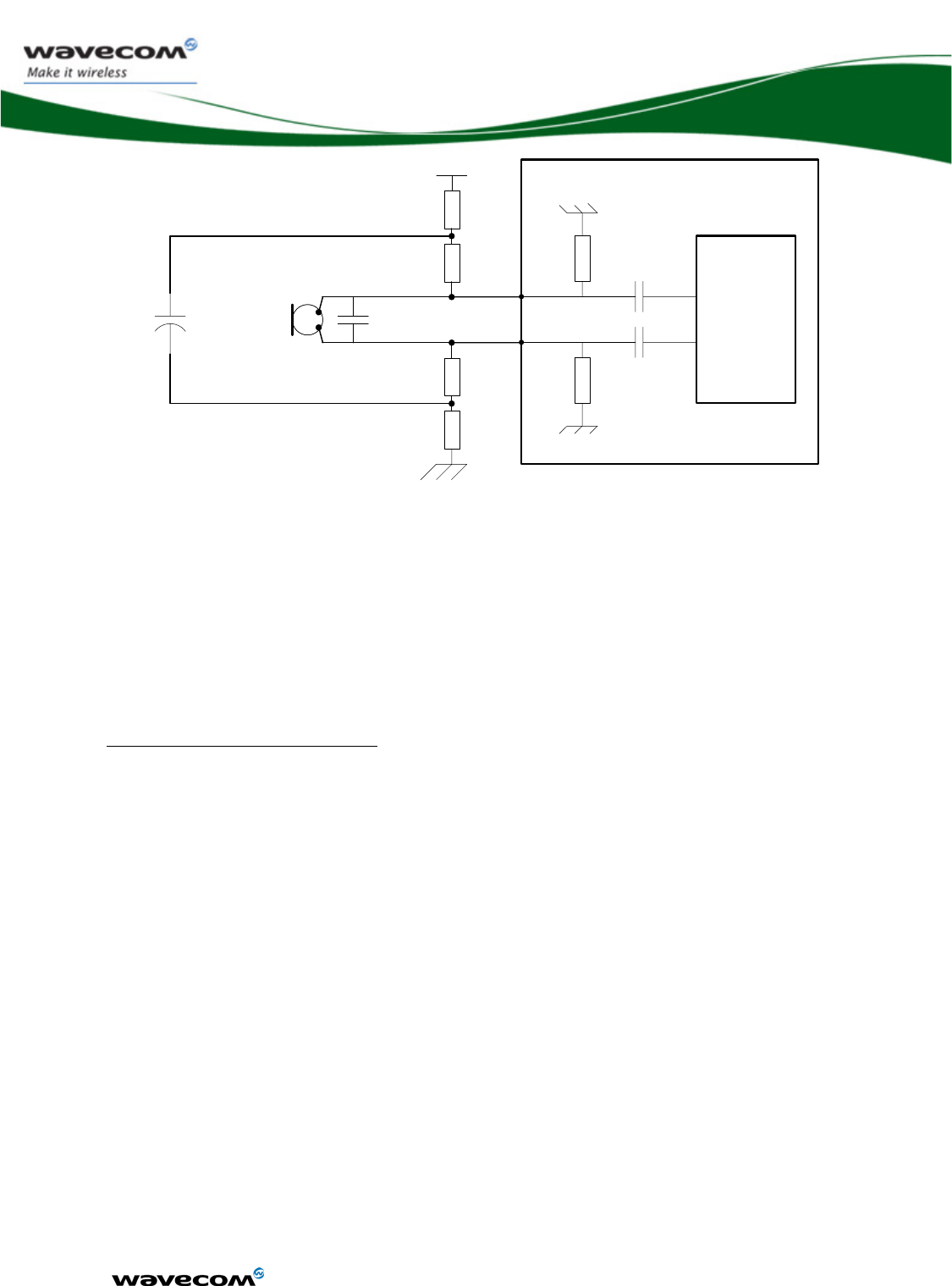
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 71 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Audio
ADC
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
100nF
100nF
WMP100
MIC1P
MIC1N
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
AC10
AB10
VCC_2V8
C1MIC
R3
R2
R1
R4
C5
Figure 22: Example of MIC1 input differential connection without LC filter
*:Z1 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.1.
The capacitor C1 is highly recommended to eliminate the TDMA noise. C1
must be close to the microphone.
Vbias can be VCC_2V8 of the WMP100 (ball R1) but it is possible to use
another 2V to 3V supply voltage depending of the micro characteristics.
Be careful, if VCC_2V8 is used TDMA noise can degrade quality.
Recommended components:
R1 : 4.7K ohm ( for Vbias equal to 2.8V )
R2, R3 : 820 ohm
R4 : 1K ohm
C1 : 12pF to 33pF (depending of the design ,needs to be tuned )
C2, C3, C4 : 47pF (need to be tuned depending on the design)
C5 : 2.2uF +/- 10%
L1, L2 : 100nH (need to be tuned depending on the design)

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.14.4.1.4 MIC1 Single-ended connection example
Audio
ADC
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
100nF
100nF
WMP100
MIC1P
MIC1N
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
AC10
AB10
L1
C2
C1
MIC
VCC_2V8
R2
R1
C5
Figure 23: Example of MIC1 input single-ended connection with LC filter
*:Z1 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.1.
The single ended design is not recommended for improve TDMA rejection
noise. Usually, it’s difficult to eliminate TDMA noise from a single ended
design.
It is recommended to add L1 and C2 footprint to add a LC EMI filter to try to
eliminate the TDMA noise.
When not used, the filter can be removed by replacing L1 by a 0 Ohm resistor
and by disconnecting C2, as the following schematic.
VCC_2V8
Audio
ADC
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
100nF
100nF
WMP100
MIC1P
MIC1N
confidential © Page : 72 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Z1*=120k Ohm
typ
AC10
AB10
C1MIC
R2
R1
C5
Figure 24: Example of MIC1 input single-ended connection without LC filter
*:Z1 is from 200Hz to 4kHz. For more characteristics refer to the chapter
3.14.1.1.1.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Recommended components:
R1: 4K7 ohm ( for Vbias equal to 2.8V )
R2: 820 ohm
C1: 12pF to 33pF (depending of the design ,needs to be tuned)
C2: Must be tuned depending of the design.
C5 : 2.2uF +/- 10%
L1: Must be tuned depending of the design.
Vbias must be very “clean” to avoid bad performance in case of single-ended
implementation. That is the reason why Vbias could be another 2 V to 3V
power supply instead of VCC_2V8 which is available on the ball R1.
CAUTION: If VCC_2V8 is used TDMA noise can degrade quality.
The capacitor C1 is highly recommended to eliminate the TDMA noise. C1
must be close to the microphone.
3.14.4.2 Speaker
3.14.4.2.1 SPK2 Differential connection
SPK2P
SPK2N
Figure 25: Example of Speaker differential connection
Impedance of the speaker amplifier output in differential mode is:
R ≤ 2Ω +/-10 %.
The connection between the WMP100 pins and the speaker must be designed
to keep the serial impedance lower than 3 Ω in differential mode.
confidential © Page : 73 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
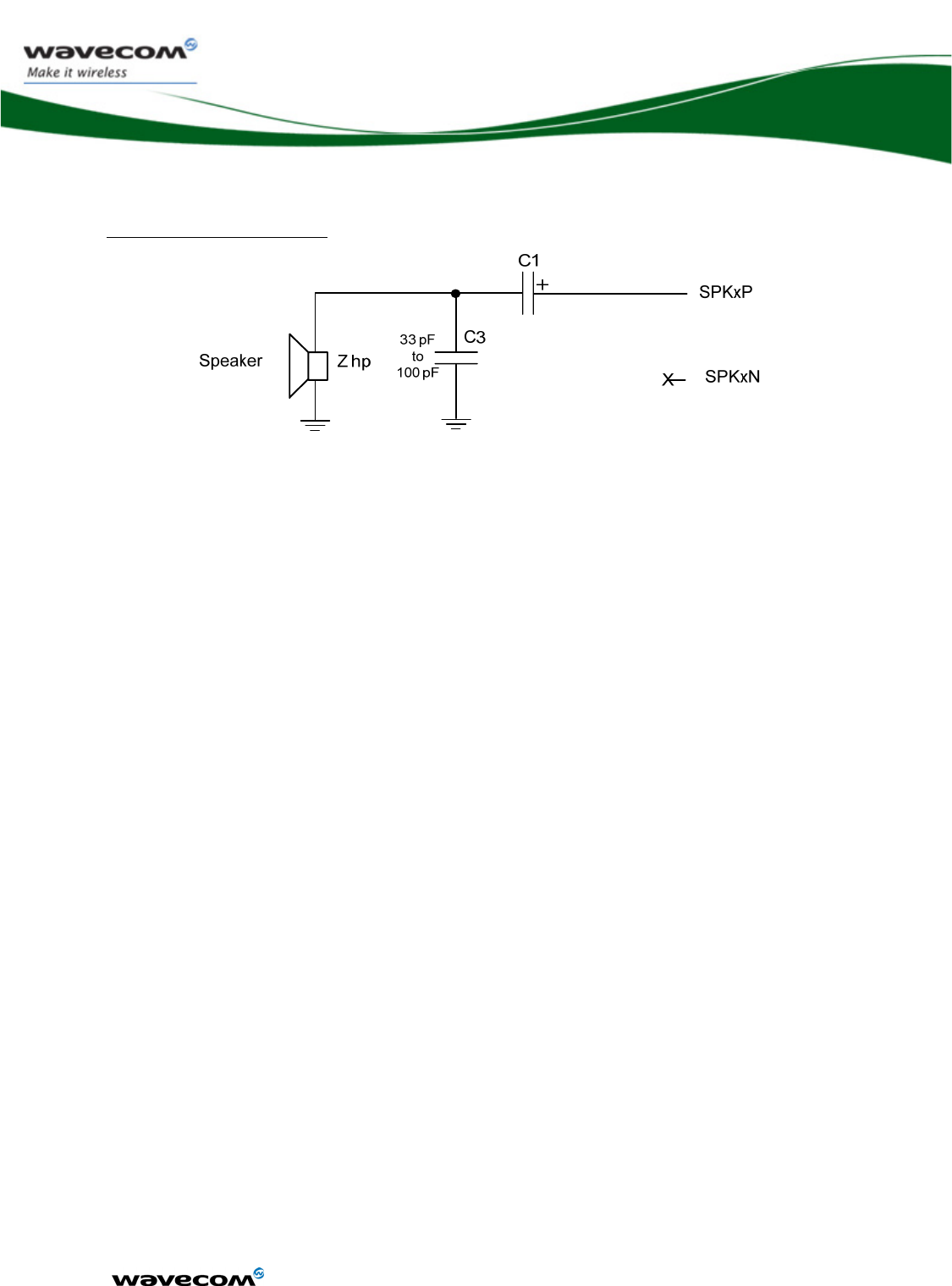
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.14.4.2.2 SPKx Single-ended connection
Typical implementation:
Figure 26: Example of Speaker single-ended connection
4.7 μF < C1 < 47 μF (depending on speaker characteristics and output power).
Using a single-ended connection includes losing of the output power (- 6 dB)
compared to a differential connection.
The connection between the WMP100 pins and the speaker must be designed
to keep the serial impedance lower than 1.5 Ω in single ended mode.
If SPKxP channel is used, SPKxN can be left opened.
If SPKxN channel is used, SPKxP can be left opened.
3.14.5 Design recommendation
3.14.5.1 General
When speakers and microphones are exposed to the external environment, it is
recommended to add ESD protection as closed as possible to the speaker or
microphone, connected between the audio lines and a good ground.
The microphone connections may be either differential or single-ended, but
using a differential connection to reject common mode noise and TDMA noise
is strongly recommended.
While using a single-ended connection, ensure to have a good ground plane, a
good filtering as well as shielding, in order to avoid any disturbance on the
audio path.
It is important to select an appropriate microphone, speaker and filtering
components to avoid TDMA noise
3.14.5.2 Recommended microphone characteristics
The impedance of the microphone has to be around 2 kΩ.
confidential © Page : 74 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Sensitivity from -40dB to –50 dB.
SNR > 50 dB.
Frequency response compatible with the GSM specifications.
To suppress TDMA noise, it is highly recommended to use microphones with
two internal decoupling capacitors:
-CM1=56pF (0402 package) for the TDMA noise coming from the
demodulation of the GSM 850 and GSM900 frequency signal.
-CM2=15pF (0402 package) for the TDMA noise coming from the
demodulation of the DCS/PCS frequency signal.
The capacitors have to be soldered in parallel of the microphone
confidential © Page : 75 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
CM
Figure 27: Microphone
3.14.5.3 Recommended speaker characteristics
Type of speakers: Electro-magnetic /10mW
Impedance: 8Ω for hands-free (SPK2)
Impedance: 32Ω for heads kit (SPK1)
Sensitivity: 110dB SPL min
Receiver frequency response compatible with the GSM specifications.
3.14.5.4 Recommended filtering components
When designing a GSM application, it is important to select the right audio
filtering components.
The strongest noise, called TDMA, is mainly due to the demodulation of the
GSM850/GSM900/DCS1800 and PCS1900 signal: A burst being produced
every 4.615ms; the frequency of the TDMA signal is equal to 216.7Hz plus
harmonics.
The TDMA noise can be suppress by filtering the RF signal using the right
decoupling components.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
The types of filtering components are:
-RF decoupling inductors
-RF decoupling capacitors
A good “Chip S-Parameter” simulator is proposed by Murata, the following link
help to find it:
http://www.murata.com/designlib/mcsil.html
Using different Murata components, we could see that the value, the package
and the current rating can have different decoupling effects.
The table below shows some examples with different Murata components:
Package 0402
confidential © Page : 76 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Filtered band GSM900 GSM 850/900 DCS/PCS
Value 100nH 56pF 15pF
Types Inductor Capacitor Capacitor
Position Serial Shunt Shunt
Manufacturer Murata Murata Murata
Rated 150mA 50V 50V
Reference LQG15HSR10J02
or
LQG15HNR10J02
GRM1555C1H560JZ01 GRM1555C1H150JZ01
or
GRM1555C1H150JB01
Package 0603
Filtered band GSM900 GSM 850/900 DCS/PCS
Value 100nH 47pF 10pF
Types Inductor Capacitor Capacitor
Position Serial Shunt Shunt
Manufacturer Murata Murata Murata
Rated 300mA 50V 50V
Reference LQG18HNR10J00
GRM1885C1H470JA01
or
GRM1885C1H470JB01
GRM1885C1H150JA01
or
GQM1885C1H150JB01
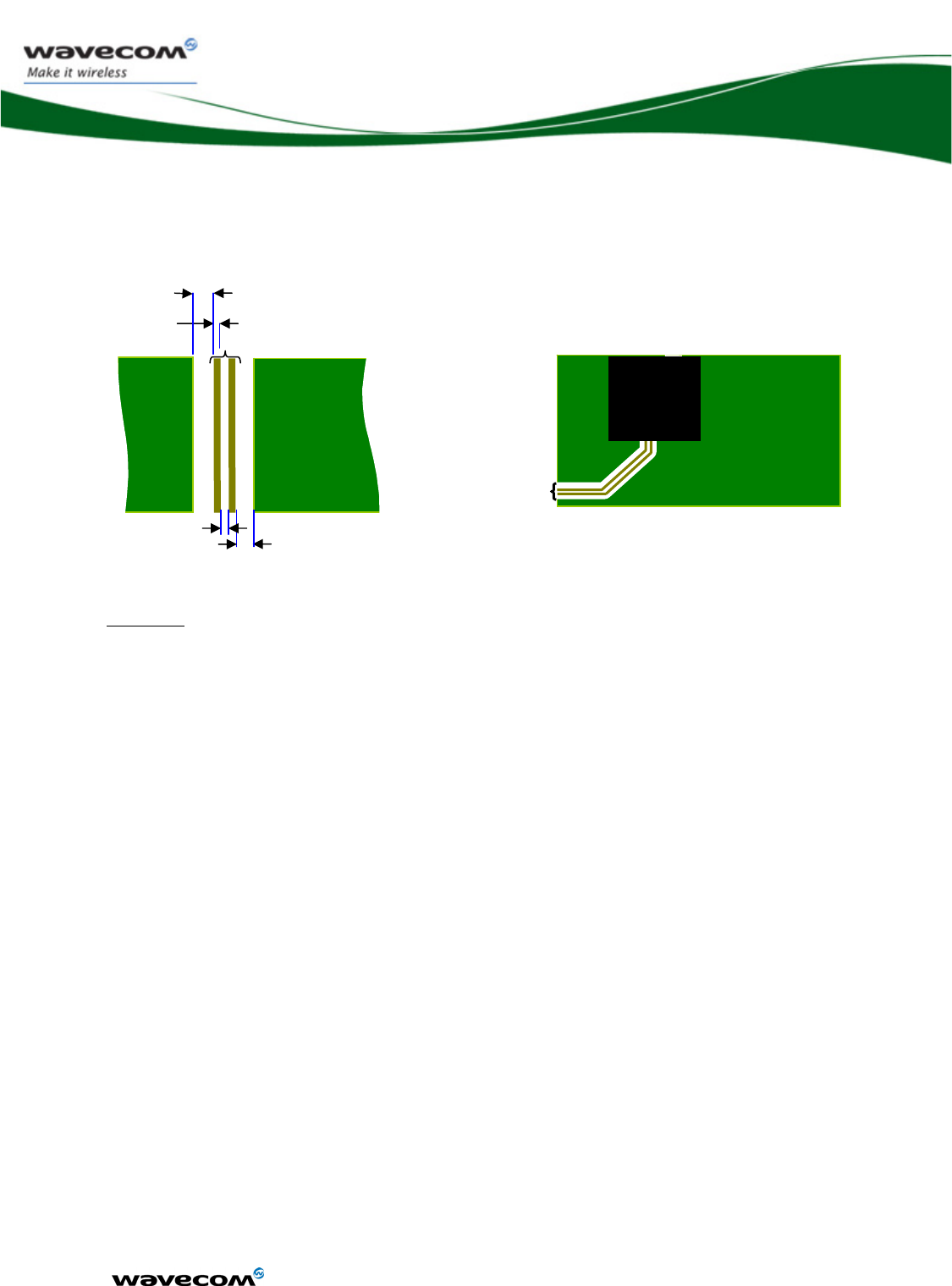
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 77 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.14.5.5 Audio track and PCB layout recommendation
To avoid TDMA noise, it is recommended to surround the audio tracks by
ground:
Figure 28: Audio track design
Remark:
Avoid digital tracks crossing under and over the audio tracks.
0.2mm min
Differential Audio line
Ground Ground
1mm
0.15mm max
1mm
Differential
Audio line
always in
parallel
Application
board
Ground
Plane
WMP100
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.15 PWM / Buzzer Output
This output is controlled by a PWM controller and can be used as buzzer or as
PWM.
3.15.1 Features
The BUZZ-OUT is an open drain one. A buzzer can be directly connected
between this output and VBATT. The maximum current is 100 mA (PEAK).
Electrical Characteristics
confidential © Page : 78 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Parameter Condition Minimum
Maximum Unit
VOL Iol = 100mA 0.4
V
IPEAK VBATT = VBATTmax
100
mA
Frequency TBD TBD
Hz
Duty cycle TBD TBD
%
3.15.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset state
Description
BUZZ-OUT U4 O Open
drain
Z PWM / Buzzer output
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” on page 32 for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8
voltage characteristics and for Reset state definition.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 79 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
BUZZ-OUT
C1
D1
VBATT
3.15.3 Application
The maximum peak current is 100 mA and the maximum average current is 40
mA. A diode against transient peak voltage must be added as described below.
R1
WMP100
Figure 29: Example of buzzer implementation
Where:
R1 must be chosen in order to limit the current at IPEAK max
C1 = 0 to 100 nF (depending on the buzzer type)
D1 = BAS16 (for example)
Recommended characteristics for the buzzer:
electro-magnetic type
Impedance: 7 to 30 Ω
Sensitivity: 90 dB SPL min @ 10 cm
Current: 60 to 90 mA
The BUZZ-OUT output can also be used to drive a LED as shown in the Figure
below:
BUZZ-OUT VBATT
« BUZZER »
D1
1
2
R1
470 Ω
Figure 30: Example of LED driven by the BUZZ-OUT output
R1 value can be accorded depending of the LED (D1) characteristics.
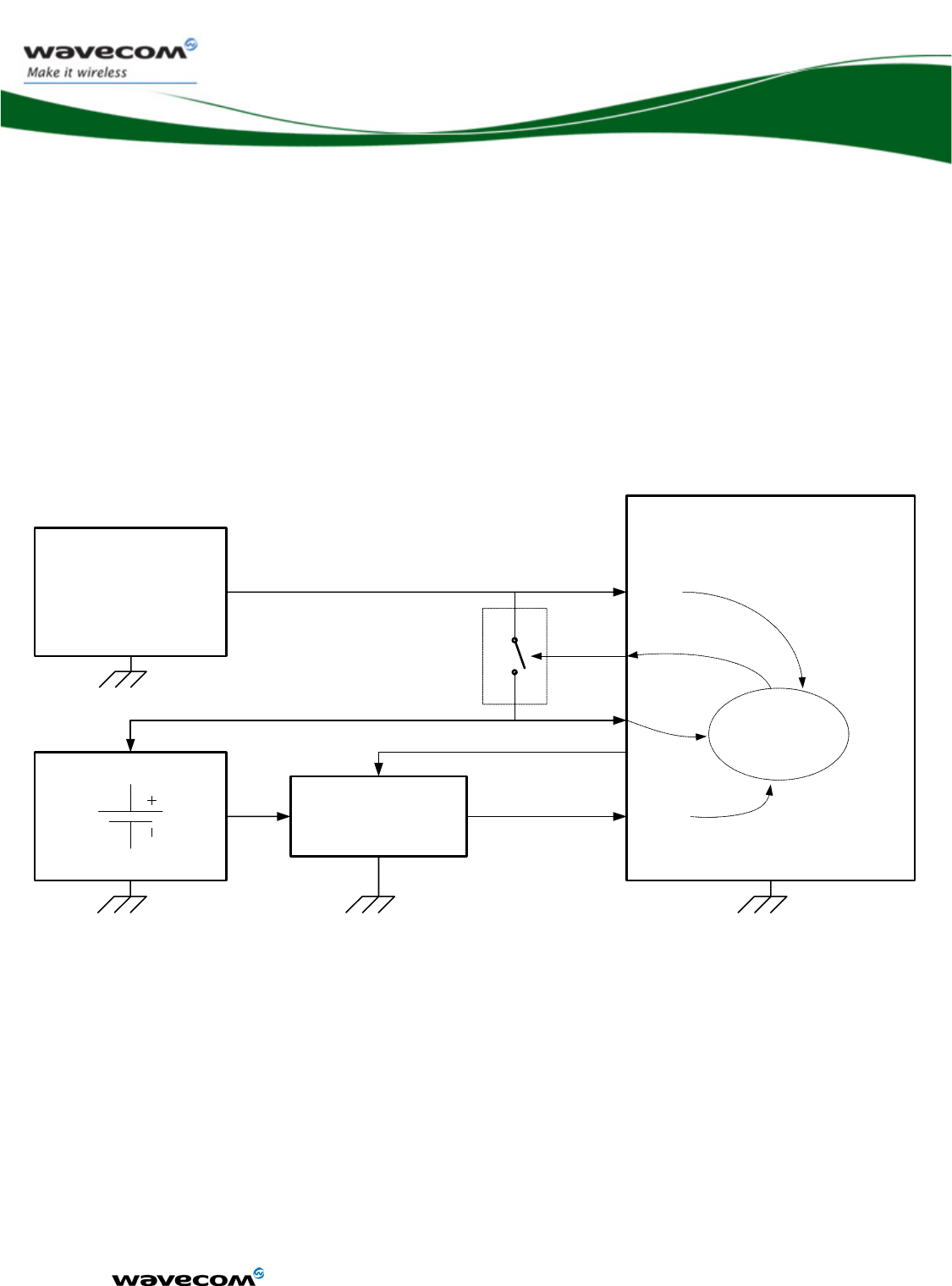
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.16 Battery charging interface
The WMP100 charging interface is able to drive the charging of different
batteries technologies by combing hardware and software controls.
3.16.1 Feature
The charging architecture of WMP100 supports 3 batteries technologies:
¾ Ni-Cd (Nickel-Cadmium)
¾ Ni-Mh (Nickel-Metal Hydride)
¾ Li-Ion (Lithium-Ion)
confidential © Page : 80 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
CHARGER
DC output
WMP100
BATTERY
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
INTERFACE
CHG-IN
VCC_2V8
NTC BAT-TEMP
VBATT-BB ALGORITHM
CONTROL
CHG-GATE
V2/V3
V4
AC1/AC2/
AD1/AD2
R1
N18
Figure 31: Charging block diagram
The software algorithm controls a switch (by CHG-GATE signal), which
connects the CHG-IN signal to the VBATT-BB signal. The algorithm controls
the frequency and the connected time of the switching. During the charging
procedure the battery charging level is controlled by the VBATT-BB
measurement. When the battery is full, the algorithm stopped the charging
procedure.
When Li-Ion battery is used, the battery temperature is monitoring through the
BAT-TEMP ADC input.
One more charging mode is provided by the WMP100. It’s called “Pre-
charging” mode, but it’s a special charging mode because it is activated only
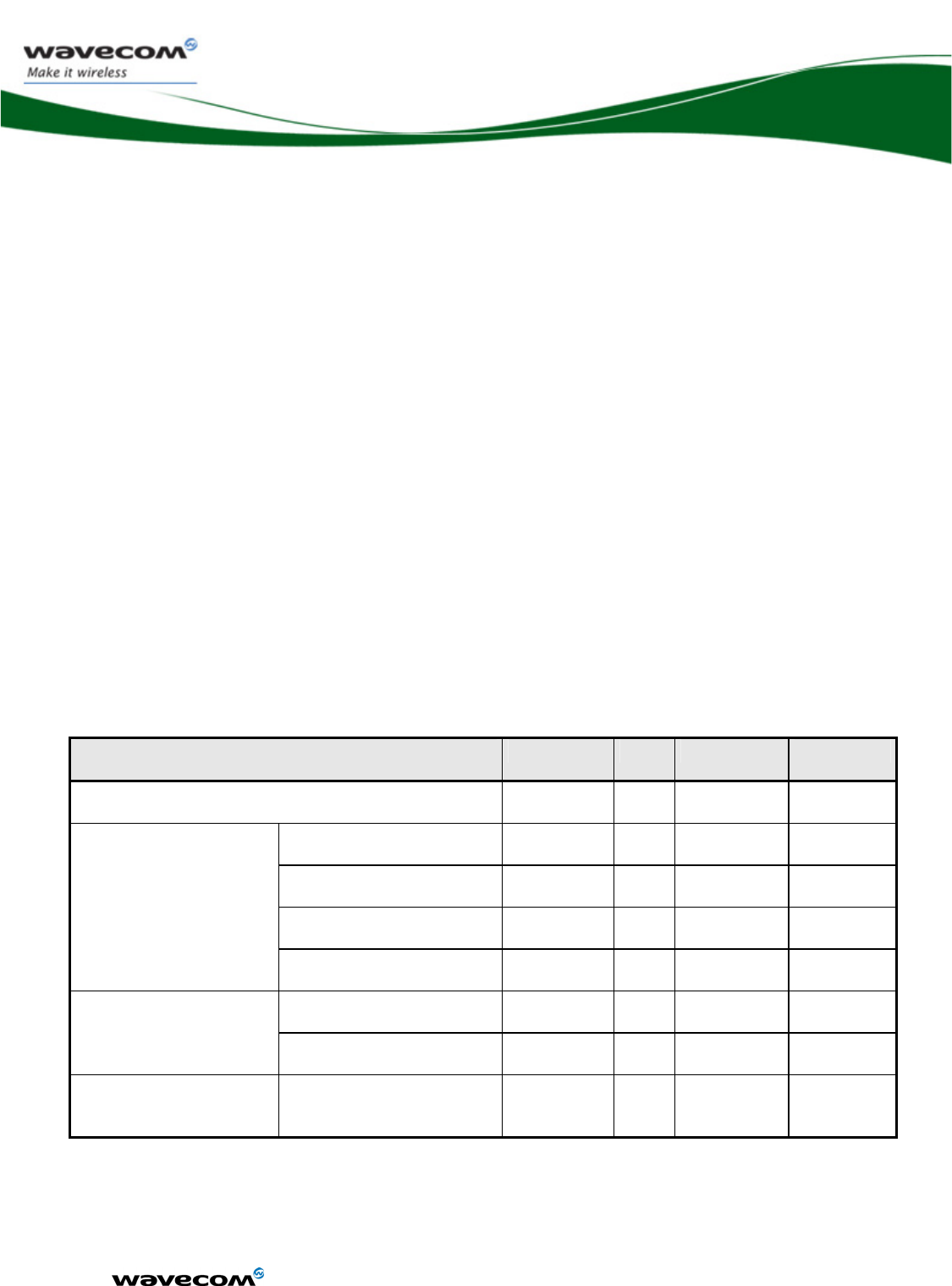
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
when the WMP100 is OFF. So the control is only performed by the hardware.
The goal of this charging mode is to prevent the battery to be damaged by
preventing the discharged under the minimum battery level.
3.16.1.1 Pre-Charging
When a charger DC power supply is connected to the CHG-IN signal and if the
voltage battery is between 2.8v and 3.2v, a constant current of 50mA is
provided to the battery.
When the battery is able to supply the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite
v1.0, the WMP100 is automatically powered on and the software algorithm is
activated to finish the charge.
Note: When pre-charging is launched, the FLASH-LED output blinks
automatically.
3.16.1.2 Temperature monitoring
The monitoring of the temperature is only available for the Li-Ion battery. The
BAT-TEMP / AUX-ADC2 (N18) ADC input must be used to sample the
temperature analog signal provided by a NTC temperature sensor which is
placed close to the battery cellular. The minimum and maximum temperature
range can be set by software command.
Electrical Characteristics of battery charging interface
Parameter Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
Charging Operating temperature 0 50 °C
resolution 10
confidential © Page : 81 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
bits
sampling rate 216 S/s
Input Impedance ( R )
1M Ω
BAT-TEMP / AUX-
ADC2
Input signal range 0 2 V
Voltage (for I=Imax) 4.6* V CHG-IN
Voltage (for I=0) 6* V
CHG-GATE Switch control by
current
30 40 50 mA
*To be parameterized as per battery manufacturer
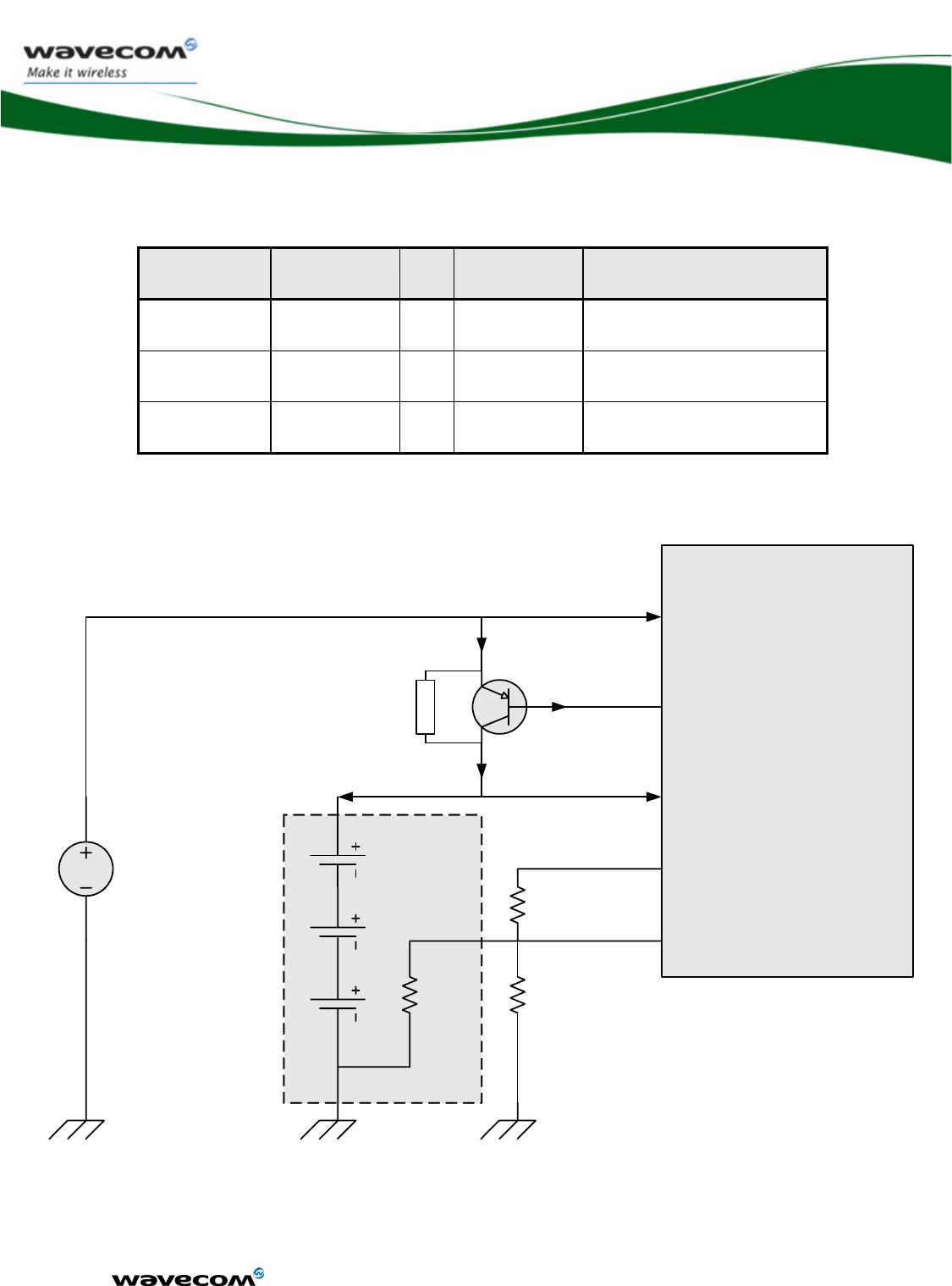
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 82 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.16.2 Pin description
Pin description of battery charging interface
Signal Pin number
I/O I/O type Description
CHG-IN V2 / V3 I Analog Current source input
CHG-GATE V4 O Analog Current source to drive
PNP transistor
BAT-TEMP /
AUX-ADC2
N18 I Analog A/D converter
3.16.3 Application
VCC_2V8
BAT-TEMP /
AUX-ADC2
VBATT-BB
CHG-GATE
CHG-IN
DC
R2
T1
WMP100
Battery cells
+ NTC
GND
OUT
NTC out
NTC
Charger
R1
R3
Figure 32: Charging schematic for Li-Ion
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
The charging schematic needs a transistor to switch the current from the
Charger DC source power supply to the battery. The control of the transistor is
performed by the WMP100 through the CHG-GATE signal.
It is important that the Charger DC power supply has a limited output current
to not damage the transistor T1.
The R1 and R2 resistors are needed only when the temperature is monitored,
typically for Li-Ion battery. The R1 is necessary to bias the NTC resistor of the
battery. The VCC_2V8 output power voltage of the WMP100 can be used to
power the bridge R1/ R2 / NTC. The R1 and R2 values have to be calculated to
have a maximum of 2volt at the BAT-TEMP / AUX-ADC2 input on the
WMP100.
The R3 resistor must be added to improve the performances of the charge.
Pre-Charging mode doesn’t use the T1 transistor, when Pre-charging is
activated, the current provided by the Charger DC power supply crosses the
WMP100 by the CHG-IN signal to the VBATT-BB to charge the battery. The
current limitation is controlled inside the WMP100.
Recommended components:
o T1 : NSL12AW from On Semiconductor
o R1 = 100K
o R2 = 270K
o R3= 5.6K (package 0402, 1/16W, +-5% is sufficient)
o NTC = 100K @ 25°C NTH4G42B104F01 from MURATA
Note:
o In this example, the transistor T1 has a maximal continuous current of
2A, so the Charger DC power supply must have an output current
limited to 2A.
o The maximum Charger output current, provided to the battery, must be
accorded to the battery electrical characteristics.
confidential © Page : 83 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 84 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.17 ON / ~OFF signal
This input is used to switch ON or OFF the Wireless Microprocessor.
A high level signal has to be provided on the pin ON/~OFF to switch ON the
Wireless Microprocessor.. The voltage of this signal has to be maintained at
0.8 x VBATT during a minimum of 4000ms. This signal can be left at high level
until switch off.
To switch OFF the Wireless Microprocessor the pin ON/OFF has to be
released. The Wireless Microprocessor can be switched off through the
Operating System.
) Warning:
All external signals must be inactive when the Wireless Microprocessor is OFF
to avoid any damage when starting and allow Wireless Microprocessor to start
and stop correctly.
3.17.1 Features
Electrical Characteristics of the signal
Parameter I/O type Minimum Maximum Unit
VIL CMOS VBATT x 0.2 V
VIH CMOS VBATT x 0.8 VBATT V
3.17.2 Pin description
Signal Pin number I/O I/O type Description
ON/∼OFF U5 I CMOS WMP100 Power ON
3.17.3 Application
VBATT
1
2
3
Switch
ON/~OFF
Figure 33: Example of ON/~OFF pin connection
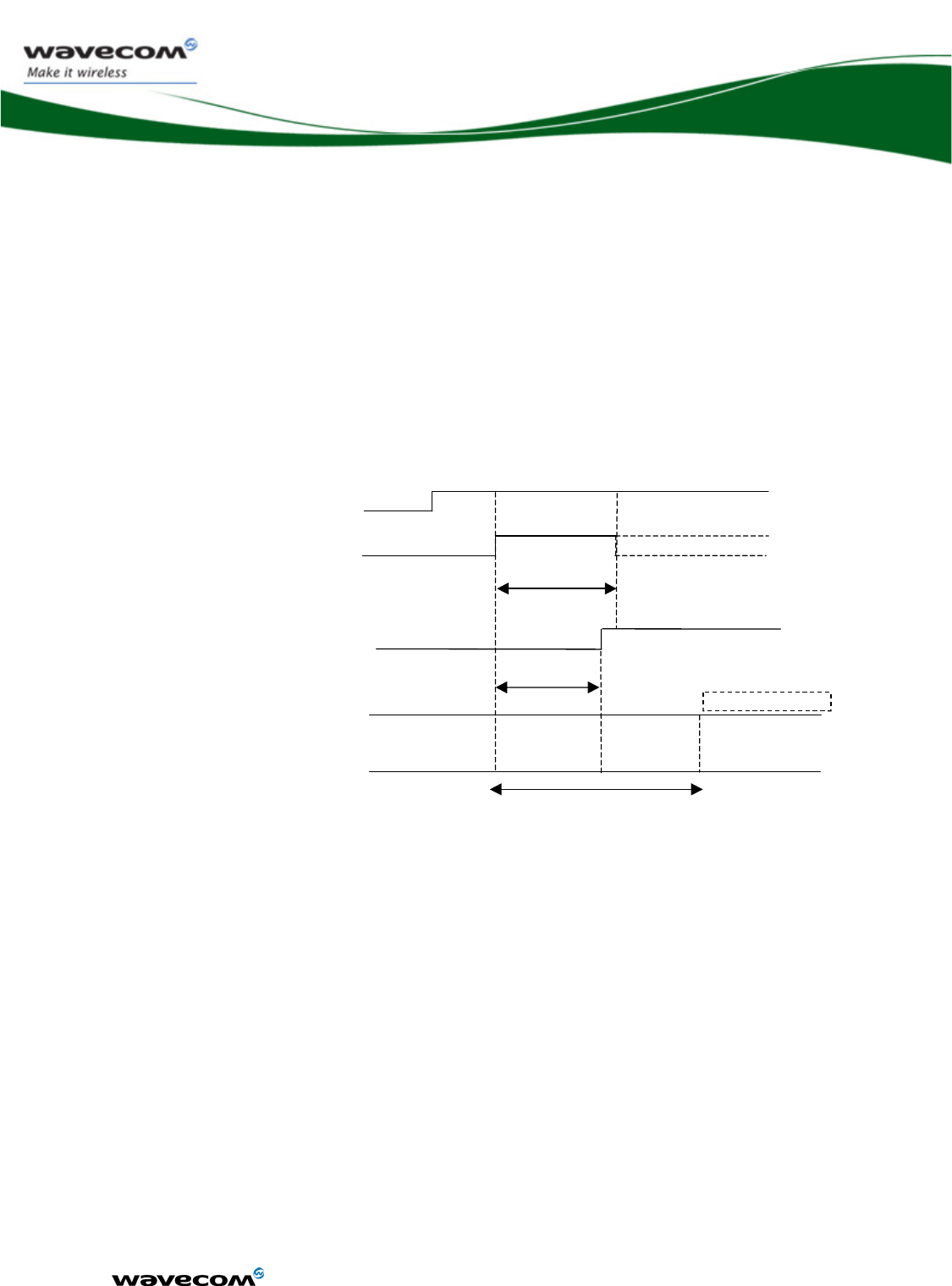
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.17.3.1 Power ON
Once WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 is powered, the application must
set the ON/OFF signal to high to start the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite
v1.0 power ON sequence. The ON/OFF signal must be held high during a
minimum delay of Ton/off-hold (Minimum hold delay on the ON/~OFF signal) to
power-ON. After this delay, an internal mechanism maintains the
WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 in power ON condition.
During the power ON sequence, an internal reset is automatically performed by
the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 for 40ms (typically). During this
phase, any external reset should be avoided during this phase.
confidential © Page : 85 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
POWER SUPPL
Y
ON/OF
F
Ton/off-hold
(2000ms min)
STATE OF THE MODULE
Module OFF
IBB+RF < 22μA
AT answers « O
K
»
Module READ
Y
SIM and Network dependent
RESET mode
IBB+RF=20 to 40mA
INTERNAL RS
T
Trst
(40ms typ)
Module ON
IBB+RF<120mA
(no loc. update)
IBB+RF = overall current consumption (Base Band + RF part)
Figure 34 : Power-ON sequence (no PIN code activated)
The duration of the firmware power-up sequence depends on:
• the need to perform a recovery sequence if the power has been lost
during a flash memory modification.
Other factors have a minor influence
• the number of parameters stored in EEPROM by the AT commands
received so far
• the ageing of the hardware components, especially the flash memory
• the temperature conditions
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
The
recommended
way to de-assert the ON/~OFF signal is to use either an AT
command or WIND indicators: the application has to detect the end of the
power-up initialization and de-assert ON/~OFF afterwards.
• Send an “AT” command and wait for the “OK” answer: once the
initialization is complete the AT interface answers « OK » to “AT” message1.
• Wait for the “+WIND: 3” message: after initialization, the WMP100/Open
AT® Software Suite v1.0, if configured to do so, will return an unsolicited
“+WIND: 3” message. The generation of this message is enabled or
disabled via an AT command.
Note:
• Please refer to the document [3] AT Command Interface Guide for Open
AT® Firmware v6.5 for more information on these commands.
Proceeding thus – by software detection - will always prevent the application
from de-asserting the ON/~OFF signal too early.
If WIND indicators are disabled or AT commands unavailable or not used, it is
still possible to de-assert ON/~OFF after a delay long enough (Ton/off-hold) to
ensure that the firmware has already completed its power-up initialization.
The table below gives the minimum values of Ton/off-hold:
Ton/off-hold minimum values
Ton/off-hold
Open AT® Firmware Safe evaluations of the firmware
power-up time
6.65 & above 8 s
The above figure take the worst cases into account: power-loss recovery
operations, slow flash memory operations in high temperature conditions, and
so on. But they are safe because they are large enough to ensure that ON/~OFF
is not de-asserted too early.
Additional notes:
1. Typical power-up initialization time figures for best cases conditions
(no power-loss recovery, fast and new flash memory…) approximate
3.5 seconds in every firmware version. But releasing ON/~OFF after
this delay does not guarantee that the application will actually start-up
if for example the power plug has been pulled off during a flash
memory operation, like a phone book entry update or an AT&W
command…
2. The ON/~OFF signal can be left at a high level until switch OFF. But
this is not recommended as it will prevent the AT+CPOF command
from performing a clean power-off. (see also <<<NOTE IN POWER OFF
CHAPTER>>> for an alternate usage)
confidential © Page : 86 / 152
1 If the application manages hardware flow control, the AT command can be sent during the
initialisation phase.
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 87 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
POWER SUPPLY
ON/OFF
AT COMMAND
STATE OF THE MODULE
3. When using a battery as power source, it is not recommended to let
this signal high:
If the battery voltage is too low and the ON/~OFF signal at low level,
an internal mechanism switches OFF the WMP100/Open AT® Software
Suite v1.0. This automatic process prevents the battery to be over
discharged and optimize its life span.
4. During the power-ON sequence, an internal reset is automatically
performed by the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 for 40 ms
(typically). Any external reset should be avoided during this phase.
5. Connecting a charger on the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0
as exactly the same effect than setting the ON/~OFF signal. In
particular the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 will not
POWER-OFF after the AT+CPOF command, unless the Charger is
disconnected.
3.17.3.2 Power OFF
To properly power OFF the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 the
application must reset the ON/OFF signal and then send the AT+CPOF
command to deregister from the network and switch off the WMP100/Open
AT® Software Suite v1.0.
Once the « OK » response is issued by the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite
v1.0, the power supply can be switched off.
AT+CPOF
Module
READY
Module OFF
IBB+RF<22µA
Network dependent
OK response
IBB+RF = overall current consumption (Base Band + RF part)
Figure 35 : Power-OFF sequence
Note:
• If the ON/~OFF pin is maintained to ON (High Level) then the module
can’t be switched OFF.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.18 BOOT signal
A specific control pin BOOT is available to download the WMP100 only if the
standard XMODEM download, controlled with AT command, is not possible.
Specific PC software, provided by WAVECOM, is needed to perform this
download, specifically for the first download of the Flash memory.
3.18.1 Features
The BOOT pin must be connected to the VCC_1V8 for this specific download.
BOOT Operating mode Comment
Leave open Normal use No download
Leave open Download XMODEM AT command for Download
AT+WDWL
1 Download specific Need WAVECOM PC software
For more information, see chapter 3.8.3.
This BOOT pin must be left open for normal use or XMODEM download.
However, in order to make development and maintenance phases easier, it is
highly recommended to set a test point, either a jumper or a switch to
VCC_1V8 (ball AD5) power supply.
3.18.2 Pin description
Signal Pin number I/O I/O type Description
BOOT W18 I 1V8 Download mode selection
3.18.3 Application
VCC_1V8
1
2
3
Switch
BOOT
Figure 36: Example of BOOT pin implementation
confidential © Page : 88 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
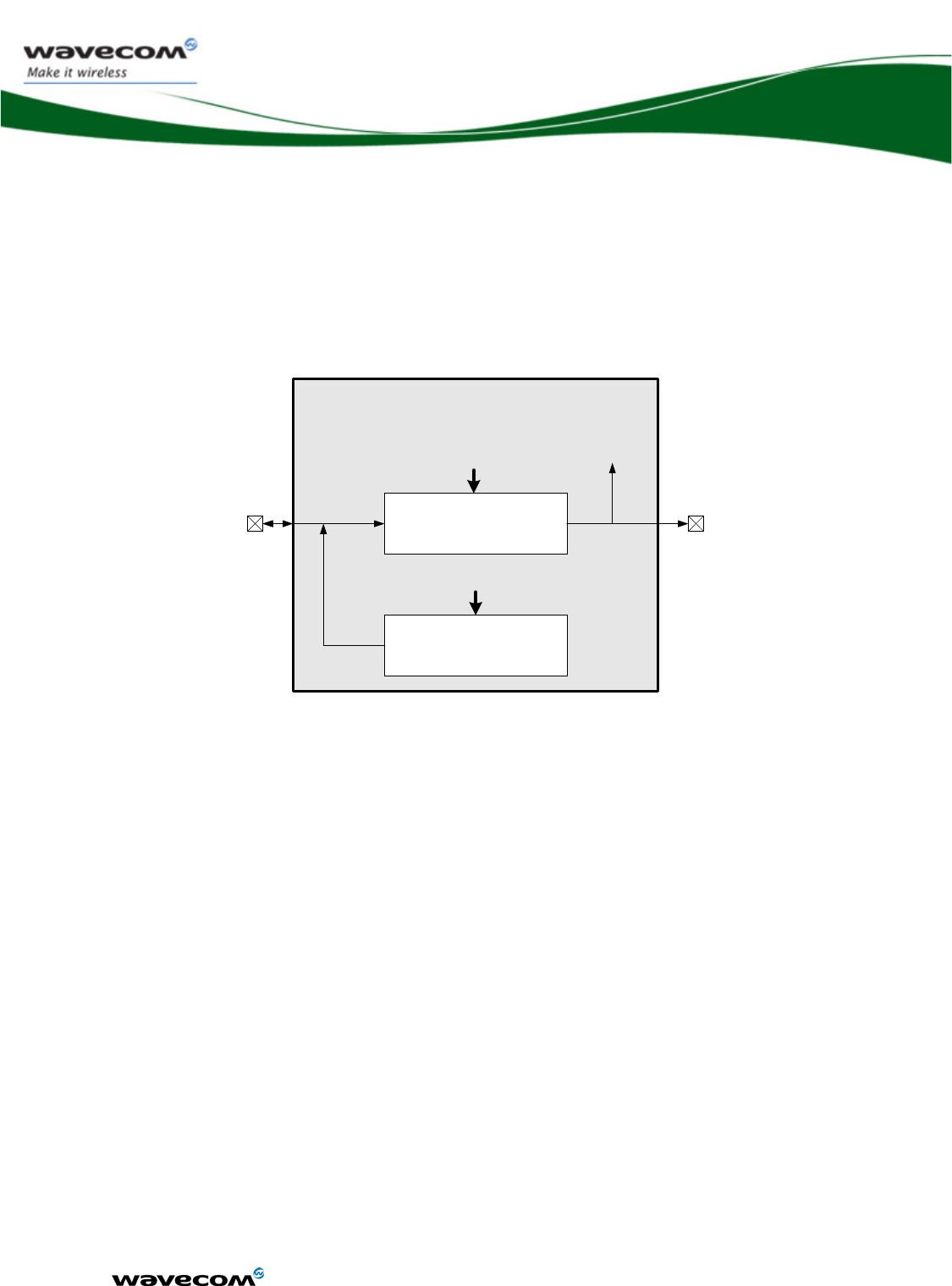
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.19 Reset signals
The WMP100 have two reset signals. The main is ~RESET which is the input
reset of the processor. The second is ~EXT-RESET which is derived from the
main reset.
3.19.1 Features
confidential © Page : 89 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Watchdog
Power
management
~RESET ~EXT-RESET
Power supply
Processor control
WMP100
to processor
internal reset
Figure 37 : Reset functional block
The ~RESET signal is an input/output signal. It is controlled as well by the user
as well by an internal voltage supervisor. This ~RESET signal drive the reset of
the processor through the watchdog unit.
The ~EXT-RESET is an output signal and is the result of the combination of the
~RESET and the watchdog reset. This signal is used to provide a reset to all
the microprocessor’s system components. Typically, the ~EXT-RESET is used
to reset the NOR Flash memories state machine.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Figure 38 : Reset waveform events
Three different reset events can occur:
o Power on reset:
The power on reset is automatically controlled by the internal power
management unit. It resets the ~RESET signal as long as the power
supply voltage VCC_1V8 is under 1.60 V typ.
The ~RESET is always reset when the VCC_1V8 is high, after what a
cancellation time is launched (ta).
The ~EXT-RESET is always reset when the ~RESET signal is high,
after what a cancellation time is launched (tb).
o External reset (~RESET):
The external reset is managed by the user or by an external event of
the WMP100. This is the asynchronous reset of the processor. The
external reset must be generated on the ~RESET signal.
The ~Reset signal must be held low during the time (tc) to reset the
microprocessor. .
o Internal reset (~EXT-RESET):
The internal reset is launched by the watchdog unit, controlled by the
processor. This reset affects only the ~EXT-RESET signal (td).
confidential © Page : 90 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Electrical Characteristics of the signals
Parameter Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
Input Impedance ( R )* 100K Ω
Input Impedance ( C ) 10n F
~Reset time (tc) 200 μs
Cancellation time (ta)
at power up only
20 40 100
ms
VH** 0.57
confidential © Page : 91 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
V
VIL 0 0.57
V
~RESET
VIH 1.33 V
Watchdog reset (td) 300 μs
Cancellation time (tb) 34 35
ms
~EXT-
RESET Delay after a ~RESET
active (te)
122
μs
First access time (tf) 17
μs
BOOT = 1 200
~CS0
Total boot
time (tg) BOOT =
Leave open
***
20
ms
* internal pull up
**VH : Hysterisis Voltage
*** Normal configuration. Refer to the chapter 3.18 for further details on the BOOT signal.
Sequence after an external reset event (~RESET)::
To activate the « emergency » reset sequence, the ~RESET signal has to be set
to low for 200μs minimum for example by a push button . As soon as the reset
is complete, the interface answers « OK » to the application.
RESET mode
IBB+RF=20 to 40mA
~EXT-RESET
STATE OF
THE
MODULE
Module
READY
tc = Min:200μs
A
T answers “OK”
Module
READY
SIM and network
dependent
Module ON
IBB+RF<120mA without
loc update
~RESET
tb = Typ:34ms
Figure 39 : Reset sequence waveform

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
At power up, the ~RESET time (ta), is performed after switching ON the
Wireless Microprocessor®. It is generated by the internal WMP100 voltage
supervisor.
The ~RESET time is provided by the internal RC component. To keep the same
time, it’s not recommended to plug another R or C component into the ~RESET
signal. Only a switch or an open drain gate is recommended.
The (tb) time is the cancellation time needed for the WMP100/Open AT®
Software Suite v1.0 initialization. (tb) time is automatically done by the
WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0 itself, after a hardware reset.
The firsts access on ~CS0 after an internal reset event (~EXT-RESET):
After an internal reset (like a Watchdog reset) the delay of the active ~CS0
signal (chip select 0 for access to the external FLASH) depend of the BOOT
signal state. Refer to the chapter 3.18 for further details on the BOOT signal.
Figure 40 : BOOT sequence waveform
3.19.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Description
~RESET V6 I/O Open
Drain*
1V8 WMP100 Reset
~EXT-RESET
AB14 O Push Drain 1V8 External Reset
* internal pull up. See the characteristics in the table §3.19.1.
confidential © Page : 92 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.19.3 Application
If used (emergency reset), it has to be driven by an open collector or an open
drain output (due to the internal pull-up resistor embedded into the Wireless
Microprocessor®) as shown in the diagram hereunder.
GND
1
2
3
Push button
~RESET
Figure 41: Example of ~RESET pin connection with push button
configuration
GND
~RESET
Reset
command T1
Rohm DTC144EE
Figure 42: Example of ~RESET pin connection with transistor configuration
Open collector or open drain transistor can be used. If an open collector is
chosen, T1 can be a Rohm DTC144EE.
Reset command ~RESET Operating mode
1 0 Reset activated
0 1 Reset inactive
confidential © Page : 93 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
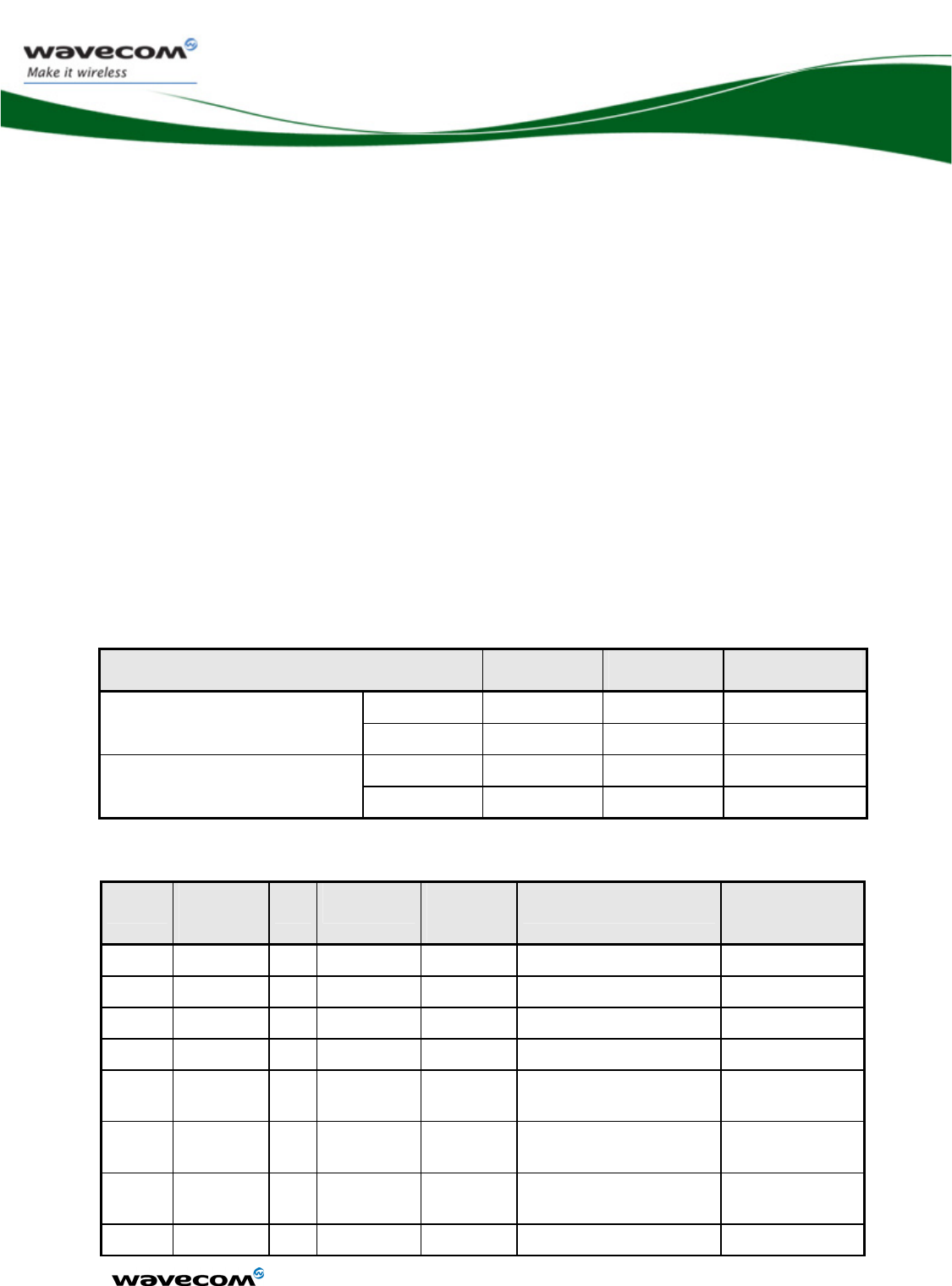
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.20 External Interrupt
The WMP100 provides up to 9 external interrupts inputs in two voltages
ranges (in 1.8V and 2.8V).
3.20.1 Features
Those interrupt inputs can be activated on:
• high to low edge
• low to high edge
• low to high and high to low edge
• low level
• high level
When used, interruptions input must not be left opened.
If not used, they have to be configured as GPIO.
Electrical characteristics of the signals
Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit
VIL 0.54
V
Interrupt pin at 1V8 VIH 1.33 V
VIL 0.84
V
Interrupt pin at 2V8 VIH 1.96 V
3.20.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
INT0 V16 I 1V8 Z External Interrupt 0 GPIO3 / A26
INT1 Y19 I 2V8 Z External Interrupt 1 GPIO25
INT2 Y17 I 1V8 Z External Interrupt 2 GPIO45
INT3 V18 I 2V8 Z External Interrupt 3 GPIO46
INT4 T18 I 2V8 Z External Interrupt 4 GPIO35 /
~SPI2-CS
INT5 M14 I 2V8 Z External Interrupt 5 GPIO31 /
~SPI1-CS
INT6 T16 I 1V8 Z External Interrupt 6 GPIO14 /
CT103-TXD2
INT7 V13 I 1V8 Z External Interrupt 7 GPIO17 /
confidential © Page : 94 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
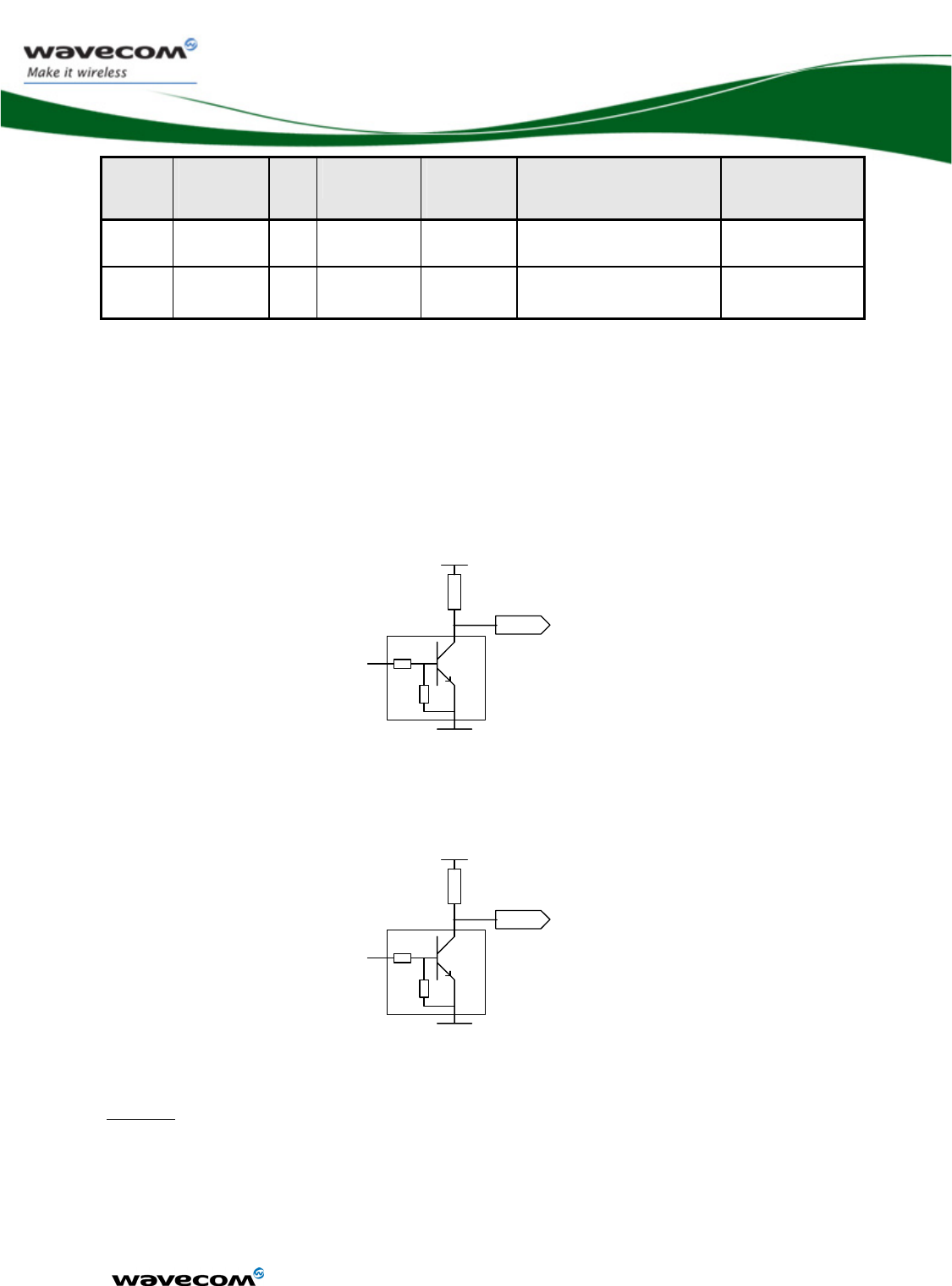
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 95 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
~CT105-
RTS2
INT8 Y3 I 1V8 Z External Interrupt 8 GPIO18 /
SIMPRES
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” on page 32 for Open drain, 2V8 and 1V8
voltage characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.20.3 Application
INTx are high impedance input type, so it is important to set the interrupt input
signal with pull up or pull down resistor if they are driven by an open drain,
open collector or by a switch. If they are driven by a push-pull transistor, no
pull up or pull down resistor is necessary.
GND
INTx
Intx
command T1
Rohm DTC144EE
VCC_1V8
R1
Figure 43: Example of INTx driving example with open collector
GND
INTx
Intx
command T1
Rohm DTC144EE
VCC_2V8
R1
Figure 44: Example of INTx driving example with open collector
Where:
R1 value can be 47K Ohm.
T1 can be a Rohm DTC144EE open collector transistor.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.21 VCC_2V8 and VCC_1V8 output
VCC_2V8 output can be used only for pull-up resistor and can be used as a
reference supply.
VCC_1V8 is used to supply the Flash and Ram memories; it can be used as
well for pull-up resistors.
Those voltages supplies are available when the WMP100 is on.
3.21.1 Features
Electrical characteristics of the signals
Parameter Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
Output voltage
1.76 1.8 1.94 V
VCC_1V8 Output Current
80 (TBC) mA
Output voltage
2.74 2.8 2.86 V
VCC_2V8 Output Current
15 mA
3.21.2 Pin description
Signal Pin number I/O I/O type Description
confidential © Page : 96 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
VCC_1V8 AD5 O Supply Digital supply
VCC_2V8 R1 O Supply Digital supply
3.21.3 Application
Those digital power supplies are mainly used to:
o VCC_1V8 is used to supply Flash and Ram memory devices
o pull-up signals such as I/O
o supply the digital transistors driving LEDs
o supply the SIMPRES signal
o act as a voltage reference for ADC interface AUX-ADC (only for VCC_2V8)
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 97 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.22 Real Time Clock
The Real Time Clock of the WMP100 need to be feeds by a 32768Hz
frequency. An internal oscillator is available to drive a crystal at the frequency
of 32768Hz.
3.22.1 Features
Those two pins are used to connect a crystal which is mandatory to setup and
to run the WMP100.
It is possible to access to the 32768 Hz signal (buffered output) on the GPIO44
(ball AB13). Refer to the chapter 3.11.
Electrical characteristics of the signal
Parameter Minimu
m
Typ Maximu
m
Unit
32kHz
oscillator input
cycle time
- 1/3276
8
- μs
32kHz
oscillator input
high time
5 - - μs
XIN_32K
32kHz
oscillator input
low time
5 - - μs
Start time 32kHz
oscillator start
time
- - 2 s
GPIO44 Delay time
with respect to
XIN_32K
- - 20 ns
3.22.2 Pin description
Signal Pin number
I/O I/O type Description
XIN_32K AC24 I analog Oscillator input
XOUT_32K AB24 O analog Oscillator output

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 98 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.22.3 Application
R1
C1 C2
X1
XIN_32K
XOUT_32K
The R1 resistor is mandatory if the crystal maximum power dissipation is
under 1μW.
The value of the components R1, C1 and C2 are tuned with the crystal MS2V-
T1S.
It is important to place the crystal close to the WMP100, to reduce as a
minimum the length of the nets.
Recommended components:
C1, C2 : 22pF
R1 : 100Kohm
X1: 32768Hz crystal. MS2V-T1S (+/- 20ppm @25°C) Microcrystal
3.22.4 Design recommendation
Exemple with the crystal. MS2V-T1S
Layer 1:
-Good ground under the crystal.
-Good ground connection of the crystal legs and the load capacitance of the
crystal.
-Crystal as close as possible to the WMP100 in order to decreases as
maximum as possible the parasite capacitance brought by the design of the
layout
Figure 45 : PCB lay out for the crystal MS2V-T1S
0.2mm
width

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Layer 2:
A complete layer of ground
3.23 BAT-RTC (Backup Battery)
The WMP100 provides an input / output to connect a Real Time Clock power
supply.
3.23.1 Features
This pin is used as a back-up power supply for the internal Real Time Clock.
The RTC is supported by the WMP100 when VBATT is available but a back-up
power supply is needed to save date and hour when the VBATT is switched
off.
confidential © Page : 99 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
2.5V
regulator
1.8V
regulator
from VBATT
to RTC
WMP100
BAT-RTC
Figure 46 : Real Time Clock power supply
If the RTC is not used this pin can be left open.
If the VBATT is available, the back-up battery can be charged by the internal
2.5V power supply regulator.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Electrical characteristics of the signal
Parameter Minimum
Typ Maximum
Unit
Input voltage 1.85 2.5 V
Input current
consumption*
3.3 μA
Output voltage 2.45 V
Output current 2 mA
*Provided by a RTC back-up battery when WMP100 is off and VBATT = 0V.
3.23.2 Pin description
Signal Pin number I/O I/O type Description
BAT-RTC U6 I/O Supply RTC Back-up supply
3.23.3 Application
Back-up Power Supply can be provided by:
• A super capacitor
• A non rechargeable battery
• A rechargeable battery cell.
3.23.3.1 Super Capacitor
Figure 47: RTC supplied by a gold capacitor
confidential © Page : 100 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
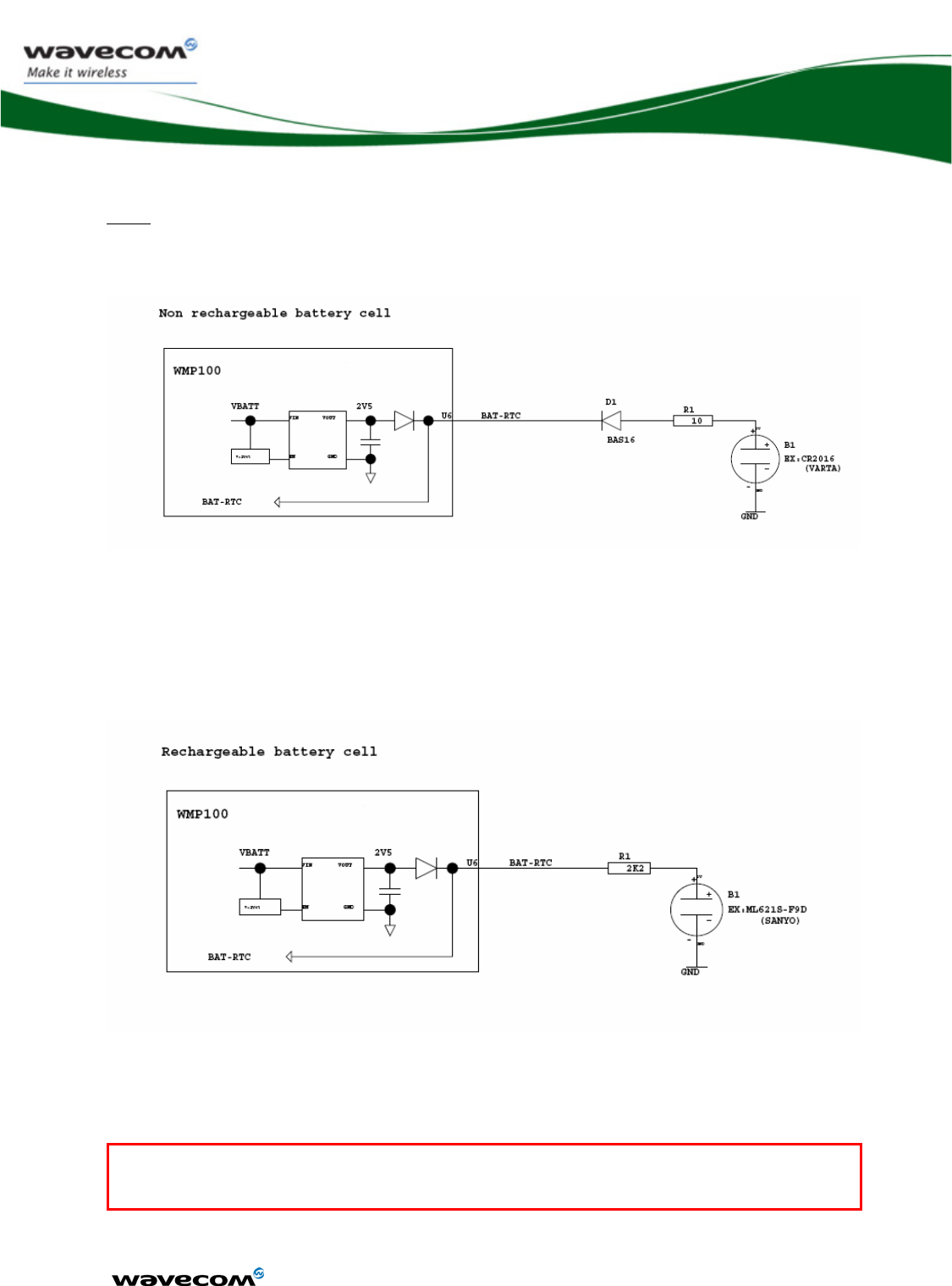
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Estimated range with 0.47 Farad Gold Cap: 25 minutes minimum.
Note: the Gold Capacitor maximum voltage is 2.5V.
3.23.3.2 Non Rechargeable battery
Figure 48: RTC supplied by a non rechargeable battery
The diode D1 is mandatory to not damage the non rechargeable battery.
Estimated range with 85 mAh battery: 800 h minimum.
3.23.3.3 Rechargeable battery cell
Figure 49: RTC supplied by a rechargeable battery cell
Estimated range with 2 mAh rechargeable battery: ~15 hours.
WARNING:
Before battery cell assembly ensure that cell voltage is lower than 2.5 V to
avoid any damage to the Wireless Microprocessor®.
confidential © Page : 101 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
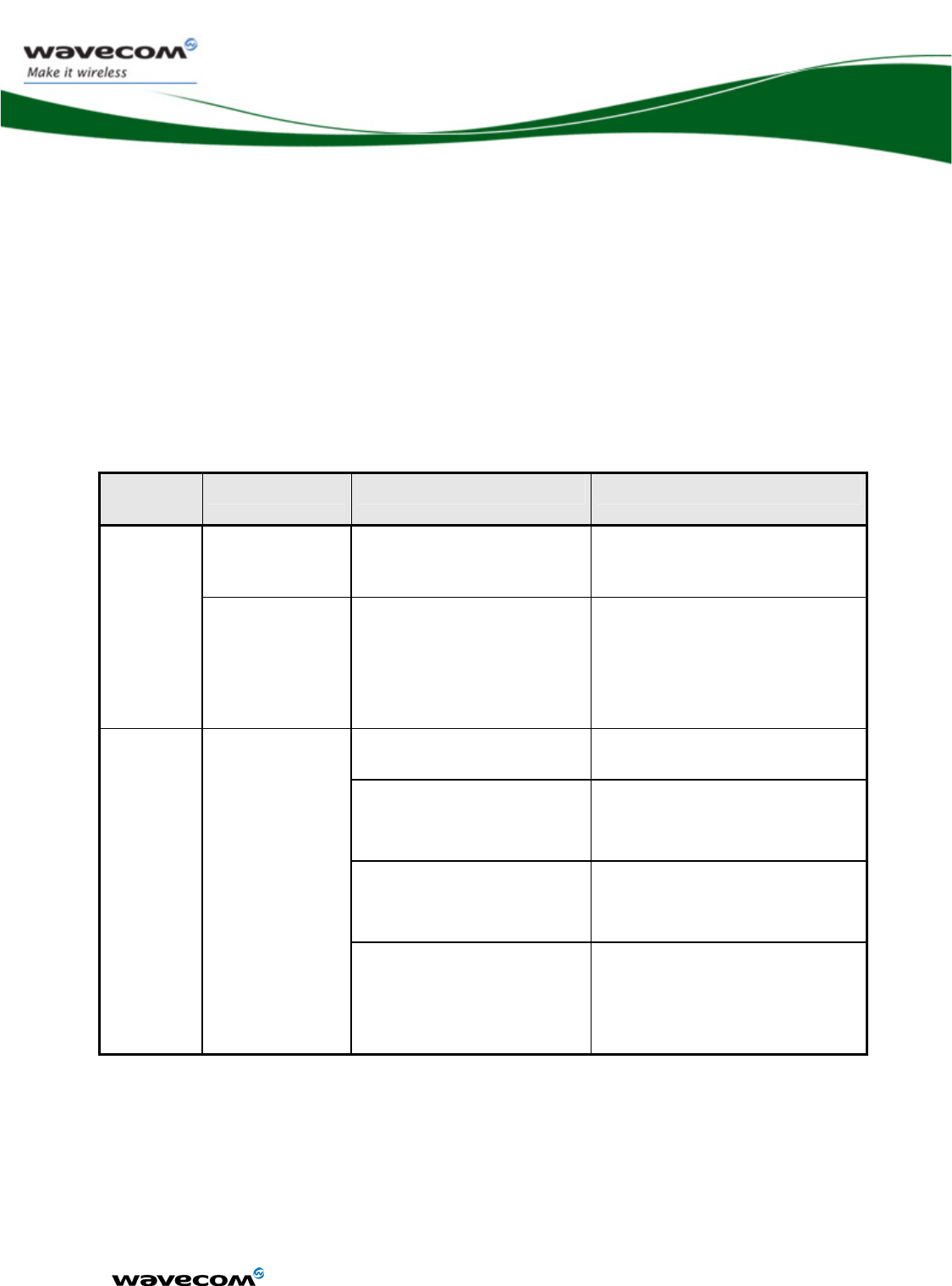
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.24 FLASH-LED signal
3.24.1 Features
FLASH LED is an open drain output. A LED and a resistor can be directly
connected between this output and VBATT.
When the WMP100 is OFF, if 2.8V < VBATT < 3.2V and a charger is connected
on CHG-IN inputs, this output indicates, by flashing (100 ms ON, 900 ms OFF)
, the pre-charging phase of the battery.
When the WMP100 is ON, this output is used to indicate the network status.
FLASH-LED status
WMP100
state
VBATT status FLASH-LED status WMP100 status
VBATT<2.8V
or VBATT>
3.2V
OFF WMP100 is OFF WMP100
OFF
2.8V < VBATT
< 3.2V
Pre-charge flash
LED ON for 100 ms,
OFF for 900 ms
WMP100 is OFF,
Pre-charging mode
confidential © Page : 102 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
(charger must be
connected on CHG-IN to
activate this mode)
Permanent WMP100 switched ON, not
registered on the network
Slow flash
LED ON for 200 ms,
OFF for 2 s
WMP100 switched ON,
registered on the network
Quick flash
LED ON for 200 ms,
OFF for 600 ms
WMP100 switched ON,
registered on the network,
communication in progress
WMP100
ON
VBATT > 3.2V
Very quick flash
LED ON for 100ms, OFF
for 200ms
WMP100 switched on,
software downloaded is
either corrupted or non-
compatible ("BAD
SOFTWARE")

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 103 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Electrical characteristics of the signal
Parameter Condition Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
VOL 0.4 V
IOUT 8 mA
The FLASH-LED state is high during the RESET time and undefined during the
software initialization time. During software initialization time, during 2
seconds max after RESET cancellation, the FLASH-LED signal is toggling and it
doesn’t provide the WMP100 status. After the 2s, the FLASH-LED provides the
true status of the Wireless Microprocessor®.
Undefined
2s
Module Status
~RESET
FLASH-LED 1
led OFF
Figure 50 : FLASH-LED state during RESET and Initialization time
3.24.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset state
Description
FLASH-
LED
U3 O Open Drain
Output
1 * LED driving
* This signal is undefined 2 seconds after the reset (initialization time).
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” on page 32 for Open drain, 2V8 and
1V8 voltage characteristics and for Reset state definition.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.24.3 Application
The GSM activity status indication signals FLASH-LED (pin U3) can be used to
drive a LED. This signal is an open-drain digital transistor according to the
WMP100 activity status.
confidential © Page : 104 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
FLASH-LED
« GSM »
D1
1
2
R1
470 Ω
VBATT
Figure 51: Example of GSM activity status implementation
R1 value can be harmonized depending of the LED (D1) characteristics.
3.25 Digital audio interface (PCM)
The Digital audio interface (PCM) interface mode allows the connectivity with
audio standard peripherals. It can be used, for example, for connecting an
external audio codec.
The programmability of this mode allows address a large range of audio
peripherals.
3.25.1 Features
• IOM-2 compatible device on physical level
• Master mode only with 6 slots by frame, user only on slot 0
• Bit rate single clock mode at 768KHz only
• 16 bits data word MSB first only
• Linear Law only (no compression law)
• Long Frame Synchronization only
• Push pull configuration on PCM-OUT and PCM-IN
The digital audio interface configuration can’t be different from the specified
features above.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
AC characteristics
Signal Description Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
Tsync_low +
Tsync_high
PCM-SYNC period 125 μs
confidential © Page : 105 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Tsync_low PCM-SYNC low time 93 μs
Tsync_high PCM-SYNC high time 32 μs
TSYNC-CLK PCM-SYNC to PCM-CLK time
-154 Ns
TCLK-cycle PCM-CLK period 1302 Ns
TIN-setup PCM-IN setup time 50 Ns
TIN-hold PCM-IN hold time 50 Ns
TOUT-delay PCM-OUT delay time 20 Ns
PCM interface consists of 4 wires:
• PCM-SYNC (output): The frame synchronization signal delivers an 8KHz
frequency pulse that synchronizes the frame data in and the frame data
out.
• PCM-CLK (output): The frame bit clock signal controls the data transfer
with the audio peripheral.
• PCM-OUT (output): The frame “data out” depending on the selected
configuration mode.
• PCM-IN (input): The frame “data in” is depending on the selected
configuration mode.
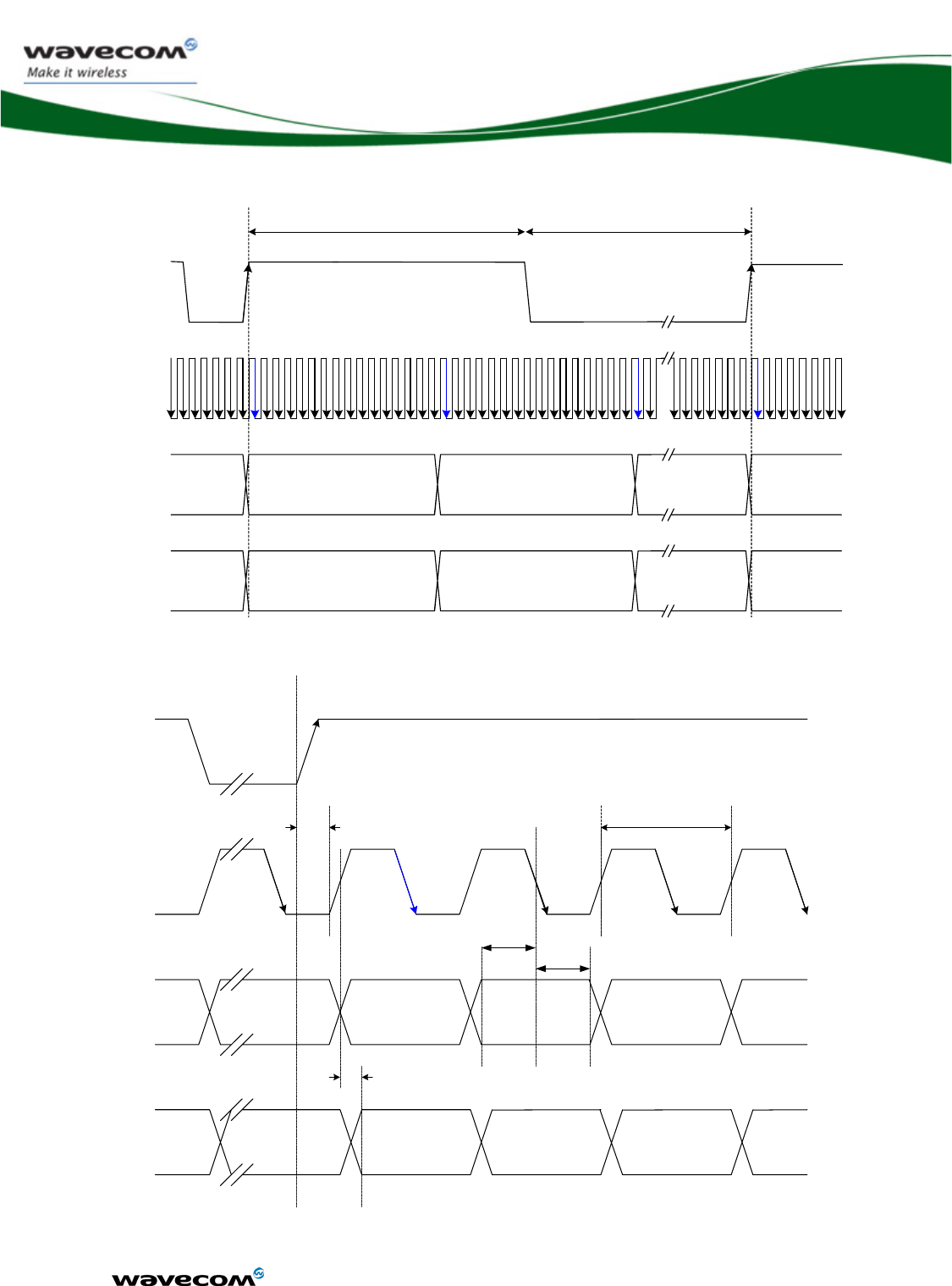
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 106 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
SLOT 0 SLOT 1 SLOT 5 SLOT 0
SLOT 0 SLOT 1 SLOT 5 SLOT 0
SLOT 5
SLOT 5
PCM-SYNC
PCM-CLK
PCM-IN
PCM-OUT
Tsync_high Tsync_low
End of frame
Begining of
frame
Figure 52 : PCM Frame waveform
TOUTdelay
TSYNC-CLK
TCLK-cycle
TIN-hold
TIN-setup
PCM-SYNC
PCM-CLK
PCM-IN
PCM-OUT
SLOT 0 bit 15 SLOT 0 bit 14 SLOT 0 bit 13SLOT 5 bit 0
SLOT 0 bit 15 SLOT 0 bit 14 SLOT 0 bit 13SLOT 5 bit 0
Figure 53 : PCM Sampling waveform

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.25.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type
Reset state Description
PCM-SYNC Y21 O 1V8 Pull down Frame synchronization
8Khz
PCM-CLK W21 O 1V8 Pull down Data clock
W22
PCM-OUT O 1V8 Pull up Data output
PCM-IN AA22 I 1V8 Pull up Data input
See chapter 3.4, “Electrical information for digital I/O” on page 32 for Open drain, 2V8 and
1V8 voltage characteristics and for Reset state definition.
3.25.3 Application TBD
3.26 USB 2.0 interface
A 5-wire USB slave interface is available, compiling with USB 2.0 protocol
signaling, but not with electrical interface, due to the not complying 5V of
VPAD-USB.
The USB interface signals are VPAD-USB, USB-DP, USB-DM, USB-DET, USB-
CN
and GND.
3.26.1 Features
¾ 12Mbit/s full speed transfer rate
¾ 3.3V typ compatible
¾ USB Softconnect feature
¾ Download feature is not supported by USB
¾ CDC 1.1 – ACM compliant
confidential © Page : 107 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 108 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Electrical characteristics of the signals
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
VPAD-USB, USB-DP, USB-DM, USB-CN 3 3.3 3.6 V
VPAD-USB Input current consumption 8 mA
NOTE:
A 5V to 3.3V typ. voltage regulator is needed between the external interface
power in line (+5V) and the WMP100 line (VPAD-USB).
3.26.2 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Description Multiplexed
with
VPAD-USB AB19 I VPAD_USB
USB Power
Supply
Not mux
USB-DP W19 I/O VPAD_USB
Differential
data interface
positive
Not mux
USB-DM AA20 I/O VPAD_USB
Differential
data interface
negative
Not mux
USB-CN Y20 O VPAD_USB
Connect (high
or low speed)
Not mux
USB-DET R14 I VCC_1V8 Detection Not mux

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 109 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.26.3 Application
A typical schematic is shown below:
Figure 54: Example of USB implementation
Recommended components:
R1,R2, R3 : 1MOhm
C1, C3 : 100nF
C2, C4 : 2.2μF
D1 : STF2002-22 from SEMTECH
U1 : LP2985AIM 3.3V from NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR
U2 : NC7SZ66L6X from FAIRCHILD
The regulator used is a 3.3V one. It is supply through J1 when the USB wire is
plugged.
USB-DET is a WMP100 External Interruption (R14) used for the USB wire
presence detection.
The EMI/RFI filter with ESD protection is D1. The D1 integrated pull up resistor
used to detection of full speed. USB-CN (Y20) drives this pull-up.
R1 and C1 have to be close J1.
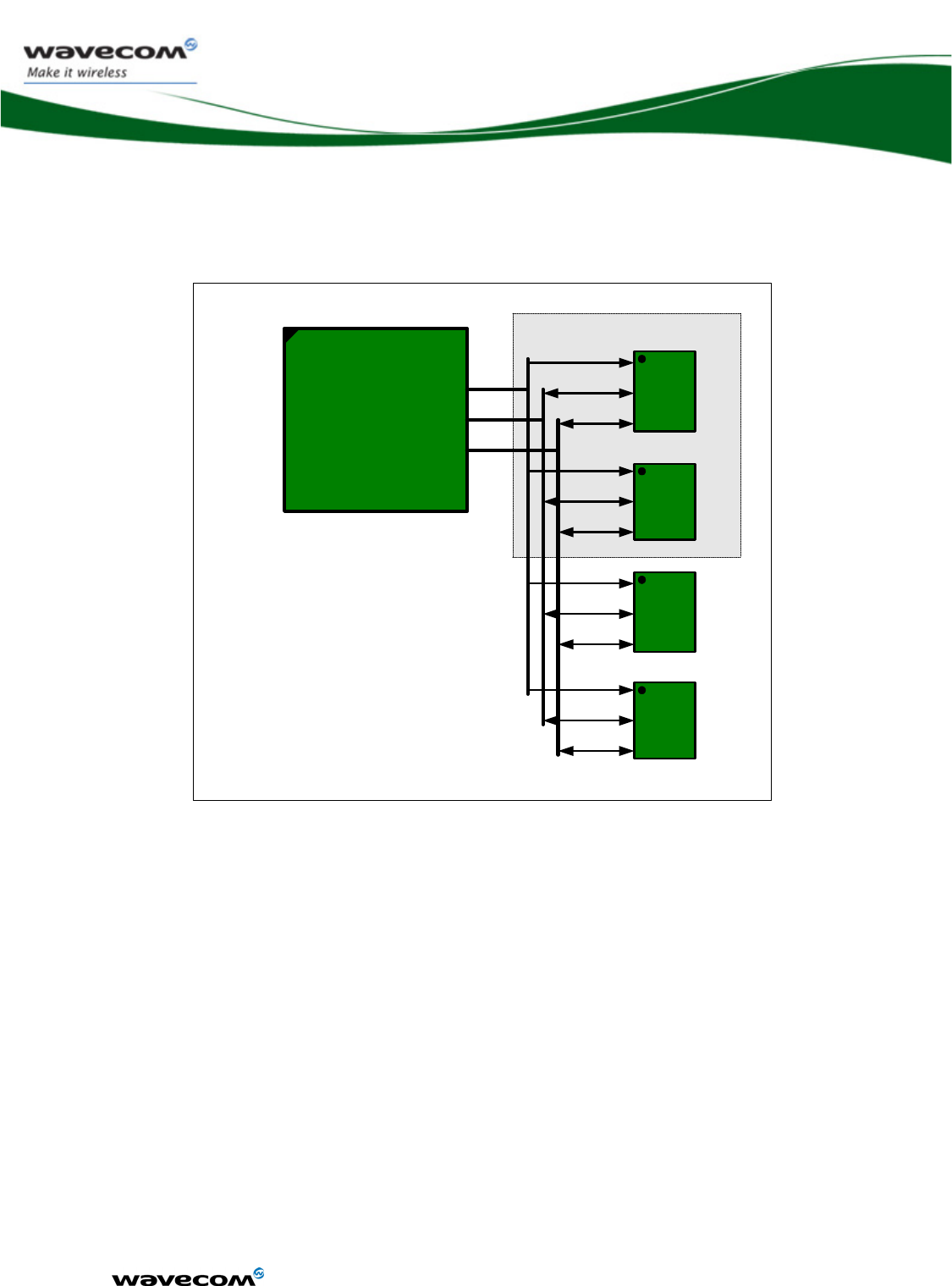
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.27 Memory interface
The memory interface is used to connect many memory parts technologies as
Flash NOR, Flash NAND, SRAM and PSRAM components.
Combo
WMP100
Processor
NOR
Flash
CS0
SRAM /
PSRAM
CS1
ADD
DATA
CTR
CS2
CS3
Figure 55: Memory bus
The interface is able to drive up to 4 independents memories. Some memories
can be enclosed in the same package, like the Combo memories.
Each Chip select space can be configured undependably.
It is mandatory that the memory connected on CS0 is the FLASH and CS1 is
the RAM.
confidential © Page : 110 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.27.1 Features
3.27.1.1 Generic Description
¾ Up to 128 MByte address range per chip select
¾ Up to 4 chip select available
¾ Support for 8, 16, and 32 bit (multiplexed synchronous mode) devices
¾ Byte enable signals for 16 bit and 32 bits operation
¾ Fully programmable timings based on hclk (a division of the ARM clock)
cycles (except for synchronous mode which is based on CLKBURST
cycles)
o individually selectable timings for read and write
o 0 to 7 clock cycles for setup
o 1 to 32 clock cycles for access cycle
o 1 to 8 clock cycles for page access cycle
o 0 to 7 clock cycles for hold
o 1 to 15 clock cycles for turnaround
¾ Page mode Flash memory support
o page size of 4, 8, 16 or 32
¾ Burst mode Flash memory support up to hclk clock frequency (for
devices sensitive to rising edge of the clock only)
o hclk, hclk/2, hclk/4 or hclk/8 burst clock output
o burst size of 4, 8, 16, 32
o WAIT input
o automatic CLKBURST power-down between accesses
¾ Intel mode (WE and OE) and Motorola mode (E and R/W) control signals
¾ Synchronous write mode
¾ Synchronous multiplexed data/address mode (x32 mode)
¾ Adaptation to word, halfword, and byte accesses to the external devices
confidential © Page : 111 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 112 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.27.1.2 Case of ST 32/8 (M36W0R5030T0ZAQF)
¾ 32 Mbits FLASH: Mandatory configuration of CS0 space :
o Bursted mode (Synchronous read / asynchronous write)Burst
frequency: 26 MHz
o Burst size: 4 half words
o 3 clock cycles for read access cycle
o 5 clock cycles for write access cycle
o 1 clock cycle for turnaround
o 16-bit wide data bus
o “Top boot” type of flash architecture
o Intel SW command set
¾ 8 Mbits SRAM: Mandatory configuration of CS1 space :
o Asynchronous mode
o Intel mode (WE and OE)
o Same configuration for Read and Write access
o 1 clock cycle for setup
o 2 clock cycles for access cycle
o 0 clock cycles for hold
o 1 clock cycle for turnaround
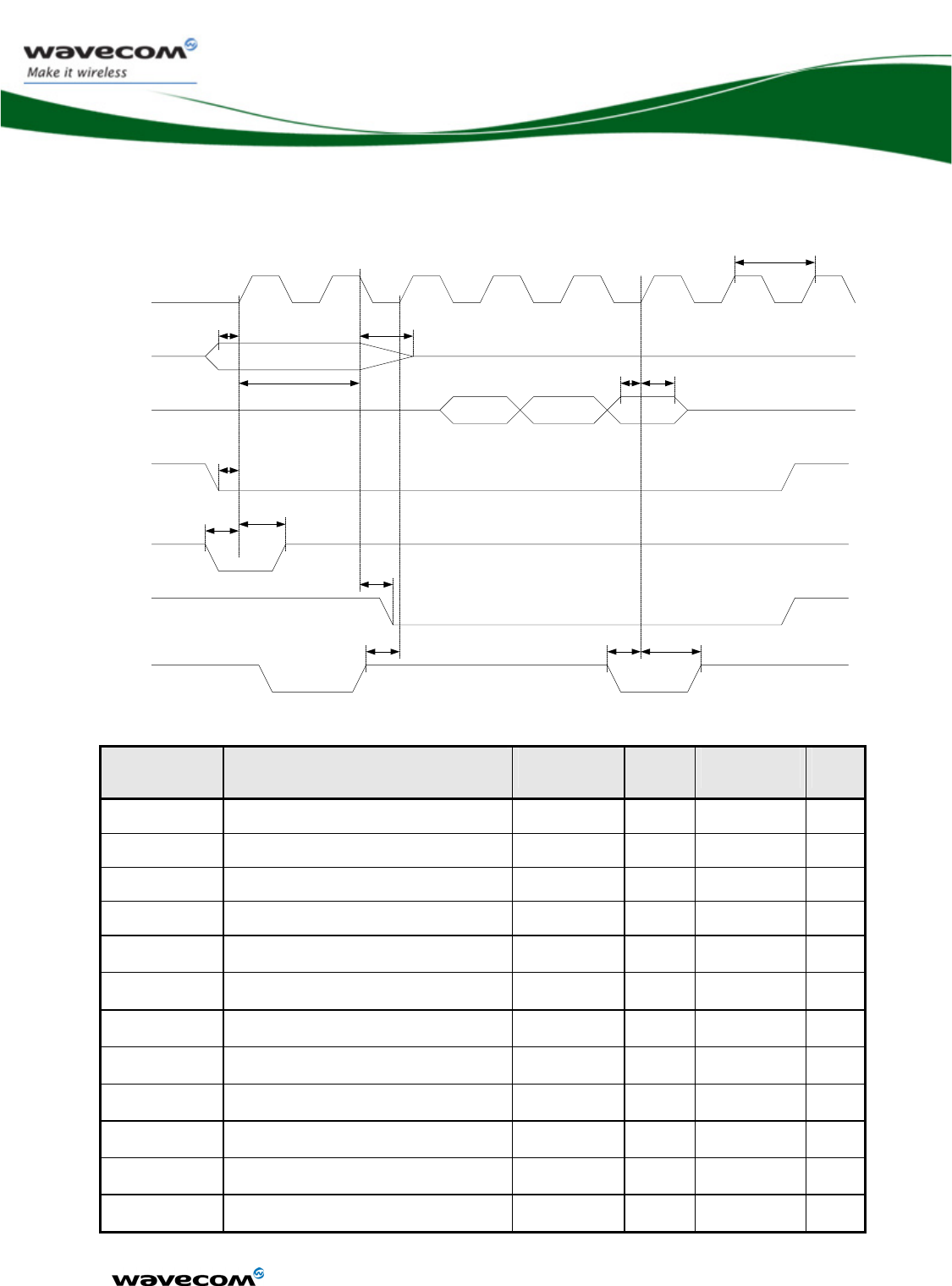
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 113 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.27.1.3 Access bus Waveform
Synchronous timing diagram
CLKBURST
DATA
~CS
~ADV
~OE
~WAIT
ADD
TCLKBURST_cycle
TADD_setup
TADD_hold
TADD_tristate
TWAIT_setup
TDATA_hold
TCS_setup
TADV_setup TADV_hold
TOE_delay
TWAIT_holdTWAIT_setup
TDATA_setup
Figure 56: Read synchronous timing
Signal Description Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
TCLKBURST CLKBURST clock period time
19 78 ns
TADD_setup Address bus setup time 7 ns
TADD_hold Address bus hold time 19 ns
TADD_tristate Address bus tristate time 10 ns
TDATA_setup Data bus setup time 5 ns
TDATA_hold Data bus hold time 3 ns
TCS_setup Chip select setup time 7 ns
TADV_setup ADV setup time 7 ns
TADV_hold ADV hold time 7 ns
TOE_delay Output Enable delay time 13 ns
TWAIT_setup Wait setup time 5 ns
TWAIT_hold Wait hold time 5 ns
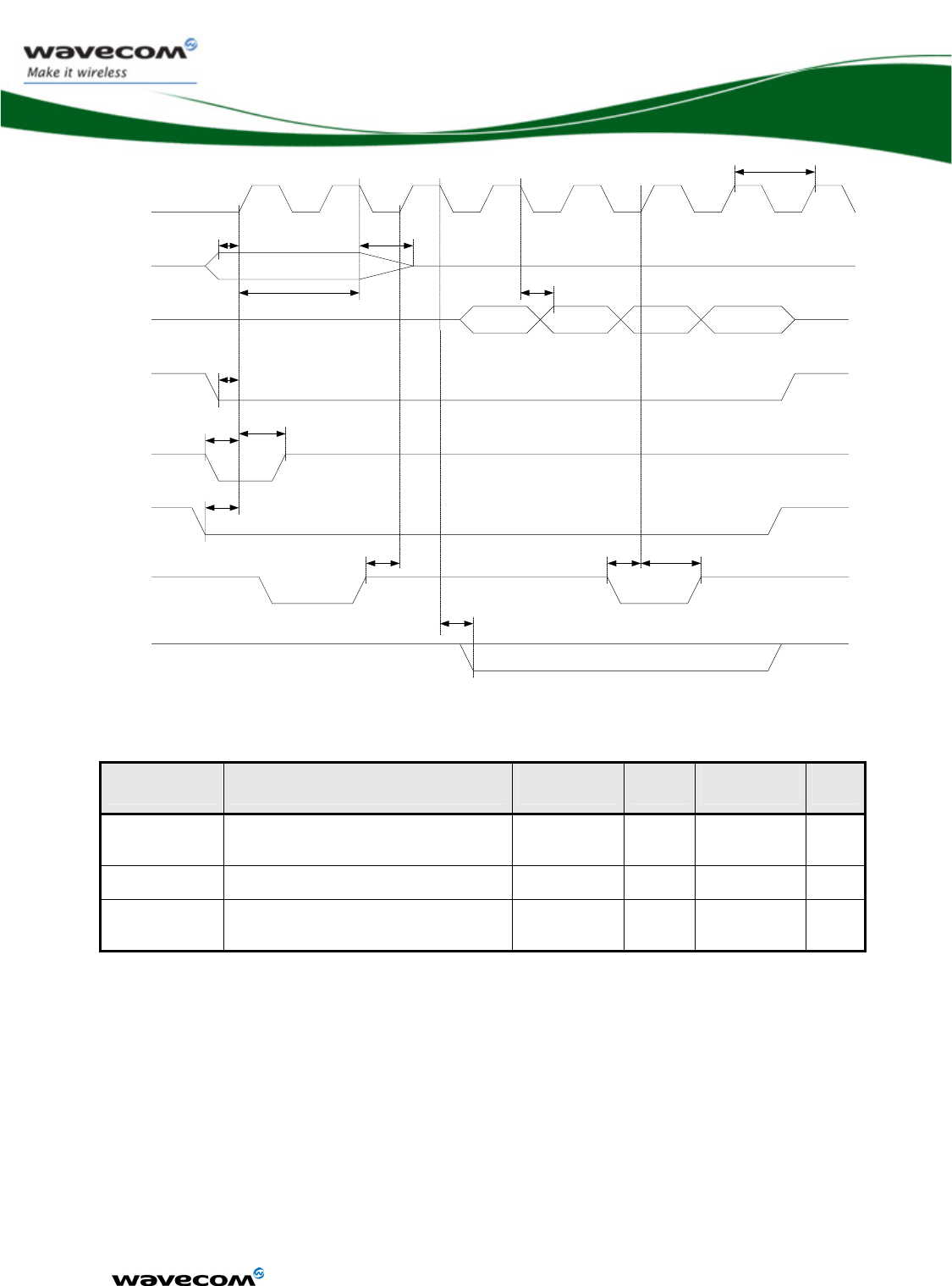
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
TCLKBURST_cycle
DATA
~CS
~ADV
~WE
~WAIT
ADD
~BE
TADD_setup
TADD_hold
CLKBURST
TADD_tristate
TWAIT_setup
TCS_setup
TADV_setup TADV_hold
TWAIT_holdTWAIT_setup
TDATA_delay
TWE_setup
TBE_delay
Figure 57: Write synchronous timing
Signal Description Minimum
Typ Maximum Unit
TDATA_delay CLKBURTS falling edge to
DATA valid delay
4 ns
TWE_setup WE to CLKBURST setup time
7 ns
TBE_delay CLKBURST falling edge to BE
delay
4 ns
confidential © Page : 114 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
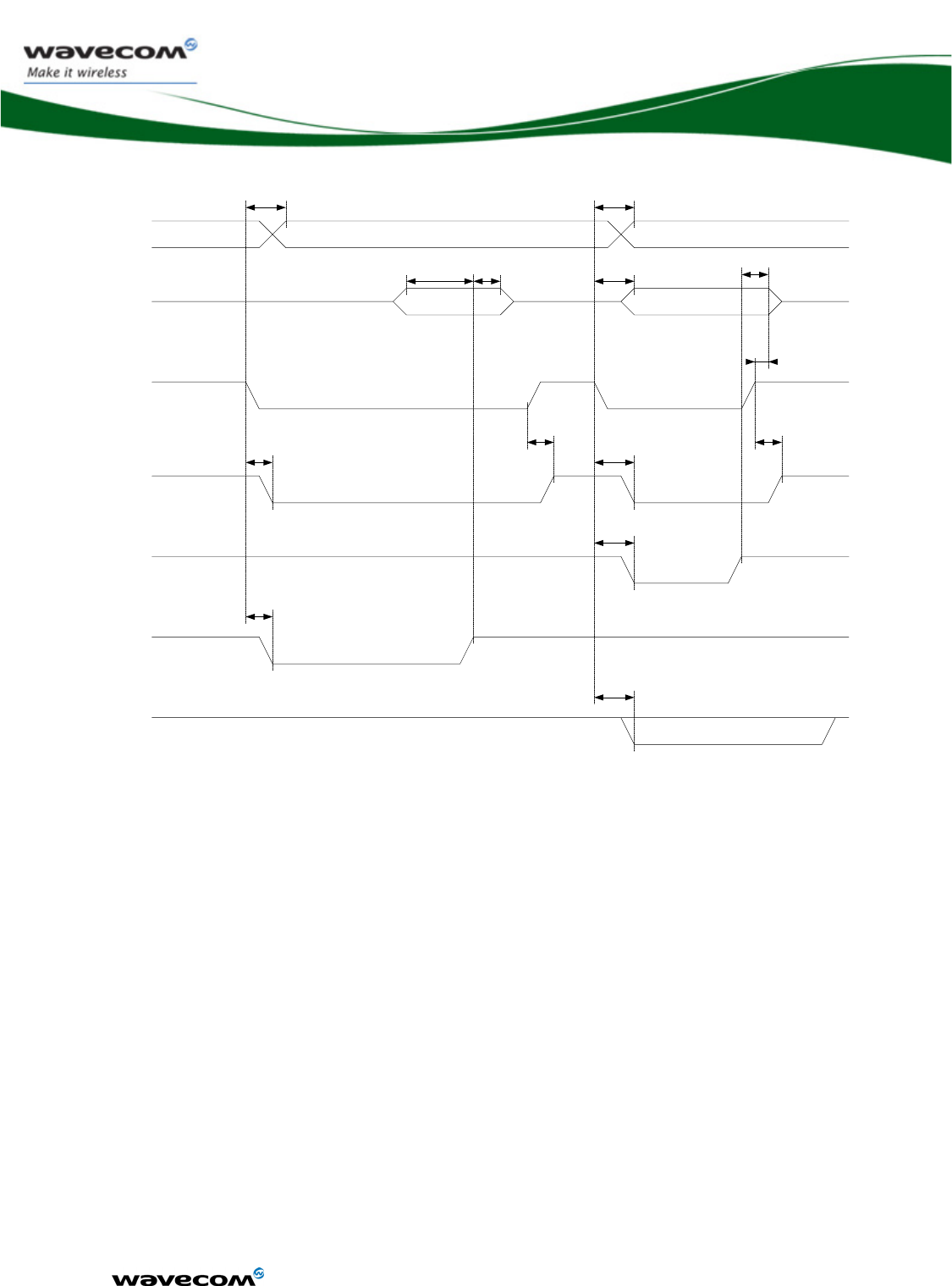
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Asynchronous time diagram
ADD
IO
~CS
~ADV
~WE
~OE
~BE
TDATA_holdTDATA_setup
TADD_delay
TADV_delay
TOE_delay
TADV_delay
TADD_delay
TDATA_delay
TADV_delay
TWE_delay
TBE_delay
TDATA_secure
TDATA_secure
TADV_delay
Figure 58: Read / Write Asynchronous timing
confidential © Page : 115 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Signal Description Minimum
Typ Maximum
Unit
TADD_delay Address delay time from Chip
Select active
3 ns
TDATA_setup Data to Output Enable setup
time
18 ns
TDATA_hold Data hold time after Output
Enable inactive
3 ns
TDATA_delay Data delay time from Chip Select
active
5 ns
TDATA_secure Data hold time after Write
Enable inactive or Chip Select
inactive
-5 ns
TADV_delay ADV delay time from Chip Select
active and inactive
3 ns
TWE_delay Write Enable delay time from
Chip Select active
3 ns
TOE_delay Output Enable delay time from
Chip Select active
5 ns
TBE_delay BE delay time from Chip Select
active
3 ns
3.27.1.4 Flash space
The Flash space (program memory) is dedicated on the CS0 pin chip select.
This memory is embedded in the Open AT® Software Suite v1.0, so this device
has to run at a special configuration of the memory bus to ensure the full
functionality of the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0.
Refer to the chapter 3.27.1.2 for the details on the configuration.
3.27.1.5 RAM space
The Ram space is dedicated on the CS1 pin chip select. This memory has to
run at a special configuration of the memory bus to ensure the full functionality
of the WMP100/Open AT® Software Suite v1.0.
Refer to the chapter 3.27.1.2 for the details on the configuration.
confidential © Page : 116 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 117 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.27.1.6 16-bit wide data bus User Space
The users’ memory space is available on chip select CS2 and CS3.
User space are freely configurable.
3.27.2 Electrical characteristics of the signals
The memory interface voltage is provided by the VCC_1V8 power supply. So it
is mandatory to supply the memories devices by VCC_1V8 power supply
voltage provided by the WMP100 Wireless Microprocessor®.
Parameter Min
Typ Max Unit
VCC_1V8 (Wireless Microprocessor® supply output)
1.76
1.9 1.94 V
FLASH 1,7 1,95 V Memory Specification
(M36W0R5030T0ZAQF) SRAM 1,7 1,95 V
3.27.3 Pin description
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset
state
Description Multiplexed
with
~WAIT R19 I 1V8 Pull up
Flash burst wait for
synchronous
operation
Not mux
~CS0 P19 O 1V8 1 Flash chip select Not mux
~CS1 R20 O 1V8 1 RAM chip select Not mux
~CS2 (*) R18 O 1V8 Z User chip select GPIO1 / A25
~CS3 T17 O 1V8 1 User chip select Not mux
CLKBURST M19 O 1V8 Z Burst Clock Not mux
~ADV U19 O 1V8 1 Burst address valid Not mux
~WE-E P20 O 1V8 1 write enable (Intel
mode) /
enable signal
(Motorola mode)
Not mux
~OE-R/W N20 O 1V8 1 output enable (Intel
mode) / read not
write (Motorola
mode)
Not mux
BE1 P18 O 1V8 1 select for 16 or 32
bits devices
Not mux
(*) Add a pull-up for the Reset State
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 118 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset state
Description Multiplexed
with
D0 W24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D1 W23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D2 AA24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D3 Y23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D4 U21 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D5 Y22 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D6 Y24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D7 V21 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D8 V20 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D9 U20 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D10 V24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D11 V22 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D12 V23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D13 AA23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D14 U23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
D15 T23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Data Not mux
A0 T19 O 1V8 1 Address Not mux
A1 U18 O 1V8 1 Address Not mux
A2 U24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A3 P24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A4 N24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A5 M21 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A6 M24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A7 N23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A8 R24 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A9 R22 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A10 P22 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A11 T22 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A12 R23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A13 M22 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A14 P21 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 119 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Pin
number
I/O I/O type Reset state
Description Multiplexed
with
A15 R21 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A16 P23 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A17 T21 I/O 1V8 Pull down Address Not mux
A18 T24 O 1V8 0 Address Not mux
A19 M23 O 1V8 0 Address Not mux
A20 N21 O 1V8 0 Address Not mux
A21 N22 O 1V8 0 Address Not mux
A22 M20 O 1V8 0 Address Not mux
A23 N19 O 1V8 0 Address Not mux
A24 U22 O 1V8 Z Address GPIO2
A25 R18 O 1V8 Z Address GPIO1 /
~CS2
A26 V16 O 1V8 Z Address GPIO3 /
INT0
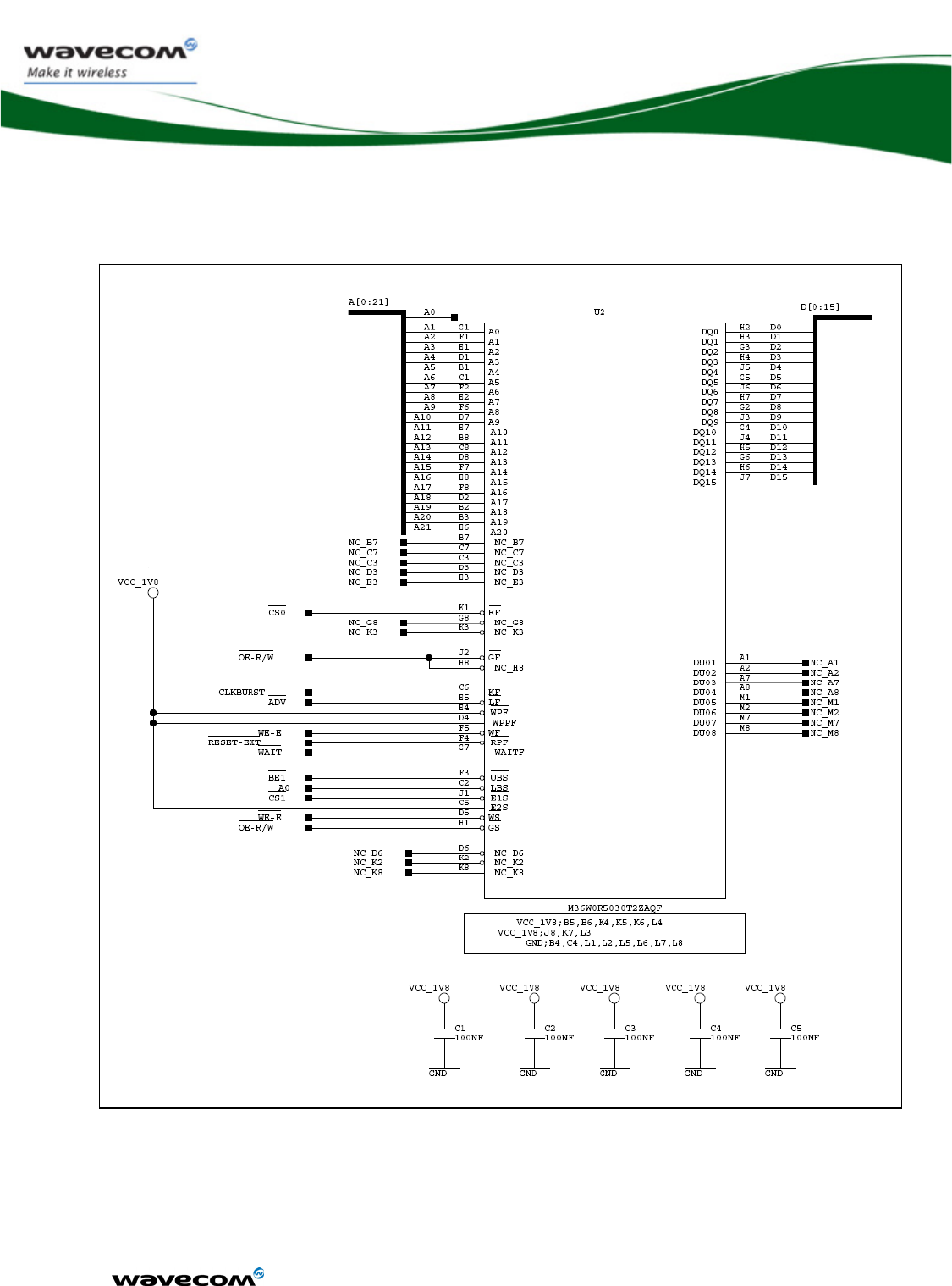
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 120 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
3.27.4 Application
An application is given with a combo memory ST (M36W0R5030T0ZAQF)
which embedded SRAM and FLASH memory
Figure 59: Memory connection schematic
NC: not connected

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
Recommended components:
• U1 : WMP100
• U2 : M36W0R5030T0ZAQF from STMicroelectronics :
o 32Mbits of Bursted Flash (synchrone), Top type.
o 8Mbits of SRAM (asynchrone).
o Temperature range from –40°C to +85°C.
o 16Bit bus Data wide type
o 1.8 Volt core and I/O type
• Decoupling capacitors: 100nF
3.27.5 Constraints
Electrical constraints:
• The Flash type must be a “Top” type, see on the part number:
M36W0R5030T0ZAQF
• The reset of the Flash must be done by the ~EXT-RESET signal, (see
RESET chapter).
• Decoupling capacitors have to be used and to be placed close to the
memory power supply pins. (see the Memory location figure below)
• The power supply VCC_1V8 is provided by the WMP100 (VCC_1V8 ball
“AD5”).
• Because it is a 16Bit bus data wide implementation, the Address signal
A0 has to be used to select the Low value of the data bus (8 bits LSB).
So ~BE1 and A0 have to be connected to ~R-UB and ~R-LB of the
memory (See schematic).
• The Flash must be connected on ~CS0 and the SRAM on the ~CS1.
PCB constraints:
• The memory must be place close to the Wireless Microprocessor® (see
the Memory location figure below)
confidential © Page : 121 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
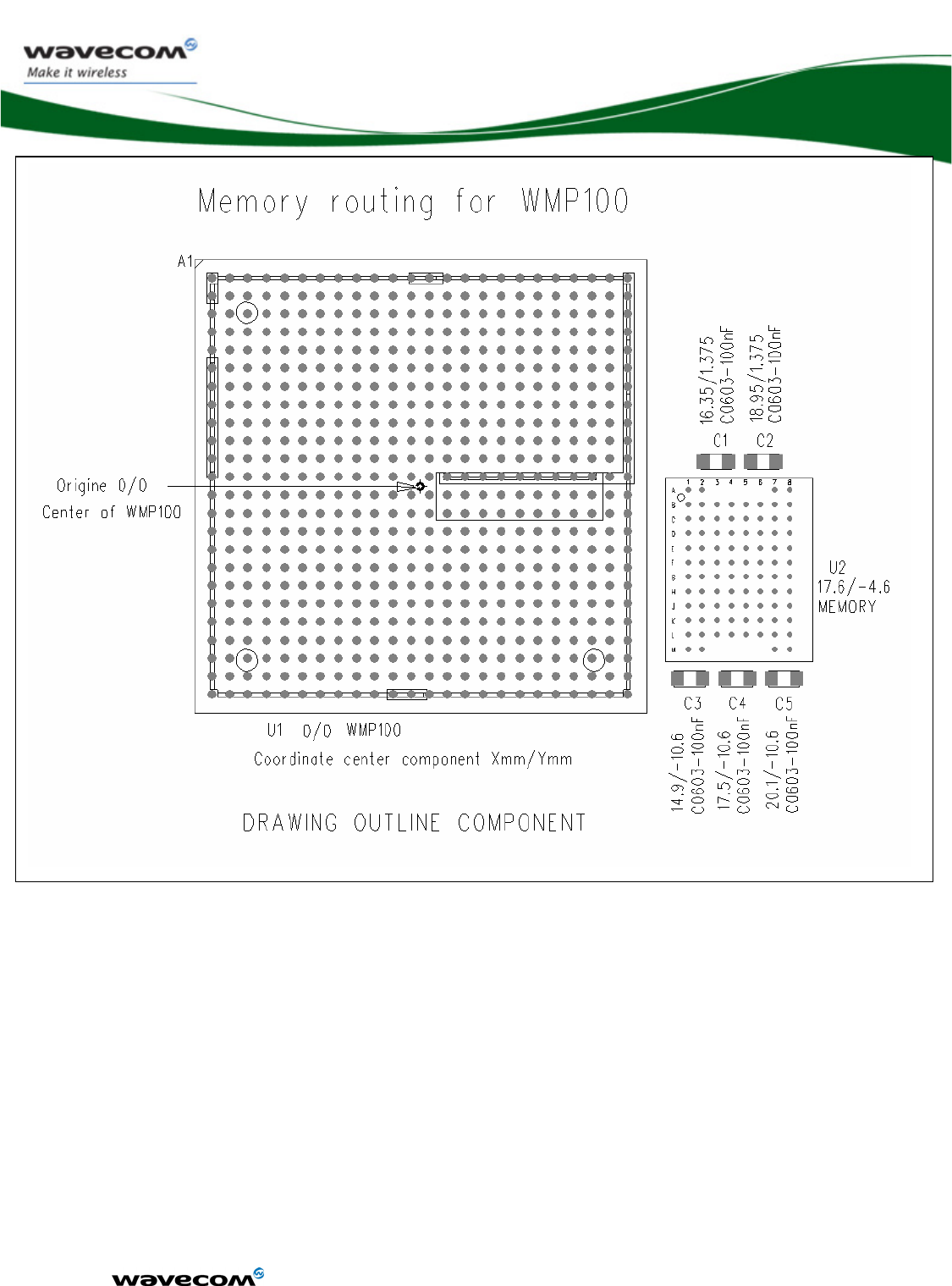
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 122 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Figure 55: Memory location
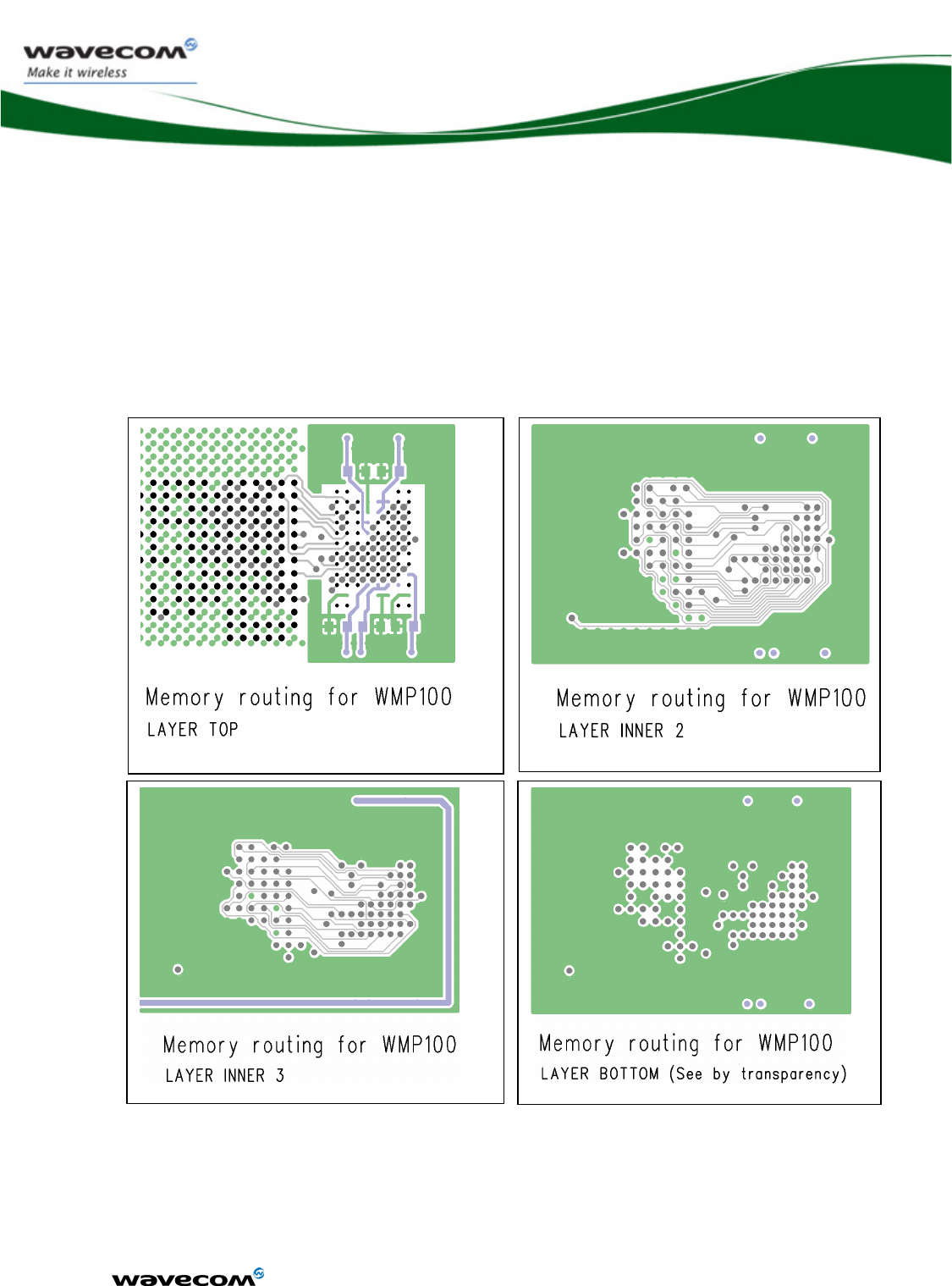
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
• All the memory bus nets must have a maximum length of 30 mm.
• It is recommended to shield around all the signals (see the Memory PCB
figure below).
• All signals must be routed with adjoining layers (see the Memory PCB
figure below). We do not recommend adding other signals between the
Wireless Microprocessor® and the memory.
• PCB structure example : 4 layers (see the Memory PCB figure below)
o Inner layer trace 100 μm, clearance 100 μm
o Layer top and bottom trace 150 μm, clearance 150 μm
confidential © Page : 123 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Figure 60: Memory PCB

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
3.28 RF interface
The impedance is 50 Ohms nominal and the DC impedance is 0 Ohm.
3.28.1 RF connection
The RF antenna connection uses a unique BGA Ball associated with
grounded BGA balls all around.
This ball must be connected, using a PCB via, to an embedded RF 50
ohms line, in order to avoid any pollution coming from base-band signals.
For the same reasons, the RF connection and the RF embedded line must
be kept 1 cm away from any noisy base-band signal. Without following
this rule the RX sensitivity might be degraded.
The other side of the embedded 50 ohms RF line can be connected to a
RF connector or a soldering pad in order to connect an antenna.
It’s also possible to use a CMS antenna or to design an antenna directly
on the same PCB.
confidential © Page : 124 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Notes:
• The WMP100 does not support an antenna switch for a car kit but this
function can be implemented externally and it can be driven using a
GPIO.
• The antenna cable and connector should be chosen in order to minimize
losses in the frequency bands used for GSM 850/900MHz and
1800/1900MHz.
• 0.5dB can be considered as a maximum value for loss between the
WMP100 and an external connector.
3.28.2 RF performances
RF performances are compliant with the ETSI recommendation GSM 05.05.
The main parameters for Receiver are:
• GSM850 Reference Sensitivity = -108 dBm Static & TUHigh
• E-GSM900 Reference Sensitivity = -108 dBm Static & TUHigh
• DCS1800 Reference Sensitivity = -107 dBm Static & TUHigh
• PCS1900 Reference Sensitivity = -107 dBm Static & TUHigh
• Selectivity @ 200 kHz : > +9 dBc
• Selectivity @ 400 kHz : > +41 dBc
• Linear dynamic range: 63 dB
• Co-channel rejection: >= 9 dBc
And for Transmitter:
• Maximum output power (EGSM & GSM850): 33 dBm +/- 2 dB at ambient
temperature
• Maximum output power (GSM1800 & PCS1900): 30 dBm +/- 2 dB at
ambient temperature

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 125 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
• Minimum output power (EGSM & GSM850): 5 dBm +/- 5 dB at ambient
temperature
• Minimum output power (GSM1800 & PCS1900): 0 dBm +/- 5 dB at
ambient temperature
3.28.3 Antenna specifications
The antenna must fulfill the following requirements:
• The optimum operating frequency depends on application. A dual Band or
a quad band antenna shall work in these frequency bands and have the
following characteristics:
WMP100 86
Characteristic E-GSM 900 DCS 1800 GSM 850 PCS 1900
TX Frequency 880 to 915
MHz
1710 to
1785 MHz
824 to 849
MHz
1850 to 1910
MHz
RX Frequency 925 to 960
MHz
1805 to
1880 MHz
869 to 894
MHz
1930 to 1990
MHz
Impedance 50 Ohms
Rx max 1.5 :1
VSWR Tx max 1.5 :1
Typical
radiated gain 0dBi in one direction at least
3.28.4 Antenna
The RF antenna connection uses a unique BGA Ball associated with
grounded BGA balls all around.
This BGA ball must be connected, using a PCB via, to an embedded RF 50
ohms line, in order to protect the antenna line from the noise coming from
base-band signals.
The figure below shows the RF ball and the ground balls around, and a
PCB via placement example.
PCB via
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 126 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Figure 61: Antenna and ground balls placement
The figure below shows the RF embedded line and the PCB via.
Figure 62: RF 50 ohms embedded line
This 50 ohms line is surrounded by two ground planes in order to protect
this antenna line from noise. The length of the line shouldn’t be too high
(more than a few cm) because of RF insertions losses. The width of the
line must be calculated in order to ensure a 50 ohms characteristic
impedance.
For the same reasons, not only the RF connection but also the RF
embedded line should be kept about 1 cm away from any (noisy) Base-
band signal in order to ensure a good RX sensitivity level.
Figure below shows a keep away area for the antenna connection point.
This restricted area must not contain any noisy base-band signals (like
any bus or clock signal).
Figure 63: Antenna connection point keep away area
The other end of the embedded 50 ohms RF line can be connected to a RF
connector or a soldering pad in order to connect an antenna.
Keep
away
area
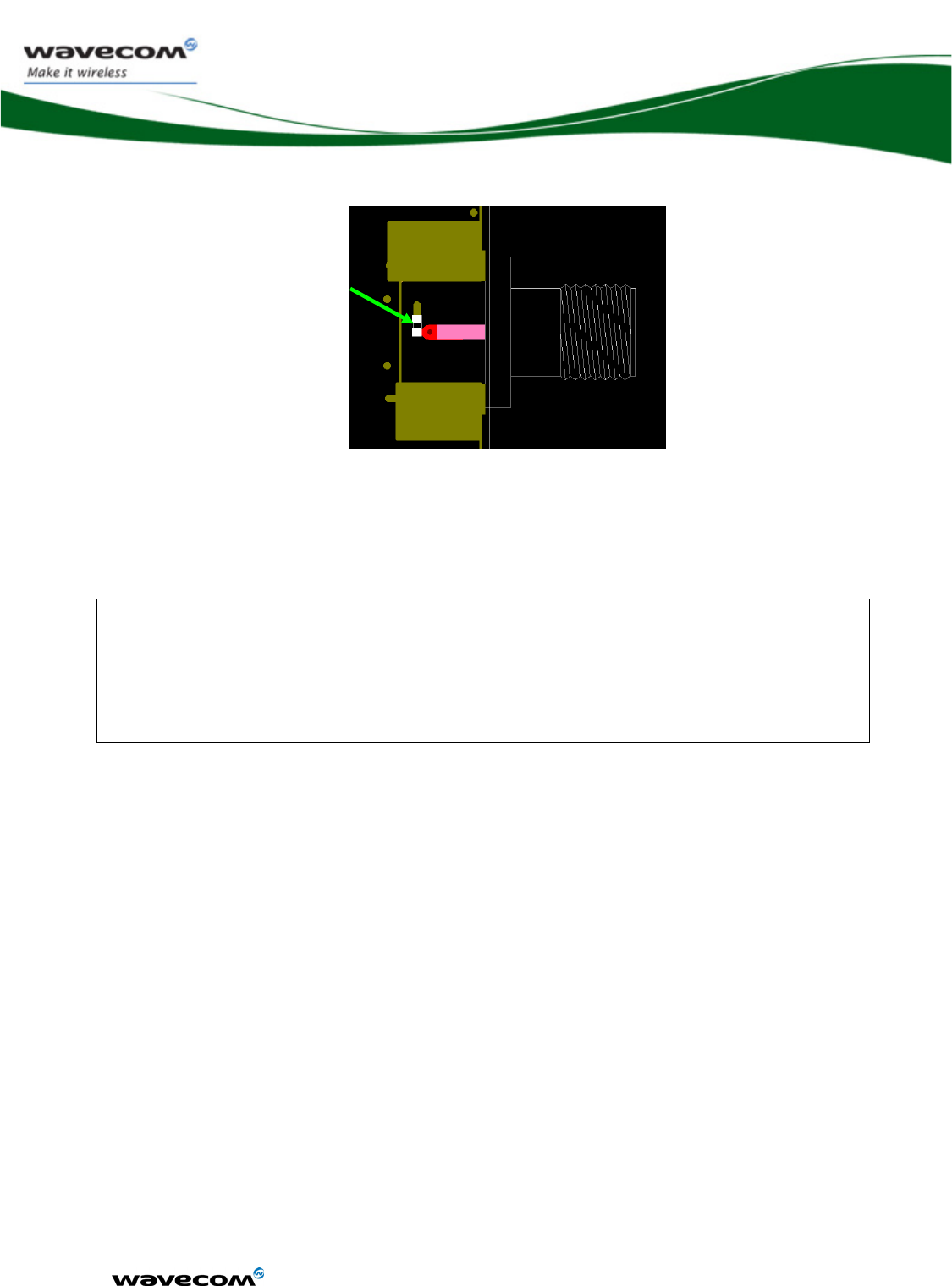
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
It’s recommended to add an ESD protection component on the antenna
line, in order to increase the final product ESD tolerance.
ESD protection
Figure 64: RF connector and ESD protection example
This ESD protection component can be an 82 nH Multi-Layer HF inductor
(0603 case). It must be connected between RF output and ground as
short as possible.
It’s also possible to use an antenna chip or to choose to design an
antenna directly on the same PCB.
WARNING:
Wavecom strongly recommends working with an antenna manufacturer either
to develop an antenna adapted to the application or to adapt an existing
solution to the application.
Both the mechanical and electrical antenna adaptation is one of the key issues
in the design of the GSM terminal.
4 Consumption measurement procedure
This chapter describes the consumption measurement procedure used to
obtain the Wireless Microprocessor consumption specification
WMP100/OASS1.0 consumption specification values are measured for all
operating modes available on this product. See the appendix of document [3]
AT Command Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5.
Consumption results are highly dependent on the hardware configuration used
during measurement, this chapter describes the hardware configuration
settings to be used to obtain optimum consumption measurements.
4.1 Hardware configuration
The hardware configuration includes both the measurement equipment and
the Wireless Microprocessor with its motherboard.
4.1.1 Equipment
Four devices are used to perform consumption measurement.
¾ A communication tester
¾ A current measuring power supply
confidential © Page : 127 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
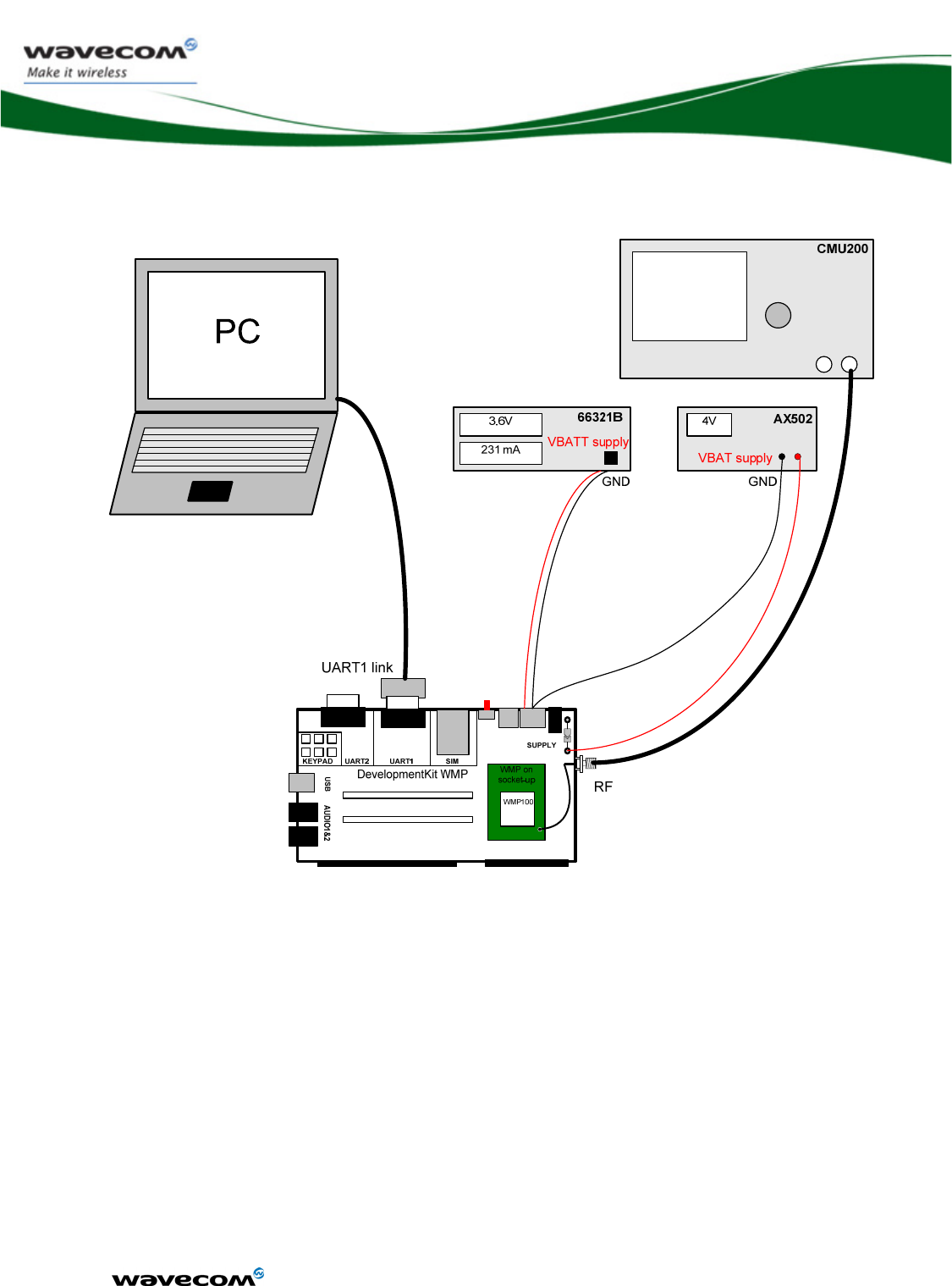
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
¾ A standalone power supply
¾ A computer, to control the Wireless Microprocessor and save
measurement data.
Figure 65: Typical hardware configuration
confidential © Page : 128 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 129 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
The communication tester is a CMU 200 from Rhode & Schwartz. This tester
offers all GSM/GPRS network configurations required and allows a wide range
of network configurations to be set.
The AX502 standalone power supply is used to supply all motherboard
components except the Wireless Microprocessor. The goal is to separate
motherboard consumption from Wireless Microprocessor consumption -which
is measured by the other power supply, the 66321B “current measuring power
supply”.
The “current measuring power supply” is also connected and controlled by the
computer (GPIB control not shown in the previous figure).
A SIM must be inserted in the Development Kit Wireless Microprocessor
during all consumption measurements.
Equipment reference list:
Device Manufacturer Reference
Communication
Tester
Rhode &
Schwartz
CMU 200 Quad Band
GSM/DCS/GPRS
Current
measuring
power supply
Agilent 66321B Used for VBATT (for WMP
alone)
Stand alone
power supply
Metrix AX502 Used for VBAT (for boards
peripherals)
4.1.2 Wireless Microprocessor motherboard
The Wireless Microprocessor board used is the Development Kit Wireless
Microprocessor V2. This board can be used to perform consumption
measurement with several settings. For a description of the settings, see
document [2] WMP100 Development Kit User Guide.
The Wireless Microprocessor is only powered by VBATT. The Development Kit
board is powered by the standalone power supply at VBAT. It is for this reason
that the link between VBATT and VBAT (J605) must be opened (by removing
the solder at the top of board in the SUPPLY area).
¾ VBATT powered by the current measuring power supply (66321B).
¾ VBAT powered by the standalone power supply (AX502).
The R600, resistor, and D603,D604 diodes (around the BAT-TEMP connector)
must be removed.
The UART2 link is not used, therefore J201, J202, J203, J204 must be opened
(by removing the solder).
The “FLASH-LED” must be not used, so J602 must be opened (by removing
the solder).

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
The USB link is not used, therefore J301, J302, J303, J304, J305 must be
opened (by removing the solder).
Around “CONFIG” area, the switch BOOT must be to OFF position.
The goal of the settings is to eliminate all bias current from VBATT and to
supply the entire board (except the Wireless Microprocessor) via VBAT only.
The standalone power supply may be set to 4 Volts.
4.1.3 SIM cards used
Consumption measurement may be performed with 3-Volt or 1.8-Volt SIM
cards. However, all specified consumption values are for a 3-Volt SIM card.
CAUTION: The SIM card is supplied by the Wireless Microprocessor,
consumption measurement results may vary depending of the SIM card used.
4.2 Software configurations
Software configuration for the equipment and Wireless Microprocessor
settings.
4.2.1 Wireless Microprocessor configuration
Wireless Microprocessor software configuration is simply performed by
selecting the operating mode to be used to perform the measurement.
A description of the operating modes and the procedure used to change
operating mode are given in the appendix of document [3] AT Command
Interface Guide for Open AT® Firmware v6.5.
An overview of the WMP100/OASS1.0 operating modes is given below:
¾ Alarm Mode
¾ Fast Idle Mode
¾ Slow Idle Mode
¾ Fast Standby Mode
¾ Slow Standby Mode
¾ Connected Mode
¾ Transfer Mode class 8 (4Rx/1Tx) (in GPRS mode)
¾ Transfer Mode class 10 (3Rx/2Tx) (in GPRS mode)
confidential © Page : 130 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 131 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
4.2.2 Equipment configuration
The communication tester is set according to Wireless Microprocessor
operating mode.
Paging during idle modes, Tx burst power, RF band and GSM/DCS/GPRS may
be selected on the communication tester.
Network analyzer configuration according to operating mode:
Operating mode Communication tester configuration
Alarm Mode N/A
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s)
Fast Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s)
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s)
Slow Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s)
Fast Standby Mode N/A
Slow Standby Mode N/A
PCL5 (TX power 33dBm)
850/900 MHz
PCL19 (TX power 5dBm)
PCL0 (TX power 30dBm)
Connected Mode
1800/1900 MHz
PCL15 (TX power 0dBm)
Gam.3 (TX power 33dBm)
850/900 MHz
Gam.17 (TX power 5dBm)
Gam.3 (TX power 30dBm)
Transfer Mode class 8
(4Rx/1Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
Gam.18 (TX power 0dBm)
Gam.3 (TX power 33dBm)
850/900 MHz
Gam.17 (TX power 5dBm)
Gam.3 (TX power 30dBm)
1800/1900 MHz
Gam.18 (TX power 0dBm)
Gam.5 (TX power 26dBm)
GPRS
Transfer Mode class 10
(3Rx/2Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
Gam.18 (TX power 0dBm)
The standalone power supply may be set from 3.2V to 4.5V.
The power supply (VBATT) used for measurement may be set from 3.2V to
4.8V according Wireless Microprocessor VBATT specifications.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 132 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
4.3 Template
This template may be used for consumption measurement, all modes and
configurations are available.
Three VBATT voltages are measured, 3.2V, 3.6V and 4.8V and the
minimum/maximum RF transmission power configurations are set and
measured.
Power consumption
Operating mode Parameters
IMIN
average
VBATT=4,8V
INOM
average
VBATT=3,6V
IMAX
average
VBATT=3,2V
IMAX
peak unit
Alarm Mode µA
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s) mA
Fast Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s) mA
Paging 9 (Rx burst occurrence ~2s) mA
Slow Idle Mode
Paging 2 (Rx burst occurrence ~0,5s) mA
Fast Standby Mode mA
Slow Standby Mode mA
PCL5 (TX power 33dBm) mA
850/900 MHz
PCL19 (TX power 5dBm) mA
PCL0 (TX power 30dBm) mA
Connected Mode
1800/1900 MHz
PCL15 (TX power 0dBm) mA
Gam.3 (TX power
33dBm) mA
850/900 MHz
Gam.17 (TX power
5dBm) mA
Gam.3 (TX power
30dBm) mA
Transfer
Mode
class 8
(4Rx/1Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
Gam.18 (TX power
0dBm) mA
Gam.3 (TX power
33dBm) mA
850/900 MHz
Gam.17 (TX power
5dBm) mA
Gam.3 (TX power
30dBm) mA
Gam.18 (TX power
0dBm) mA
GPRS
Transfer
Mode
class 10
(3Rx/2Tx)
1800/1900 MHz
Gam.18 (TX power
0dBm) mA
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 133 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
5 Technical specifications
5.1 Ball Grid Array pin out
Signal Name Description I/O Voltage
Domain MUX MUX MUX Ball number
VBATT-RF Power Supply I VBATT VBATT-RF _ _ A12, A13, A14, B12,
B13, B14
VBATT-BB Power Supply I VBATT VBATT-BB _ _ AC1, AC2, AD1, AD2
RF-OUT Radio antenna
connection I/O Analog RF RF-OUT _ _ B23
VCC_2V8 Power Supply O VCC_2V8 VCC_2V8 _ _ R1
VCC_1V8 Power Supply O VCC_1V8 VCC_1V8 _ _ AD5
BAT-RTC Power Supply I/O BAT-RTC BAT-RTC _ _ U6
SIM-CLK SIM clock O 1V8 / 2V9 SIM-CLK _ _ Y2
~SIM-RST SIM reset O 1V8 / 2V9 ~SIM-RST _ _ Y1
SIM-IO SIM data I/O 1V8 / 2V9 SIM-IO _ _ W1
SIM-VCC SIM power supply O 1V8 / 2V9 SIM-VCC _ _ W2
SIMPRES /
INT8 /
GPIO18
SIM presence
detection I/O VCC_1V8 SIMPRES INT8 GPIO18 Y3
MIC1P Microphone input
1 positive I Analog MIC1P _ _ AC10
MIC1N Microphone input
1 negative I Analog MIC1N _ _ AB10
MIC2P Microphone input
2 positive I Analog MIC2P _ _ AC9
MIC2N Microphone input
2 negative I Analog MIC2N _ _ AB9
SPK1P Speaker output 1
positive O Analog SPK1P _ _ AC8
SPK1N Speaker output 1
negative O Analog SPK1N _ _ AB8
SPK2P Speaker output 2
positive O Analog SPK2P _ _ AC7
SPK2N Speaker output 2
negative O Analog SPK2N _ _ AB7
CHG-IN Charger input
voltage I Analog CHG-IN _ _ V2, V3
CHG-GATE Charger transistor
control output O Analog
current CHG-GATE _ _ V4
AUX-ADC2 /
BAT-TEMP
Analog to Digital
converter 3 I Analog
AUX-ADC2 /
BAT-TEMP _ _ N18
AUX-ADC1 Analog to Digital
converter 2 I Analog AUX-ADC1 _ _ M17
AUX-ADC0 Analog to Digital
converter 1 I Analog AUX-ADC0 _ _ N17
AUX-DAC0 Digital to Analog
converter O Analog AUX-DAC0 _ _ V14
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 134 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Name Description I/O Voltage
Domain MUX MUX MUX Ball number
XIN_32K Oscillator crystal
input I Analog XIN_32K _ _ AC24
XOUT_32K Oscillator crystal
output O Analog XOUT_32K _ _ AB24
~RESET Input Reset signal I/O VCC_1V8 ~RESET _ _ V6
~EXT-RESET Output External
reset O VCC_1V8 ~EXT-
RESET _ _ AB14
BOOT BOOT control I VCC_1V8 BOOT _ _ W18
Flash LED WMP100 Status
LED O
Open Drain
VBATT
Flash LED _ _ U3
BUZZ-OUT Buzzer output
control O
Open Drain
VBATT
BUZZ-OUT _ _ U4
ROW0 /
GPIO9
Row Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 ROW0 GPIO9 _ AC23
ROW1 /
GPIO10
Row Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 ROW1 GPIO10 _ AD22
ROW2 /
GPIO11
Row Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 ROW2 GPIO11 _ AD21
ROW3 /
GPIO12
Row Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 ROW3 GPIO12 _ AC22
ROW4 /
GPIO13
Row Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 ROW4 GPIO13 _ AD23
COL0 / GPIO4 Column Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 COL0 GPIO4 _ AD19
COL1 / GPIO5 Column Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 COL1 GPIO5 _ AD20
COL2 / GPIO6 Column Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 COL2 GPIO6 _ AC20
COL3 / GPIO7 Column Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 COL3 GPIO7 _ AC19
COL4 / GPIO8 Column Scan of
keypad I/O VCC_1V8 COL4 GPIO8 _ AC21
PCM-SYNC PCM frame
synchronization O VCC_1V8 PCM-SYNC _ _ Y21
PCM-CLK PCM clock O VCC_1V8 PCM-CLK _ _ W21
PCM-OUT PCM data output O VCC_1V8 PCM-OUT _ _ W22
PCM-IN PCM data input I VCC_1V8 PCM-IN _ _ AA22
CT103 / TXD1
/ GPIO36
Transmit serial
data I/O VCC_2V8 CT103 /
TXD1 GPIO36 _ R17
CT104 /
RXD1 /
GPIO37
Receive serial data I/O VCC_2V8 CT104 /
RXD1 GPIO37 _ T13
~CT105 /
RTS1 /
GPIO38
Ready To Send I/O VCC_2V8 ~CT105 /
RTS1 GPIO38 _ Y18
~CT106 /
CTS1 /
GPIO39
Clear To Send I/O VCC_2V8 ~CT106 /
CTS1 GPIO39 _ N15
~CT107 /
DSR1 Data Set Ready I/O VCC_2V8 ~CT107 /
DSR1 GPIO40 _ T12
~CT108-2 /
DTR1 /
GPIO41
Data Serial Ready I/O VCC_2V8 ~CT108-2 /
DTR1 GPIO41 _ M16
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 135 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Name Description I/O Voltage
Domain MUX MUX MUX Ball number
~CT109 /
DCD1 /
GPIO43
Data Carrier
Detect I/O VCC_2V8 ~CT109 /
DCD1 GPIO43 _ AB16
~CT125 / RI1
/ GPIO42 Ring Indicator I/O VCC_2V8 ~CT125 /
RI1 GPIO42 _ AA18
CT103 / TXD2
/ INT6 /
GPIO14
Transmit serial
data I/O VCC_1V8 CT103 /
TXD2 INT6 GPIO14 T16
CT104 /
RXD2 /
GPIO15
Receive serial data I/O VCC_1V8 CT104 /
RXD2 GPIO15 _ U17
~CT105 /
RTS2 / INT7 /
GPIO17
Ready To Send I/O VCC_1V8 ~CT105 /
RTS2 INT7 GPIO17 V13
~CT106 /
CTS2 /
GPIO16
Clear To Send I/O VCC_1V8 ~CT106 /
CTS2 GPIO16 _ W17
SCL / GPIO26 I²C serial clock I/O Open drain SCL GPIO26 _ AA15
SDA / GPIO27 I²C serial data I/O Open Drain SDA GPIO27 _ AA16
SPI1-CLK /
GPIO28 SPI serial clock I/O VCC_2V8 SPI1-CLK GPIO28 _ U15
SPI1-IO /
GPIO29
SPI serial data
input and output I/O VCC_2V8 SPI1-IO GPIO29 _ V12
SPI1-I /
GPIO30
SPI serial data
input only input I/O VCC_2V8 SPI1-I GPIO30 _ R13
SPI1-CS /
INT5 /
GPIO31
SPI chip select I/O VCC_2V8 SPI1-CS INT5 GPIO31 M14
SPI2-CLK /
GPIO32 SPI serial clock I/O VCC_2V8 SPI2-CLK GPIO32 _ R15
SPI2-IO /
GPIO33
SPI serial data
input and output I/O VCC_2V8 SPI2-IO GPIO33 _ M13
SPI2-I /
GPIO34
SPI serial data
input only input I/O VCC_2V8 SPI2-I GPIO34 _ U16
SPI2-CS /
INT4 /
GPIO35
SPI chip select I/O VCC_2V8 SPI2-CS INT4 GPIO35 T18
INT3 /
GPIO46 SPI chip select I/O VCC_2V8 INT3 GPIO46 _ V18
USB-DP Universal Serial
Bus Data positive I/O VPAD-USB USB-DP _ _ W19
USB-DM Universal Serial
Bus Data negative I/O VPAD-USB USB-DM _ _ AA20
USB-CN Universal Serial
Bus Connect O VPAD-USB USB-CN _ _ Y20
USB-DET Universal Serial
Bus interruption I VCC_1V8 USB-DET _ _ R14
GPIO44 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO44 _ _ AB13
GPIO19 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO19 _ _ AA17
GPIO21 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO21 _ _ AA13
GPIO20 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO20 _ _ Y13
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 136 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Name Description I/O Voltage
Domain MUX MUX MUX Ball number
GPIO47 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_1V8 GPIO47 _ _ Y15
GPIO48 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_1V8 GPIO48 _ _ Y16
GPIO0 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_1V8 GPIO0 _ _ W15
GPIO24 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO24 _ _ N16
GPIO22 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO22 _ _ M15
GPIO23 General Purpose
Input Output I/O VCC_2V8 GPIO23 _ _ V17
INT0 / A26 /
GPIO3 Interruption input I/O VCC_1V8 INT0 A26 GPIO3 V16
INT1 /
GPIO25 Interruption input I/O VCC_2V8 INT1 GPIO25 _ Y19
INT2 /
GPIO45 Interruption input I/O VCC_1V8 INT2 GPIO45 _ Y17
A0 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A0 _ _ T19
A1 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A1 _ _ U18
A2 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A2 _ _ U24
A3 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A3 _ _ P24
A4 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A4 _ _ N24
A5 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A5 _ _ M21
A6 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A6 _ _ M24
A7 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A7 _ _ N23
A8 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A8 _ _ R24
A9 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A9 _ _ R22
A10 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A10 _ _ P22
A11 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A11 _ _ T22
A12 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A12 _ _ R23
A13 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A13 _ _ M22
A14 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A14 _ _ P21
A15 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A15 _ _ R21
A16 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A16 _ _ P23
A17 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A17 _ _ T21
A18 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A18 _ _ T24
A19 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A19 _ _ M23
A20 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A20 _ _ N21
A21 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A21 _ _ N22
A22 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A22 _ _ M20
A23 Address bus O VCC_1V8 A23 _ _ N19
A24 / GPIO2 Address bus I/O VCC_1V8 A24 GPIO2 _ U22
D0 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D0 _ _ W24
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 137 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Name Description I/O Voltage
Domain MUX MUX MUX Ball number
D1 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D1 _ _ W23
D2 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D2 _ _ AA24
D3 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D3 _ _ Y23
D4 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D4 _ _ U21
D5 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D5 _ _ Y22
D6 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D6 _ _ Y24
D7 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D7 _ _ V21
D8 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D8 _ _ V20
D9 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D9 _ _ U20
D10 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D10 _ _ V24
D11 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D11 _ _ V22
D12 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D12 _ _ V23
D13 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D13 _ _ AA23
D14 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D14 _ _ U23
D15 Data bus I/O VCC_1V8 D15 _ _ T23
~WAIT Burst Wait signal I VCC_1V8 ~WAIT _ _ R19
~CS0 Chip select Flash O VCC_1V8 ~CS0 _ _ P19
~CS1 Chip select RAM O VCC_1V8 ~CS1 _ _ R20
~CS2 / A25 /
GPIO1 Chip select I/O VCC_1V8 ~CS2 A25 GPIO1 R18
~CS3 Chip select O VCC_1V8 ~CS3 _ _ T17
CLKBURST Burst clock O VCC_1V8 CLKBURST _ _ M19
~ADV Burst address
valid signal O VCC_1V8 ~ADV _ _ U19
~WE-E Write enable O VCC_1V8 ~WE-E _ _ P20
~OE-R/W Read enable O VCC_1V8 ~OE-R/W _ _ N20
BE1 2nd byte enable O VCC_1V8 BE1 _ _ P18
BE3 4th byte enable O VCC_1V8 BE3 _ _ T20

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 138 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Signal Name Description I/O Voltage
Domain MUX MUX MUX Ball number
GND Ground
A1, A10, A11, A15, A16, A17, A18, A19, A2, A20, A21, A22, A23, A24, A3,
A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, B1, B10, B11, B15, B16, B17, B18, B19, B20, B21,
B22, B24, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, C1, C10, C11, C12, C13, C14, C15,
C16, C17, C18, C19, C20, C21, C22, C23, C24, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9,
D1, D10, D11, D12, D13, D14, D15, D16, D17, D18, D19, D2, D20, D21,
D22, D23, D24, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, E1, E10, E11, E12, E13, E14,
E15, E16, E17, E18, E19, E2, E20, E21, E22, E23, E24, E3, E4, E5, E6, E7, E8,
E9, F1, F10, F11, F12, F13, F14, F15, F16, F17, F18, F19, F2, F20, F21, F22,
F23, F24, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8, F9, G1, G10, G11, G12, G13, G14, G15,
G16, G17, G18, G19, G2, G20, G21, G22, G23, G24, G3, G4, G5, G6, G7, G8,
G9, H1, H10, H11, H12, H13, H14, H15, H16, H17, H18, H19, H2, H20, H21,
H22, H23, H24, H3, H4, H5, H6, H7, H8, H9, J1, J10, J11, J12, J13, J14,
J15, J16, J17, J18, J19, J2, J20, J21, J22, J23, J24, J3, J4, J5, J6, J7, J8,
J9, K1, K10, K11, K12, K13, K14, K15, K16, K17, K18, K19, K2, K20, K21,
K22, K23, K24, K3, K4, K5, K6, K7, K8, K9, L1, L10, L11, L12, L13, L14, L15,
L16, L17, L18, L19, L2, L20, L21, L22, L23, L24, L3, L4, L5, L6, L7, L8, L9,
M1, M10, M11, M12, M18, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, N1, N10,
N2, N3, N7, N8, N9, P1, P10, P13, P14, P15, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9,
R10, R11, R12, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, T1, T10, T11, T14, T15, T2,
T8, T9, U1, U10, U11, U12, U13, U14, U2, U7, U8, U9, V1, V10, V11, V15,
V7, V8, V9, W10, W11, W12, W13, W14, W16, W3, W6, W7, W8, W9, Y10,
Y12, Y14, Y7, AA1, AA10, AA11, AA12, AA14, AA19, AA2, AA21, AA3, AA4,
AA5, AA6, AA7, AA8, AA9, AB1, AB12, AB15, AB17, AB18, AB2, AB21,
AB22, AB23, AB3, AB4, AB5, AB6, AC12, AC13, AC14, AC15, AC16, AC17,
AC18, AC3, AC4, AC5, AC6, AD10, AD11, AD12, AD13, AD14, AD15, AD16,
AD17, AD18, AD24, AD3, AD4, AD6, AD7, AD8, AD9
RESERVED
Do not connect.
(Left opened)
B2, C2, N11, N12, N13, N14, N4, N5, N6, P11, P12, P16, P17, R16, T3, T4,
T5, T6, T7, V19, V5, W20, W4, W5, Y11, Y4, Y5, Y6, Y8, Y9, AB11, AB20,
AC11
* The I/O direction information is concerning only the nominal signal. When the signal is
configured in GPIO, it can always be an Input or an Output.
** For more information about the multiplexing of those signals, see “General purpose input
/output” chapter 3.11

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 139 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
5.2 Environmental Specifications
Wavecom specify following temperature range of WMP100 product
The WMP100 is compliant with following operating class
Conditions Temperature range
Operating / Class A -20 °C to +55°C
Operating / Storage / Class B -40 °C to +85°C
Function Status Classification:
Class A:
The WMP100 shall have full function during and after an external influence.
The GSM performance shall meet the minimum ETSI requirements.
Class B:
Any functions can be out of specified tolerances. All the functions will be going
back to normal tolerances automatically after that the external influence has
been removed. Performance is allowed to go outside of the minimum ETSI
requirements, but it must be possible to connect a call and send an SMS.
Q2686 ENVIRONNEMENTAL CLASSES
TYPE OF TEST STANDARDS STORAGE TRANSPORTATION OPERATING (PORT USE)
Class 1.2 Class 2.3 Class 7.3
Cold IEC 68-2.1 -25° C 72 h -40° C 72 h -20° C (GSM900) 16 h
Ab test -10° C (GSM1800/1900) 16h
Dry heat IEC 68-2.2 +70° C 72 h +70° C 72 h +55° C 16 h
Bb test
Change of temperature IEC 68-2.14 -40° / +30° C 5 cycles -20° / +30° C (GSM900) 3 cycles
Na/Nb test t1 = 3 h -10° / +30° C (GSM1800/1900):
3 cycles t1 = 3 h
Damp heat IEC 68-2.30 +30° C 2 cycles +40° C 2 cycles +40° C 2 cycles
cyclic Db test 90% - 100% RH 90% - 100% RH 90% - 100% RH
variant 1 variant 1 variant 1
Damp heat IEC 68-2.56 +30° C 4 days +40° C 4 days +40° C 4 days
Cb test
Sinusoidal vibration IEC 68-2.6 5 - 62 Hz : 5 mm / s
Fc test 62 - 200Hz : 2 m / s2
3 x 5 sweep cycles
5 - 20 Hz : 0.96 m2 / s3 10 -12 Hz : 0.96 m2 / s3
Random vibration IEC 68-3.36 20 - 500Hz : - 3 dB / oct 12 - 150Hz : - 3 dB / oct
wide band Fdb test 3 x 10 min 3 x 30 min
Figure 66 : Environmental classes

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 140 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
5.3 MSL level
The WMP100 is MSL 3 and 2 reflows are allowed in customer side including
one for rework of the component.
If the product is double side, the WMP100 should be assembled on the side
that will see only one reflow.
5.4 Mechanical specifications
5.4.1 Physical characteristics
The WMP100 has a complete self-contained shield.
• Overall dimensions :25 x 25 x 3.65 mm
• Weight: 4.25 g
5.4.2 Mechanical drawings
The next page gives the mechanical specifications of WMP100.
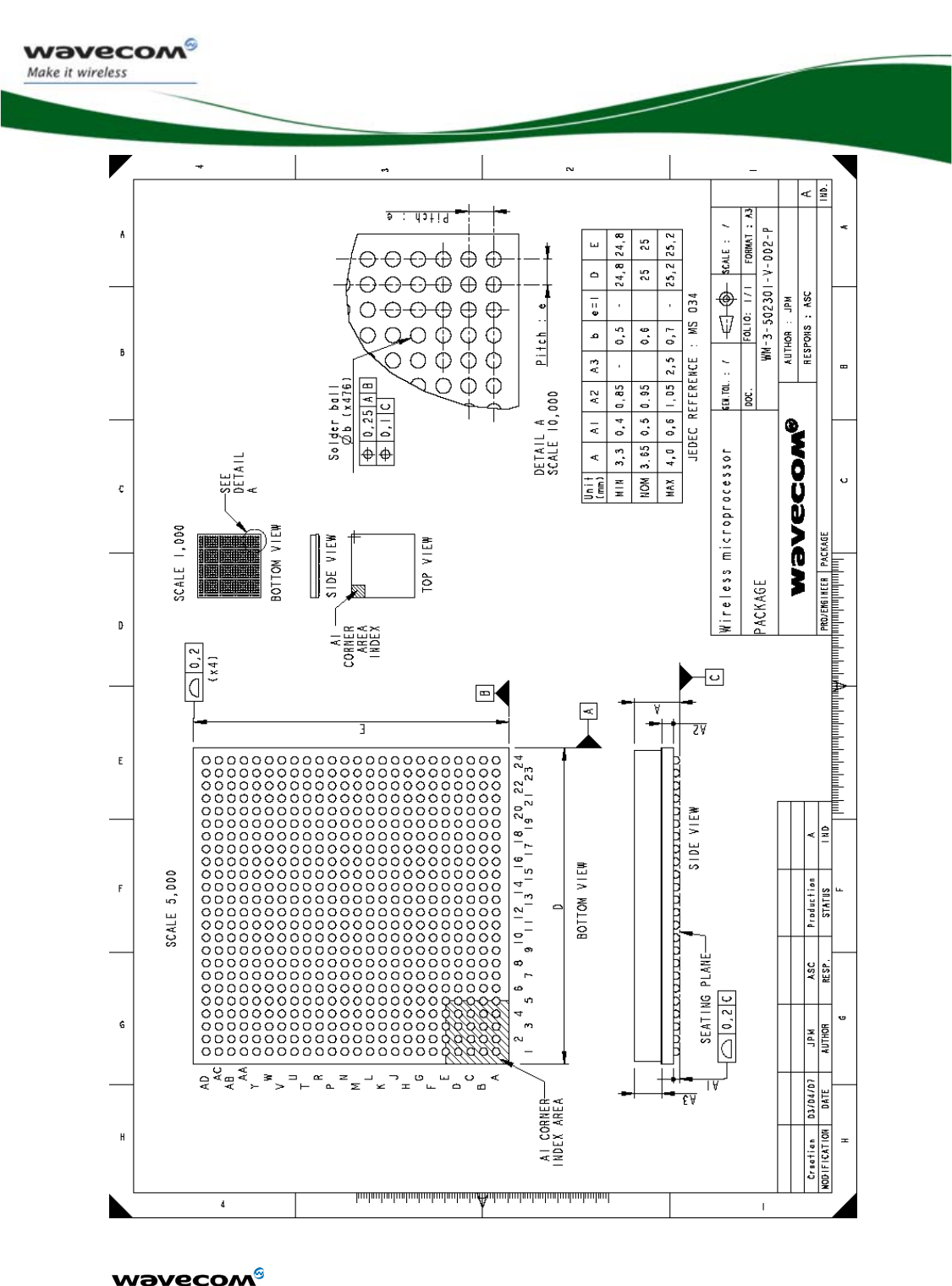
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 141 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Figure 67 : Mechanical drawing
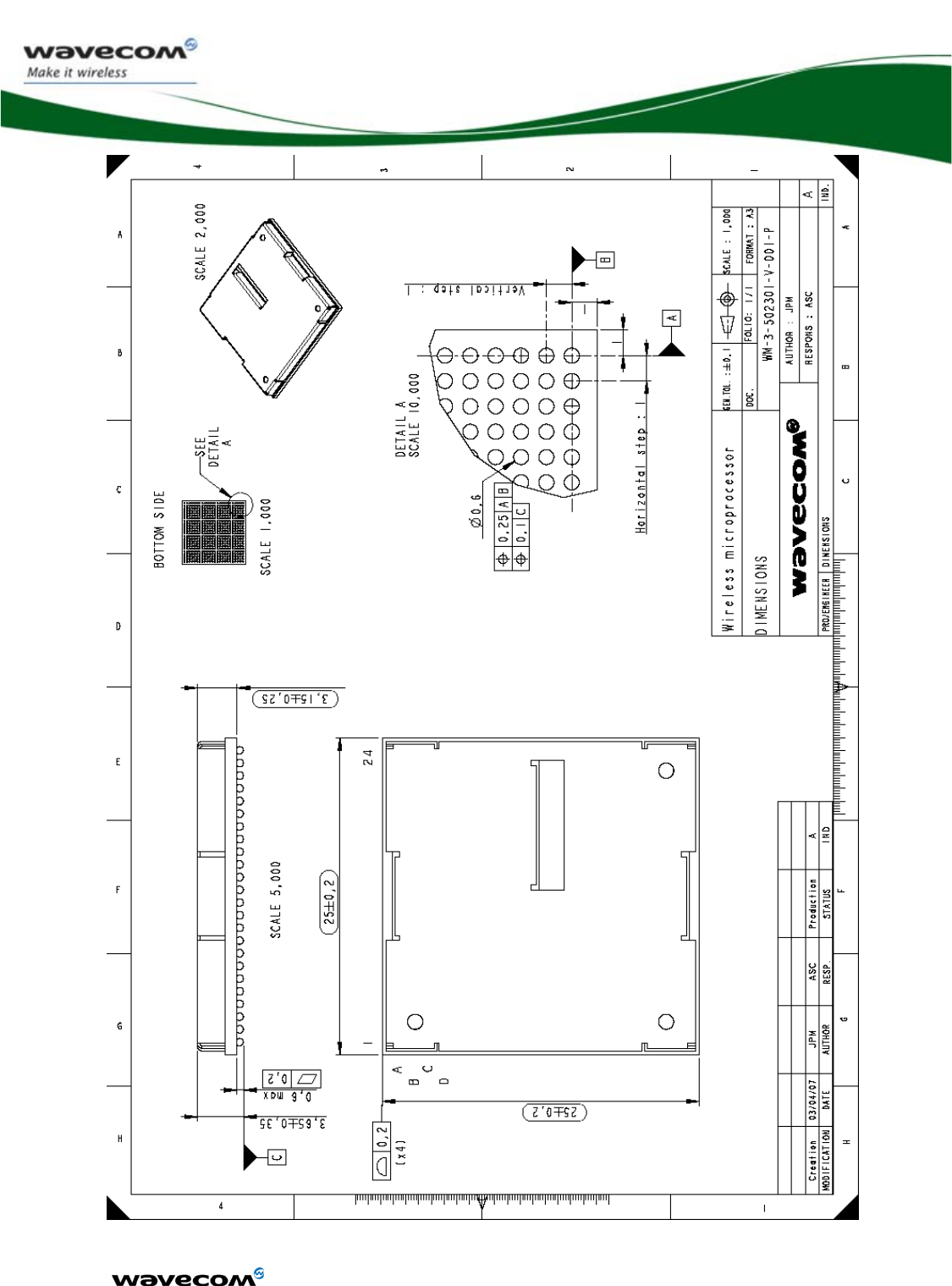
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 142 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Figure 68 : Mechanical drawing

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
5.4.3 Mechanical constraints
Wavecom recommend the customer to check on their own application if the
WMP100 can withstand their mechanical environment.
5.5 PCB specifications
Due to the density of connections, the PCB stack should be the following:
4 layers (track / distance 100 μm / 100 μm, with though-holes vias Diam 0.25,
pad 0.5 mm), but 6 layers may be necessary according to the functionality
needed (track / distance 150 μm / 150 μm may be possible).
6 Peripheral devices references
6.1 SIM Card Reader
• ITT CANNON CCM03 series (see http://www.ittcannon.com )
• AMPHENOL C707 series (see http://www.amphenol.com )
• JAE (see http://www.jae.com )
Drawer type:
• MOLEX 99228-0002 (connector) / MOLEX 91236-0002 (holder) (see
http://www.molex.com )
6.2 Microphone
Possible suppliers:
• HOSIDEN
• PANASONIC
• PEIKER
6.3 Speaker
Possible suppliers:
• SANYO
• HOSIDEN
• PRIMO
• PHILIPS
confidential © Page : 143 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
6.4 Antenna Cable
The following cable reference has been qualified for being mounted on
WMP100:
• RG178
• TBD
6.5 GSM antenna
GSM antennas and support for antenna adaptation can be obtained from
manufacturers such as:
• ALLGON (http://www.allgon.com )
• IRSCHMANN (http://www.hirschmann.com/ )
confidential © Page : 144 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 145 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
7 Noises and design
7.1 EMC recommendations
The EMC tests have to be performed as soon as possible on the application to
detect any possible problem.
When designing, special attention should be paid to:
• Possible spurious emission radiated by the application to the RF receiver
in the receiver band
• ESD protection is mandatory for all peripherals accessible from outside
(SIM, serial link, etc.)
• EMC protection on audio input/output (filters against 900MHz
emissions)
• Biasing of the microphone inputs
• Length of the SIM interface lines (preferably <10cm)
• Ground plane: WAVECOM recommends having a common ground plane
for analog / digital / RF grounds.
• Metallic case or plastic casing with conductive paint are recommended
Note:
The WMP100 does not include any protection against overvoltage.
7.2 Power Supply
The power supply is one of the key issues in the design of a GSM terminal.
A weak power supply design could affect in particular:
• EMC performances.
• the emissions spectrum
• the phase error and frequency error
WARNING:
Careful attention should be paid to:
• Quality of the power supply: low ripple, PFM or PSM systems should be
avoided (PWM converter preferred).
• Capacity to deliver high current peaks in a short time (pulsed radio
emission).
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 146 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
8 Appendix
8.1 Standards and Recommendations
GSM ETSI, 3GPP, GCF and NAPRD03 recommendations for Phase II.
Specification Reference Title
3GPP TS 45.005 v5.5.0
(2002-08) Release 5
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE. Radio
Access Network; Radio transmission and reception
GSM 02.07 V8.0.0 (1999-
07)
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
Mobile Stations (MS) features (GSM 02.07 version
8.0.0 Release 1999)
GSM 02.60 V8.1.0 (1999-
07)
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service
description, Stage 1 (GSM 02.60 version 8.1.0 Release
1999)
GSM 03.60 V7.9.0 (2002-
09)
Technical Specification Group Services and System
Aspects;
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); Service
description; Stage 2 (Release 1998)
3GPP TS 43.064 V5.0.0
(2002-04)
Technical Specification Group GERAN; Digital cellular
telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General Packet
Radio Service (GPRS); Overall description of the GPRS
radio interface; Stage 2 (Release 5)
3GPP TS 03.22 V8.7.0
(2002-08)
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE. Radio
Access Network; Functions related to Mobile Station
(MS) in idle mode and group receive mode; (Release
1999)
3GPP TS 03.40 V7.5.0
(2001-12)
Technical Specification Group Terminals;
Technical realization of the Short Message Service
(SMS)
(Release 1998)
3GPP TS 03.41 V7.4.0
(2000-09)
Technical Specification Group Terminals; Technical
realization of Cell Broadcast Service (CBS) (Release
1998)
ETSI EN 300 903 V8.1.1
(2000-11)
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
Transmission planning aspects of the speech service in
the GSM
Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) system (GSM
03.50 version 8.1.1 Release 1999)
WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 147 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Specification Reference Title
3GPP TS 04.06 V8.2.1
(2002-05)
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE Radio Access
Network; Mobile Station - Base Station System (MS -
BSS) interface; Data Link (DL) layer specification
(Release 1999)
3GPP TS 04.08 V7.18.0
(2002-09)
Technical Specification Group Core Network;
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
Mobile radio interface layer 3 specification (Release
1998)
3GPP TS 04.10 V7.1.0
(2001-12)
Technical Specification Group Core Networks;
Mobile radio interface layer 3 Supplementary services
specification; General aspects (Release 1998)
3GPP TS 04.11 V7.1.0
(2000-09)
Technical Specification Group Core Network; Digital
cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
Point-to-Point (PP) Short Message Service (SMS)
support on mobile radio interface
(Release 1998)
3GPP TS 45.005 v5.5.0
(2002-08)
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE. Radio
Access Network; Radio transmission and reception
(Release 5)
3GPP TS 45.008 V5.8.0
(2002-08)
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE
Radio Access Network; Radio subsystem link control
(Release 5)
3GPP TS 45.010 V5.1.0
(2002-08)
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE
Radio Access Network; Radio subsystem
synchronization (Release 5)
3GPP TS 46.010 V5.0.0
(2002-06)
Technical Specification Group Services and System
Aspects;
Full rate speech; Transcoding (Release 5)
3GPP TS 46.011 V5.0.0
(2002-06)
Technical Specification Group Services and System
Aspects;
Full rate speech; Substitution and muting of lost
frames for
full rate speech channels (Release 5)
3GPP TS 46.012 V5.0.0
(2002-06)
Technical Specification Group
Services and System
Aspects;
Full rate speech; Comfort noise aspect for full rate
speech traffic channels (Release 5)

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 148 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
Specification Reference Title
3GPP TS 46.031 V5.0.0
(2002-06)
Technical Specification Group Services and System
Aspects;
Full rate speech; Discontinuous Transmission (DTX) for
full rate speech traffic channels (Release 5)
3GPP TS 46.032 V5.0.0
(2002-06)
Technical Specification Group Services and System
Aspects;
Full rate speech; Voice Activity Detector (VAD) for full
rate speech traffic channels (Release 5)
TS 100 913V8.0.0 (1999-
08)
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
General on Terminal Adaptation Functions (TAF) for
Mobile Stations (MS) (GSM 07.01 version 8.0.0
Release 1999)
GSM 09.07 V8.0.0 (1999-
08)
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+);
General requirements on interworking between the
Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) and the
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) or Public
Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) (GSM 09.07
version 8.0.0 Release 1999)
3GPP TS 51.010-1 v5.0.0
(2002-09)
Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE ; Radio
Access Network ;Digital cellular telecommunications
system (Phase 2+);Mobile Station (MS) conformance
specification; Part 1: Conformance specification
(Release 5)
3GPP TS 51.011 V5.0.0
(2001-12)
Technical Specification Group Terminals; Specification
of the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment
(SIM - ME) interface (Release 5)
ETS 300 641 (1998-03) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2);
Specification of the 3 Volt Subscriber Identity Module -
Mobile Equipment (SIM-ME) interface (GSM 11.12
version 4.3.1)
GCF-CC V3.7.1 (2002-08) Global Certification Forum – Certification criteria
NAPRD03 V2.6.0 (2002-06)
North America Permanent Reference Document
for
PTCRB tests

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 149 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
The Wireless Microprocessor WMP100 connected to a development kit board
application is certified to be in accordance with the following Rules and
Regulations of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
Power listed on the Gant is conducted for Part 22 and conducted for Part 24.
This device contains EGSM/GPRS Class 10 functions in the 900 and 1800MHz
Band, which are not operational in U.S. Territories.
This device can be used only for mobile and fixed applications. The antenna(s)
used for this transmitter must be installed at a distance of minimum 20 cm
from all persons and must not be co-located or operated with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Users and installers must be provided with antenna installation instructions
and transmitter operating conditions for satisfying RF exposure compliance.
Antennas used for this OEM module must not exceed 0.9 dBi gain for GSM
850 MHz and 7.1 dBi for GSM 1900 MHz for fixed operating configurations.
For mobile operations the gain must not exceed 0.9 dBi for GSM 850 MHz and
3.1 dBi for GSM 1900 MHz. This device is approved as a module to be
installed in other devices.
Installed in portable devices, the RF exposure condition requires a separate
mandatory equipment authorization for the final device.
The license module will have a FCC ID label on the module itself. The FCC ID
label must be visible through a window or it must be visible when an access
panel, door or cover is easily removed.
If not, a second label must be placed on the outside of the device that contains
the following text: FCC ID: O9EWMP100
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
o This device may not cause harmful interference.
o This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 150 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
8.2 Safety recommendations (for information only)
IMPORTANT
FOR THE EFFICIENT AND SAFE OPERATION OF YOUR GSM APPLICATION
BASED ON WMP100
PLEASE READ THIS INFORMATION CAREFULLY
8.2.1 RF safety
8.2.1.1 General
Your GSM terminal is based on the GSM standard for cellular technology. The
GSM standard is spread all over the world. It covers Europe, Asia and some
parts of America and Africa. This is the most used telecommunication
standard.
Your GSM terminal is actually a low power radio transmitter and receiver. It
sends out and receives radio frequency energy. When you use your GSM
application, the cellular system which handles your calls controls both the
radio frequency and the power level of your cellular modem.
8.2.1.2 Exposure to RF energy
There has been some public concern about possible health effects of using
GSM terminals. Although research on health effects from RF energy has
focused on the current RF technology for many years, scientists have begun
research regarding newer radio technologies, such as GSM. After existing
research had been reviewed, and after compliance to all applicable safety
standards had been tested, it has been concluded that the product was fitted
for use.
If you are concerned about exposure to RF energy there are things you can do
to minimize exposure. Obviously, limiting the duration of your calls will reduce
your exposure to RF energy. In addition, you can reduce RF exposure by
operating your cellular terminal efficiently by following the below guidelines.
8.2.1.3 Efficient terminal operation
For your GSM terminal to operate at the lowest power level, consistent with
satisfactory call quality:
If your terminal has an extendible antenna, extend it fully. Some models allow
you to place a call with the antenna retracted. However your GSM terminal
operates more efficiently with the antenna fully extended.
Do not hold the antenna when the terminal is « IN USE ». Holding the antenna
affects call quality and may cause the modem to operate at a higher power
level than needed.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
confidential © Page : 151 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.
8.2.1.4 Antenna care and replacement
Do not use the GSM terminal with a damaged antenna. If a damaged antenna
comes into contact with the skin, a minor burn may result. Replace a damaged
antenna immediately. Consult your manual to see if you may change the
antenna yourself. If so, use only a manufacturer-approved antenna. Otherwise,
have your antenna repaired by a qualified technician.
Use only the supplied or approved antenna. Unauthorized antennas,
modifications or attachments could damage the terminal and may contravene
local RF emission regulations or invalidate type approval.
8.2.2 General safety
8.2.2.1 Driving
Check the laws and the regulations regarding the use of cellular devices in the
area where you have to drive as you always have to comply with them. When
using your GSM terminal while driving, please:
• give full attention to driving,
• pull off the road and park before making or answering a call if driving
conditions so require.
8.2.2.2 Electronic devices
Most electronic equipment, for example in hospitals and motor vehicles is
shielded from RF energy. However RF energy may affect some improperly
shielded electronic equipment.
8.2.2.3 Vehicle electronic equipment
Check your vehicle manufacturer representative to determine if any on-board
electronic equipment is adequately shielded from RF energy.
8.2.2.4 Medical electronic equipment
Consult the manufacturer of any personal medical devices (such as
pacemakers, hearing aids, etc...) to determine if they are adequately shielded
from external RF energy.
Turn your terminal OFF in health care facilities when any regulations posted in
the area instruct you to do so. Hospitals or health care facilities may be using
RF monitoring equipment.

WM_DEV_WUP_PTS_005
March 19, 2007
8.2.2.5 Aircraft
Turn your terminal OFF before boarding any aircraft.
• Use it on the ground only with crew permission.
• Do not use it in the air.
To prevent possible interference with aircraft systems, Federal Aviation
Administration (FAA) regulations require you to have permission from a crew
member to use your terminal while the aircraft is on the ground. To prevent
interference with cellular systems, local RF regulations prohibit using your
modem while airborne.
8.2.2.6 Children
Do not allow children to play with your GSM terminal. It is not a toy. Children
could hurt themselves or others (by poking themselves or others in the eye
with the antenna, for example). Children could damage the modem, or make
calls that increase your modem bills.
8.2.2.7 Blasting areas
To avoid interfering with blasting operations, turn your unit OFF when in a
« blasting area » or in areas posted: « turn off two-way radio ». Construction
crews often use remote control RF devices to set off explosives.
8.2.2.8 Potentially explosive atmospheres
Turn your terminal OFF when in any area with a potentially explosive
atmosphere. It is rare, but your application or its accessories could generate
sparks. Sparks in such areas could cause an explosion or fire resulting in bodily
injuries or even death.
Areas with a potentially explosive atmosphere are often, but not always, clearly
marked. They include fuelling areas such as petrol stations; below decks on
boats; fuel or chemical transfer or storage facilities; and areas where the air
contains chemicals or particles, such as grain, dust, or metal powders.
Do not transport or store flammable gas, liquid, or explosives, in the
compartment of your vehicle which contains your terminal or accessories.
Before using your terminal in a vehicle powered by liquefied petroleum gas
(such as propane or butane) ensure that the vehicle complies with the relevant
fire and safety regulations of the country in which the vehicle is to be used.
confidential © Page : 152 / 152
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged
without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à
des tiers sans son autorisation préalable.

GR/GS64 Charging Interface
Page: 1/1
APPLICATION NOTE
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WAVECOM S.A. - 3 esplanade du Foncet - 92442 Issy-les-Moulineaux Cedex - France - Tel: +33(0)1 46 29 08 00 - Fax: +33(0)1 46 29 08 08
Wavecom, Inc. - 430 Davis Drive - Suite 300 - Research Triangle Park, NC 27709 - USA - Tel: +1 919 237 4000 - Fax: +1 919 237 4140
WAVECOM Asia Pacific Ltd. - Unit 201-207, 2P
nd
P Floor - Bio-Informatics Centre - No. 2 Science Park West Avenue - Hong Kong Science Park,
Shatin - New Territories, Hong Kong - Tel: +852 2824 0254 - Fax: +852 2824 0255